Abstract
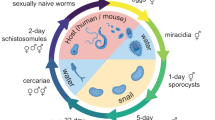
Schistosoma mansoni is the primary causative agent of schistosomiasis, which affects 200 million individuals in 74 countries. We generated 163,000 expressed-sequence tags (ESTs) from normalized cDNA libraries from six selected developmental stages of the parasite, resulting in 31,000 assembled sequences and 92% sampling of an estimated 14,000 gene complement. By analyzing automated Gene Ontology assignments, we provide a detailed view of important S. mansoni biological systems, including characterization of metazoa-specific and eukarya-conserved genes. Phylogenetic analysis suggests an early divergence from other metazoa. The data set provides insights into the molecular mechanisms of tissue organization, development, signaling, sexual dimorphism, host interactions and immune evasion and identifies novel proteins to be investigated as vaccine candidates and potential drug targets.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. TDR Strategic Direction for Research: Schistosomiasis (World Health Organization, Geneve, 2002).
King, C.L. Initiation and regulation of disease in schistosomiasis. in Schistosomiasis (ed. Mahmoud, A.A.F.) 213–264 (Imperial College Press, London, 2001).
Doenhoff, M.J., Kusel, J.R., Coles, G.C. & Cioli, D. Resistance of Schistosoma mansoni to praziquantel: is there a problem? Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 96, 465–469 (2002).
Dunne, D. & Mountford, A. Resistance to infection in humans and animal models. in Schistosomiasis (ed. Mahmoud, A.A.F.) 133–211 (Imperial College Press, London, 2001).
Coulson, P.S. The radiation-attenuated vaccine against schistosomes in animal models: paradigm for a human vaccine? Adv. Parasitol. 39, 271–336 (1997).
Hausdorf, B. Early evolution of the bilateria. Syst. Biol. 49, 130–142 (2000).
Simpson, A.J., Sher, A. & McCutchan, T.F. The genome of Schistosoma mansoni: isolation of DNA, its size, bases and repetitive sequences. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 6, 125–137 (1982).
Santos, T.M. et al. Analysis of the gene expression profile of Schistosoma mansoni cercariae using the expressed sequence tag approach. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 103, 79–97 (1999).
Williams, S.A. & Johnston, D.A. Helminth genome analysis: the current status of the filarial and schistosome genome projects. Filarial Genome Project. Schistosome Genome Project. Parasitology 118 Suppl, S19–S38 (1999).
Soares, M.B. et al. Construction and characterization of a normalized cDNA library. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 9228–9232 (1994).
Dias-Neto, E. et al. Minilibraries constructed from cDNA generated by arbitrarily primed RT–PCR: an alternative to normalized libraries for the generation of ESTs from nanogram quantities of mRNA. Gene 186, 135–142 (1997).
Dias-Neto, E. et al. Shotgun sequencing of the human transcriptome with ORF expressed sequence tags. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3491–3496 (2000).
Adams, M.D. et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287, 2185–2195 (2000).
Dehal, P. et al. The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: insights into chordate and vertebrate origins. Science 298, 2157–2167 (2002).
The C. elegans Sequencing Consortium. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science 282, 2012–2018 (1998).
Manning, G., Whyte, D.B., Martinez, R., Hunter, T. & Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 298, 1912–1934 (2002).
Osman, A., Niles, E.G. & LoVerde, P.T. Identification and characterization of a Smad2 homologue from Schistosoma mansoni, a transforming growth factor-β signal transducer. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 10072–10082 (2001).
Pappas, P.W. Membrane transport in helminth parasites: a review. Exp. Parasitol. 37, 469–530 (1975).
Skelly, P.J., Kim, J.W., Cunningham, J. & Shoemaker, C.B. Cloning, characterization, and functional expression of cDNAs encoding glucose transporter proteins from the human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 4247–4253 (1994).
Racoosin, E.L., Davies, S.J. & Pearce, E.J. Caveolae-like structures in the surface membrane of Schistosoma mansoni. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 104, 285–297 (1999).
Xu, X. & Caulfield, J.P. Characterization of human low density lipoprotein binding proteins on the surface of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 57, 229–235 (1992).
Mair, G.R., Maule, A.G., Day, T.A. & Halton, D.W. A confocal microscopical study of the musculature of adult Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology 121, 163–170 (2000).
Halton, D.W. & Gustafsson, M.K.S. Functional morphology of the platyhelminth nervous system. Parasitology 113, S47–S72 (1996).
Dorsey, C.H., Cousin, C.E., Lewis, F.A. & Stirewalt, M.A. Ultrastructure of the Schistosoma mansoni cercaria. Micron 33, 279–323 (2002).
Hoffmann, K.F., Davis, E.M., Fischer, E.R. & Wynn, T.A. The guanine protein coupled receptor rhodopsin is developmentally regulated in the free-living stages of Schistosoma mansoni. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 112, 113–123 (2001).
Pax, R.A. & Bennett, J.L. Neurobiology of parasitic platyhelminths: possible solutions to the problems of correlating structure with function. Parasitology 102 Suppl, S31–S39 (1991).
Smart, D. et al. Peptides related to the Diploptera punctata allatostatins in nonarthropod invertebrates: an immunocytochemical survey. J. Comp. Neurol. 347, 426–432 (1994).
Pryor, S.C. & Elizee, R. Evidence of opiates and opioid neuropeptides and their immune effects in parasitic invertebrates representing three different phyla: Schistosoma mansoni, Theromyzon tessulatum, Trichinella spiralis. Acta Biol. Hung. 51, 331–341 (2000).
de Mendonca, R.L., Escriva, H., Bouton, D., Laudet, V. & Pierce, R.J. Hormones and nuclear receptors in schistosome development. Parasitol. Today 16, 233–240 (2000).
