Abstract
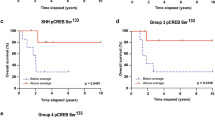
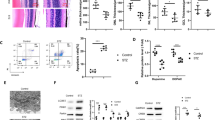
Control of cellular survival and proliferation is dependent on extracellular signals and is a prerequisite for ordered tissue development and maintenance. Activation of the cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB) by phosphorylation has been implicated in the survival of mammalian cells. To define its roles in the mouse central nervous system, we disrupted Creb1 in brain of developing and adult mice using the Cre/loxP system. Mice with a Crem−/− background and lacking Creb in the central nervous system during development show extensive apoptosis of postmitotic neurons. By contrast, mice in which both Creb1 and Crem are disrupted in the postnatal forebrain show progressive neurodegeneration in the hippocampus and in the dorsolateral striatum. The striatal phenotype is reminiscent of Huntington disease and is consistent with the postulated role of CREB-mediated signaling in polyglutamine-triggered diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mattson, M.P. Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1, 120–129 (2000).
Shaywitz, A.J. & Greenberg, M.E. CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 821–861 (1999).
Mayr, B. & Montminy, M. Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2, 599–609 (2001).
Silva, A.J., Kogan, J.H., Frankland, P.W. & Kida, S. CREB and memory. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 127–148 (1998).
Jean, D., Harbison, M., McConkey, D.J., Ronai, Z. & Bar-Eli, M. CREB and its associated proteins act as survival factors for human melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 24884–24890 (1998).
Riccio, A., Ahn, S., Davenport, C.M., Blendy, J.A. & Ginty, D.D. Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science 286, 2358–2361 (1999).
Somers, J.P., DeLoia, J.A. & Zeleznik, A.J. Adenovirus-directed expression of a nonphosphorylatable mutant of CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein) adversely affects the survival, but not the differentiation, of rat granulosa cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 13, 1364–1372 (1999).
Bonni, A. et al. Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science 286, 1358–1362 (1999).
Finkbeiner, S. CREB couples neurotrophin signals to survival messages. Neuron 25, 11–14 (2000).
Du, K. & Montminy, M. CREB is a regulatory target for the protein kinase Akt/PKB. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 32377–32379 (1998).
Blendy, J.A., Kaestner, K.H., Schmid, W., Gass, P. & Schütz, G. Targeting of the CREB gene leads to up-regulation of a novel CREB mRNA isoform. EMBO J. 15, 1098–1106 (1996).
Hummler, E. et al. Targeted mutation of the CREB gene: compensation within the CREB/ATF family of transcription factors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 5647–5651 (1994).
Rudolph, D. et al. Impaired fetal T cell development and perinatal lethality in mice lacking the cAMP response element binding protein. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 4481–4486 (1998).
Nantel, F. et al. Spermiogenesis deficiency and germ-cell apoptosis in CREM-mutant mice. Nature 380, 159–162 (1996).
Blendy, J.A., Kaestner, K.H., Weinbauer, G.F., Nieschlag, E. & Schütz, G. Severe impairment of spermatogenesis in mice lacking the CREM gene. Nature 380, 162–165 (1996).
Tronche, F. et al. Disruption of the glucocorticoid receptor gene in the nervous system results in reduced anxiety. Nature Genet. 23, 99–103 (1999).
Pugazhenthi, S. et al. Akt/protein kinase B up-regulates Bcl-2 expression through cAMP- response element-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10761–10766 (2000).
Wilson, B.E., Mochon, E. & Boxer, L.M. Induction of bcl-2 expression by phosphorylated CREB proteins during B-cell activation and rescue from apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 5546–5556 (1996).
van den Akker, E. et al. Targeted inactivation of Hoxb8 affects survival of a spinal ganglion and causes aberrant limb reflexes. Mech. Dev. 89, 103–114 (1999).
