Abstract
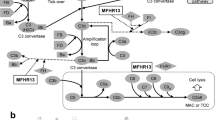
Factor H (FH) is an abundant regulator of complement activation and protects host cells from self-attack by complement. Here we provide insight into the regulatory activity of FH by solving the crystal structure of the first four domains of FH in complex with its target, complement fragment C3b. FH interacted with multiple domains of C3b, covering a large, extended surface area. The structure indicated that FH destabilizes the C3 convertase by competition and electrostatic repulsion and that FH enables proteolytic degradation of C3b by providing a binding platform for protease factor I while stabilizing the overall domain arrangement of C3b. Our results offer general models for complement regulation and provide structural explanations for disease-related mutations in the genes encoding both FH and C3b.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidt, C.Q., Herbert, A.P., Hocking, H.G., Uhrin, D. & Barlow, P.N. Translational mini-review series on complement factor H: Structural and functional correlations for factor H. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 151, 14–24 (2008).
Liszewski, M.K., Farries, T.C., Lublin, D.M., Rooney, I.A. & Atkinson, J.P. Control of the complement system. Adv. Immunol. 61, 201–283 (1996).
Prosser, B.E. et al. Structural basis for complement factor H linked age-related macular degeneration. J. Exp. Med. 204, 2277–2283 (2007).
Meri, S. Loss of self-control in the complement system and innate autoreactivity. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1109, 93–105 (2007).
de Cordoba, S.R. & de Jorge, E.G. Translational mini-review series on complement factor H: genetics and disease associations of human complement factor H. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 151, 1–13 (2008).
Lambris, J.D., Ricklin, D. & Geisbrecht, B.V. Complement evasion by human pathogens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 132–142 (2008).
Schneider, M.C. et al. Neisseria meningitidis recruits factor H using protein mimicry of host carbohydrates. Nature 458, 890–893 (2009).
Ricklin, D. & Lambris, J.D. Complement-targeted therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 1265–1275 (2007).
Noris, M. & Remuzzi, G. Translational mini-review series on complement factor H: therapies of renal diseases associated with complement factor H abnormalities: atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 151, 199–209 (2008).
Gordon, D.L., Kaufman, R.M., Blackmore, T.K., Kwong, J. & Lublin, D.M. Identification of complement regulatory domains in human factor H. J. Immunol. 155, 348–356 (1995).
Schmidt, C.Q. et al. A new map of glycosaminoglycan and C3b binding sites on factor H. J. Immunol. 181, 2610–2619 (2008).
Hocking, H.G. et al. Structure of the N-terminal region of complement factor H and conformational implications of disease-linked sequence variations. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 9475–9487 (2008).
Okemefuna, A.I. et al. The regulatory SCR-1/5 and cell surface-binding SCR-16/20 fragments of factor H reveal partially folded-back solution structures and different self-associative properties. J. Mol. Biol. 375, 80–101 (2008).
Janssen, B.J., Christodoulidou, A., McCarthy, A., Lambris, J.D. & Gros, P. Structure of C3b reveals conformational changes that underlie complement activity. Nature 444, 213–216 (2006).
Wiesmann, C. et al. Structure of C3b in complex with CRIg gives insights into regulation of complement activation. Nature 444, 217–220 (2006).
Becherer, J.D., Alsenz, J., Esparza, I., Hack, C.E. & Lambris, J.D. Segment spanning residues 727-768 of the complement C3 sequence contains a neoantigenic site and accommodates the binding of CR1, factor H, and factor B. Biochemistry 31, 1787–1794 (1992).
Lambris, J.D. et al. Dissection of CR1, factor H, membrane cofactor protein, and factor B binding and functional sites in the third complement component. J. Immunol. 156, 4821–4832 (1996).
Oran, A.E. & Isenman, D.E. Identification of residues within the 727-767 segment of human complement component C3 important for its interaction with factor H and with complement receptor 1 (CR1, CD35). J. Biol. Chem. 274, 5120–5130 (1999).
Janssen, B.J. et al. Structures of complement component C3 provide insights into the function and evolution of immunity. Nature 437, 505–511 (2005).
Gros, P., Milder, F.J. & Janssen, B.J. Complement driven by conformational changes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 48–58 (2008).
Rooijakkers, S.H.M. et al. Structural and functional implications of the complement convertase stabilized by a staphylococcal inhibitor. Nat. Immunol. advance online publication, doi:10.1038/ni.1756 (7 June 2009).
Hourcade, D.E., Mitchell, L., Kuttner-Kondo, L.A., Atkinson, J.P. & Medof, M.E. Decay-accelerating factor (DAF), complement receptor 1 (CR1), and factor H dissociate the complement AP C3 convertase (C3bBb) via sites on the type A domain of Bb. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 1107–1112 (2002).
Lukacik, P. et al. Complement regulation at the molecular level: the structure of decay-accelerating factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 1279–1284 (2004).
Kuttner-Kondo, L. et al. Structure-based mapping of DAF active site residues that accelerate the decay of C3 convertases. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 18552–18562 (2007).
Harris, C.L., Abbott, R.J., Smith, R.A., Morgan, B.P. & Lea, S.M. Molecular dissection of interactions between components of the alternative pathway of complement and decay accelerating factor (CD55). J. Biol. Chem. 280, 2569–2578 (2005).
Luo, B.H., Carman, C.V. & Springer, T.A. Structural basis of integrin regulation and signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 619–647 (2007).
Goicoechea de Jorge, E. et al. Gain-of-function mutations in complement factor B are associated with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 240–245 (2007).