Saule, P. et al. Early variations of host thyroxine and interleukin-7 favor Schistosoma mansoni development. J. Parasitol. 88, 849–855 (2002).
Snyder, S.D., Loker, E.S., Johnston, D.A. & Rollinson, D. The Schistosomatidae: Advances in Phylogenetics and Genomics. in The Interrelationships of Platyhelminthes (eds. Littlewood, D.T.J. & Bray, R.A.) 194–199 (Taylor and Francis, London, 2000).
Basch, P.F. Schistosoma mansoni: nucleic acid synthesis in immature females from single-sex infections, paired in vitro with intact males and male segments. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 90, 389–392 (1988).
DeMarco, R., Kowaltowski, A.T., Mortara, R.A. & Verjovski-Almeida, S. Molecular characterization and immunolocalization of Schistosoma mansoni ATP-diphosphohydrolase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 307, 831–838 (2003).
Fulford, A.J., Butterworth, A.E., Ouma, J.H. & Sturrock, R.F. A statistical approach to schistosome population dynamics and estimation of the life-span of Schistosoma mansoni in man. Parasitology 110 (Pt 3), 307–316 (1995).
Murphy, C.T. et al. Genes that act downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 424, 277–283 (2003).
Hu, P. et al. Role of membrane proteins in permeability barrier function: uroplakin ablation elevates urothelial permeability. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 283, F1200–F1207 (2002).
Skelly, P.J., Da'dara, A. & Harn, D.A. Suppression of cathepsin B expression in Schistosoma mansoni by RNA interference. Int. J. Parasitol. 33, 363–369 (2003).
Boyle, J.P., Wu, X.J., Shoemaker, C.B. & Yoshino, T.P. Using RNA interference to manipulate endogenous gene expression in Schistosoma mansoni sporocysts. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 128, 205–215 (2003).
Wilson, R.A. & Barnes, P.E. The formation and turnover of the membranocalyx on the tegument of Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology 74, 61–71 (1977).
Dissous, C. & Capron, A. Convergent evolution of tropomyosin epitopes. Parasitol. Today 11, 45–46 (1995).
Ramos, C.R. et al. Gene structure and M20T polymorphism of the Schistosoma mansoni Sm14 fatty acid-binding protein. Molecular, functional, and immunoprotection analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 12745–12751 (2003).
van der Kleij, D. et al. A novel host-parasite lipid cross-talk. Schistosomal lyso-phosphatidylserine activates toll-like receptor 2 and affects immune polarization. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 48122–48129 (2002).
Cutts, L. & Wilson, R.A. Elimination of a primary schistosome infection from rats coincides with elevated IgE titres and mast cell degranulation. Parasite Immunol. 19, 91–102 (1997).
Damonneville, M., Pierce, R.J., Verwaerde, C. & Capron, A. Allergens of Schistosoma mansoni. II. Fractionation and characterization of S. mansoni egg allergens. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 73, 248–255 (1984).
Salter, J.P. et al. Cercarial elastase is encoded by a functionally conserved gene family across multiple species of schistosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 24618–24624 (2002).
Mansour, T.E. Chemotherapeutic Targets in Parasites (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2002).
Fietto, J.L., DeMarco, R. & Verjovski-Almeida, S. Use of degenerate primers and touchdown PCR for construction of cDNA libraries. Biotechniques 32, 1404–1411 (2002).
Paquola, A., Nishiyama, M. Jr., Reis, E.M., daSilva, A.M. & Verjovski-Almeida, S. ESTWeb: bioinformatics services for EST sequencing projects. Bioinformatics 19, 1587–1588 (2003).
Huang, X. & Madan, A. CAP3: A DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res. 9, 868–877 (1999).
Stekel, D.J., Git, Y. & Falciani, F. The comparison of gene expression from multiple cDNA libraries. Genome Res. 10, 2055–2061 (2000).
Acknowledgements
E.D.N. thanks Associação Beneficente Alzira Denise Hertzog da Silva for financial support, D. Rollinson for providing schistosome isolates from Africa and Lebanon and M.G. dos Reis and N. Lucena for providing isolates from northeast Brazil. This project was financed by Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Sao Paulo and by the Brazilian Ministry of Science and Technology, Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico. The York schistosomiasis group received support from the Biology and Biotechnology Science Research Council, Wellcome Trust and the European Commission Research for Development Programme, Sector Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verjovski-Almeida, S., DeMarco, R., Martins, E. et al. Transcriptome analysis of the acoelomate human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Nat Genet 35, 148–157 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1237
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1237
This article is cited by
-
Multiomic analysis of Schistosoma mansoni reveals unique expression profiles in cercarial heads and tails
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Optimization of Expression and Purification of Schistosoma mansoni Antigens in Fusion with Rhizavidin
Molecular Biotechnology (2021)
-
The evolution of TNF signaling in platyhelminths suggests the cooptation of TNF receptor in the host-parasite interplay
Parasites & Vectors (2020)
-
The antischistosomal potential of GSK-J4, an H3K27 demethylase inhibitor: insights from molecular modeling, transcriptomics and in vitro assays
Parasites & Vectors (2020)
-
A novel progesterone receptor membrane component (PGRMC) in the human and swine parasite Taenia solium: implications to the host-parasite relationship
Parasites & Vectors (2018)