Abstract
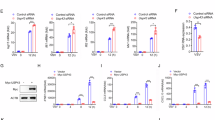
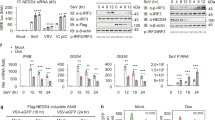
Stringent control of the type I interferon signaling pathway is important for maintaining host immune responses and homeostasis, yet the molecular mechanisms responsible for its tight regulation are still poorly understood. Here we report that the pattern-recognition receptor NLRP4 regulated the activation of type I interferon mediated by double-stranded RNA or DNA by targeting the kinase TBK1 for degradation. NLRP4 recruited the E3 ubiquitin ligase DTX4 to TBK1 for Lys48 (K48)-linked polyubiquitination at Lys670, which led to degradation of TBK1. Knockdown of either DTX4 or NLRP4 abrogated K48-linked ubiquitination and degradation of TBK1 and enhanced the phosphorylation of TBK1 and the transcription factor IRF3. Our results identify a previously unrecognized role for NLRP4 in the regulation of type I interferon signaling and provide molecular insight into the mechanisms by which NLRP4-DTX4 targets TBK1 for degradation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takeuchi, O. & Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140, 805–820 (2010).
Schroder, K. & Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 140, 821–832 (2010).
Chiu, Y.H., Macmillan, J.B. & Chen, Z.J. RNA polymerase III detects cytosolic DNA and induces type I interferons through the RIG-I pathway. Cell 138, 576–591 (2009).
Ablasser, A. et al. RIG-I-dependent sensing of poly(dA:dT) through the induction of an RNA polymerase III-transcribed RNA intermediate. Nat. Immunol. 10, 1065–1072 (2009).
Zhang, Z. et al. The helicase DDX41 senses intracellular DNA mediated by the adaptor STING in dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 12, 959–965 (2011).
Unterholzner, L. et al. IFI16 is an innate immune sensor for intracellular DNA. Nat. Immunol. 11, 997–1004 (2010).
Moore, C.B. et al. NLRX1 is a regulator of mitochondrial antiviral immunity. Nature 451, 573–577 (2008).
Tattoli, I. et al. NLRX1 is a mitochondrial NOD-like receptor that amplifies NF-κB and JNK pathways by inducing reactive oxygen species production. EMBO Rep. 9, 293–300 (2008).
Benko, S., Magalhaes, J.G., Philpott, D.J. & Girardin, S.E. NLRC5 limits the activation of inflammatory pathways. J. Immunol. 185, 1681–1691 (2010).
Cui, J. et al. NLRC5 negatively regulates the NF-κB and type I interferon signaling pathways. Cell 141, 483–496 (2010).
Jounai, N. et al. NLRP4 negatively regulates autophagic processes through an association with beclin1. J. Immunol. 186, 1646–1655 (2011).
Fiorentino, L. et al. A novel PAAD-containing protein that modulates NF-κB induction by cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 35333–35340 (2002).
Li, S., Wang, L., Berman, M., Kong, Y.Y. & Dorf, M.E. Mapping a dynamic innate immunity protein interaction network regulating type I interferon production. Immunity 35, 426–440 (2011).
Wang, C. et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1 'preferentially' promotes TLR-mediated production of type I interferon. Nat. Immunol. 10, 744–752 (2009).
Honda, K. & Taniguchi, T. IRFs: master regulators of signalling by Toll-like receptors and cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 644–658 (2006).
Honda, K. et al. Spatiotemporal regulation of MyD88-IRF-7 signalling for robust type-I interferon induction. Nature 434, 1035–1040 (2005).
Radivojac, P. et al. Identification, analysis, and prediction of protein ubiquitination sites. Proteins 78, 365–380 (2010).
Xue, Y., Li, A., Wang, L., Feng, H. & Yao, X. PPSP: prediction of PK-specific phosphorylation site with Bayesian decision theory. BMC Bioinformatics 7, 163 (2006).
Fitzgerald, K.A. et al. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 4, 491–496 (2003).
Thurston, T.L., Ryzhakov, G., Bloor, S., von Muhlinen, N. & Randow, F. The TBK1 adaptor and autophagy receptor NDP52 restricts the proliferation of ubiquitin-coated bacteria. Nat. Immunol. 10, 1215–1221 (2009).
Weidberg, H. & Elazar, Z. TBK1 mediates crosstalk between the innate immune response and autophagy. Sci. Signal. 4, pe39 (2011).
Ryzhakov, G. & Randow, F. SINTBAD, a novel component of innate antiviral immunity, shares a TBK1-binding domain with NAP1 and TANK. EMBO J. 26, 3180–3190 (2007).
Chau, T.L. et al. Are the IKKs and IKK-related kinases TBK1 and IKK-ɛ similarly activated? Trends Biochem. Sci. 33, 171–180 (2008).
Lei, C.Q. et al. Glycogen synthase kinase 3β regulates IRF3 transcription factor-mediated antiviral response via activation of the kinase TBK1. Immunity 33, 878–889 (2010).
Liew, F.Y., Xu, D., Brint, E.K. & O'Neill, L.A. Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 446–458 (2005).
Karin, M., Lawrence, T. & Nizet, V. Innate immunity gone awry: linking microbial infections to chronic inflammation and cancer. Cell 124, 823–835 (2006).
You, F. et al. PCBP2 mediates degradation of the adaptor MAVS via the HECT ubiquitin ligase AIP4. Nat. Immunol. 10, 1300–1308 (2009).
O'Neill, L.A. When signaling pathways collide: positive and negative regulation of toll-like receptor signal transduction. Immunity 29, 12–20 (2008).
Xia, X. et al. NLRX1 negatively regulates TLR-induced NF-κB signaling by targeting TRAF6 and IKK. Immunity 34, 843–853 (2011).
Barbie, D.A. et al. Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature 462, 108–112 (2009).
Meylan, E. et al. Requirement for NF-κB signalling in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 462, 104–107 (2009).
Ou, Y.H. et al. TBK1 directly engages Akt/PKB survival signaling to support oncogenic transformation. Mol. Cell 41, 458–470 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Balachandran (Fox Chase Cancer Center) for VSV-eGFP; Y.-J. Liu and Z. Zhang (The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center) for the STING expression plasmid; and A.A. Ajibade for critical reading of the manuscript. Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31000394 to J.C.), the National Cancer Institute, the US National Institutes of Health (CA090327, CA101795, CA121191, CA116408 and CA094327 to R.-F.W.), the Cancer Research Institute and The Methodist Hospital Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.C., Y.L. and L.Z. designed and did the experiments, J.C. and R.-F.W. wrote the manuscript; D.L. and Z.S. provided reagents and technical assistance; and H.Y.W. and R.-F.W. supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–14 and Methods (PDF 2668 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, J., Li, Y., Zhu, L. et al. NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting the kinase TBK1 for degradation via the ubiquitin ligase DTX4. Nat Immunol 13, 387–395 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2239
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2239
This article is cited by
-
Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 4 promotes thyroid cancer progression through stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1
Functional & Integrative Genomics (2023)
-
Early innate immune response triggered by the human respiratory syncytial virus and its regulation by ubiquitination/deubiquitination processes
Journal of Biomedical Science (2022)
-
TRIM18 is a critical regulator of viral myocarditis and organ inflammation
Journal of Biomedical Science (2022)
-
Population genomics of an icefish reveals mechanisms of glacier-driven adaptive radiation in Antarctic notothenioids
BMC Biology (2022)
-
Blockade of USP14 potentiates type I interferon signaling and radiation-induced antitumor immunity via preventing IRF3 deubiquitination
Cellular Oncology (2022)