Sahu, A., Isaacs, S.N., Soulika, A.M. & Lambris, J.D. Interaction of vaccinia virus complement control protein with human complement proteins: factor I-mediated degradation of C3b to iC3b1 inactivates the alternative complement pathway. J. Immunol. 160, 5596–5604 (1998).
DiScipio, R.G. Ultrastructures and interactions of complement factors H and I. J. Immunol. 149, 2592–2599 (1992).
Yadav, V.N., Pyaram, K., Mullick, J. & Sahu, A. Identification of hot spots in the variola virus complement inhibitor (SPICE) for human complement regulation. J. Virol. 82, 3283–3294 (2008).
Fritzinger, D.C. et al. Functional characterization of human C3/cobra venom factor hybrid proteins for therapeutic complement depletion. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 33, 105–116 (2009).
Licht, C. et al. Deletion of Lys224 in regulatory domain 4 of factor H reveals a novel pathomechanism for dense deposit disease (MPGN II). Kidney Int. 70, 42–50 (2006).
Saunders, R.E., Goodship, T.H., Zipfel, P.F. & Perkins, S.J. An interactive web database of factor H-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome mutations: insights into the structural consequences of disease-associated mutations. Hum. Mutat. 27, 21–30 (2006).
Fremeaux-Bacchi, V. et al. Mutations in complement C3 predispose to development of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 112, 4948–4952 (2008).
Caprioli, J. et al. Complement factor H mutations and gene polymorphisms in haemolytic uraemic syndrome: the C-257T, the A2089G and the G2881T polymorphisms are strongly associated with the disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12, 3385–3395 (2003).
Hageman, G.S. et al. A common haplotype in the complement regulatory gene factor H (HF1/CFH) predisposes individuals to age-related macular degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7227–7232 (2005).
Abrera-Abeleda, M.A. et al. Variations in the complement regulatory genes factor H (CFH) and factor H related 5 (CFHR5) are associated with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type II (dense deposit disease). J. Med. Genet. 43, 582–589 (2006).
Kondo, N., Honda, S., Kuno, S. & Negi, A. Coding variant I62V in the complement factor H gene is strongly associated with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Ophthalmology 116, 304–310 (2009).
Dragon-Durey, M.A. et al. Heterozygous and homozygous factor h deficiencies associated with hemolytic uremic syndrome or membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis: report and genetic analysis of 16 cases. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15, 787–795 (2004).
Liszewski, M.K. et al. Dissecting sites important for complement regulatory activity in membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46). J. Biol. Chem. 275, 37692–37701 (2000).
Coleman, H.R., Chan, C.C., Ferris, F.L. III & Chew, E.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 372, 1835–1845 (2008).
Lambris, J.D., Dobson, N.J. & Ross, G.D. Release of endogenous C3b inactivator from lymphocytes in response to triggering membrane receptors for beta 1H globulin. J. Exp. Med. 152, 1625–1644 (1980).
Evans, P. Scaling and assessment of data quality. Acta Crystallographica Section D 62, 72–82 (2006).
McCoy, A.J. et al. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 (2007).
Stein, N. CHAINSAW: a program for mutating pdb files used as templates in molecular replacement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41, 641–643 (2008).
Bouma, B. et al. Adhesion mechanism of human β2-glycoprotein I to phospholipids based on its crystal structure. EMBO J. 18, 5166–5174 (1999).
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004).
Winn, M.D., Murshudov, G.N. & Papiz, M.Z. Macromolecular TLS refinement in REFMAC at moderate resolutions. Methods Enzymol. 374, 300–321 (2003).
Adams, P.D. et al. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 58, 1948–1954 (2002).
Alsenz, J., Lambris, J.D., Schulz, T.F. & Dierich, M.P. Localization of the complement-component-C3b-binding site and the cofactor activity for factor I in the 38kDa tryptic fragment of factor H. Biochem. J. 224, 389–398 (1984).
Acknowledgements
We thank the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility for synchrotron radiation facilities; beamline scientists of the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility and the European Molecular Biology Laboratory for assistance; M. Pangburn (University of Texas at Tyler) for the CFH clone; P. Barlow (University of Edinburgh) for FH(19–20) protein; and M.A. Hadders for critical reading of the manuscript and comments. Supported by the Council for Chemical Sciences of the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (P.G.) and the US National Institutes of Health (J.D.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.W. purified C3 and C3b; Y.-Q.W. expressed and purified FH(1–4) and did cofactor assays; D.R. did decay acceleration, antibody competition and direct binding studies; J.W. crystallized the complex, collected data and determined, refined and analyzed the structure; B.J.C.J. helped with all stages of structure determination and analysis; J.D.L. and P.G. conceived and supervised the project; and J.W., D.R. and P.G. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9, Tables 1–2 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 4779 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Wu, YQ., Ricklin, D. et al. Structure of complement fragment C3b–factor H and implications for host protection by complement regulators. Nat Immunol 10, 728–733 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1755
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1755
This article is cited by
-
Insight into mode-of-action and structural determinants of the compstatin family of clinical complement inhibitors
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Invariant surface glycoprotein 65 of Trypanosoma brucei is a complement C3 receptor
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Reg4 and complement factor D prevent the overgrowth of E. coli in the mouse gut
Communications Biology (2020)
-
Spatially conserved motifs in complement control protein domains determine functionality in regulators of complement activation-family proteins
Communications Biology (2019)
-
C3 glomerulopathy — understanding a rare complement-driven renal disease
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2019)