Dragatsis, I., Levine, M.S. & Zeitlin, S. Inactivation of Hdh in the brain and testis results in progressive neurodegeneration and sterility in mice. Nature Genet. 26, 300–306 (2000).
Mangiarini, L. et al. Exon 1 of the HD gene with an expanded CAG repeat is sufficient to cause a progressive neurological phenotype in transgenic mice. Cell 87, 493–506 (1996).
Lalonde, R. Motor abnormalities in weaver mutant mice. Exp. Brain Res. 65, 479–481 (1987).
Yamada, M. et al. Loss of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons in mice lacking STAM1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 3807–3819 (2001).
Clarke, G. et al. A one-hit model of cell death in inherited neuronal degenerations. Nature 406, 195–199 (2000).
Shimohata, T. et al. Expanded polyglutamine stretches interact with TAFII130, interfering with CREB-dependent transcription. Nature Genet. 26, 29–36 (2000).
Nucifora, F.C. et al. Interference by huntingtin and atrophin-1 with CBP-mediated transcription leading to cellular toxicity. Science 291, 2423–2428 (2001).
McCampbell, A. et al. CREB-binding protein sequestration by expanded polyglutamine. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 2197–2202 (2000).
Steffan, J.S. et al. The Huntington's disease protein interacts with p53 and CREB-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6763–6768 (2000).
Wyttenbach, A. et al. Polyglutamine expansions cause decreased CRE-mediated transcription and early gene expression changes prior to cell death in an inducible cell model of Huntington's disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 1829–1845 (2001).
Vonsattel, J.P. et al. Neuropathological classification of Huntington's disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 44, 559–577 (1985).
Bleckmann, S.C. et al. Activating transcription factor 1 and CREB are important for cell survival during early mouse development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 1919–1925 (2002).
Mantamadiotis, T., Taraviras, S., Tronche, F. & Schütz, G. PCR-based strategy for genotyping mice and ES cells harboring loxP sites. Biotechniques 25, 968–972 (1998).
Mayford, M. et al. Control of memory formation through regulated expression of a CaMKII transgene. Science 274, 1678–1683 (1996).
Kellendonk, C. et al. Inducible site-specific recombination in the brain. J. Mol. Biol. 285, 175–182 (1999).
Rossi, J.M. et al. Genomic analysis using a yeast artificial chromosome library with mouse DNA inserts. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 2456–2460 (1992).
Sikorski, R.S. & Hieter, P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 122, 19–27 (1989).
Birren, B., Green, E.D., Klapholz, S., Myers, R.M. & Roskams, J. (eds) Analyzing DNA (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Stride, E. Greiner and K. Unsicker for critical reading of the manuscript; E. Schmid, S. Ridder, A. Klewe-Nebenius, H. Glaser, S. Fehsenfeld, K. Anlag and T. Panek for expert technical assistance and N. Pollet, I. del Barco Barrantes and E. Casanova for stimulating discussions. This work was supported by grants from the European Community and the Deutsches Forschungsgemeinschaft and Forschergruppe (to G.S.). T.L. was supported by fellowships from the Human Frontier Science Program Organization and the Swiss National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mantamadiotis, T., Lemberger, T., Bleckmann, S. et al. Disruption of CREB function in brain leads to neurodegeneration. Nat Genet 31, 47–54 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng882
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng882
This article is cited by
-
Protectin conjugates in tissue regeneration 1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting ferroptosis
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Sustained CREB phosphorylation by lipid-peptide liquid crystalline nanoassemblies
Communications Chemistry (2023)
-
5-HT4 Receptor is Protective for MPTP-induced Parkinson’s Disease Mice Via Altering Gastrointestinal Motility or Gut Microbiota
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2023)
-
Therapeutic implications of phosphorylation- and dephosphorylation-dependent factors of cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) in neurodegeneration
Pharmacological Reports (2023)
-
Activity-dependent regulation of the BAX/BCL-2 pathway protects cortical neurons from apoptotic death during early development
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)