Abstract
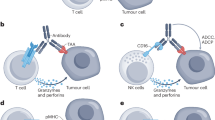
The potential of bispecific T cell–engaging antibodies is hindered by manufacturing challenges and short serum half-life. We circumvented these limitations by treating mice with in vitro–transcribed pharmacologically optimized, nucleoside-modified mRNA encoding the antibody. We achieved sustained endogenous synthesis of the antibody, which eliminated advanced tumors as effectively as the corresponding purified bispecific antibody. Because manufacturing of pharmaceutical mRNA is fast, this approach could accelerate the clinical development of novel bispecific antibodies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 July 2017
In the version of this article initially published, in the “Polymer/lipid-based formulation of mRNA” section of the Online Methods, the text incorrectly stated that mRNA was in 190 ml rather than 190 µl of cold DMEM. The error has been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions of the article.
References
Garber, K. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13, 799–801 (2014).
Kantarjian, H. et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 376, 836–847 (2017).
Bargou, R. et al. Science 321, 974–977 (2008).
Spiess, C., Zhai, Q. & Carter, P.J. Mol. Immunol. 67 (2 Pt. A), 95–106 (2015).
Topp, M.S. et al. J. Clin. Oncol. 29, 2493–2498 (2011).
Sahin, U., Karikó, K. & Türeci, Ö. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13, 759–780 (2014).
Karikó, K., Buckstein, M., Ni, H. & Weissman, D. Immunity 23, 165–175 (2005).
Karikó, K. et al. Mol. Ther. 16, 1833–1840 (2008).
Anderson, B.R. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 5884–5892 (2010).
Karikó, K., Muramatsu, H., Ludwig, J. & Weissman, D. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, e142 (2011).
Holtkamp, S. et al. Blood 108, 4009–4017 (2006).
Micke, P. et al. Int. J. Cancer 135, 2206–2214 (2014).
Schuler, M. et al. Ann. Oncol. 27, 207–242 (2016).
Sahin, U. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 7624–7634 (2008).
Stadler, C.R. et al. OncoImmunology 5, e1091555 (2015).
Sahin, U., Türeci, Ö., Brandenburg, G. & Usener, D. US patent 8,425,902 (2013).
Sahin, U. et al. US patent 9,487,584 (2016).
Roovers, R.C. et al. Br. J. Cancer 78, 1407–1416 (1998).
Lanzavecchia, A. & Scheidegger, D. Eur. J. Immunol. 17, 105–111 (1987).
Traunecker, A., Lanzavecchia, A. & Karjalainen, K. EMBO J. 10, 3655–3659 (1991).
Gallie, D.R., Tanguay, R.L. & Leathers, V. Gene 165, 233–238 (1995).
Vallazza, B. et al. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 6, 471–499 (2015).
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the following colleagues: S. Wöll, S. Kühne and M. Erdeljan for immunohistochemistry and data acquisition, N. Brüne for clinical chemistry data, A. Jendretzki, M. LeGall and S. Wessel for construct design and preparation, and K. Schmoldt for performing the in vitro assays. We would also like to acknowledge I. Biermann for supporting the in vivo studies, H. Muramatsu, M. Baiersdörfer, K. Beilstein, S. Fesser and team for IVT mRNA synthesis and characterization and for bioluminescence studies, T. Beissert and team for cell line transduction and K. Reuter for advice on in vivo experiments. Special thanks are given to C. Huber for inspiring discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.R.S., H.B.-M., L.C., K.K., Ö.T. and U.S. were engaged in study conception and interpretation and contributed to the critical revision of the manuscript. C.R.S. designed the study and participated in in vivo experiment execution and in general data analysis and interpretation. H.B.-M. was involved in study design, especially of in vitro experiments, and in data analysis and interpretation. L.C. designed, executed and interpreted immunoblot analyses and performed recombinant protein purification. B.H. established, executed and interpreted ELISA assays and performed in vitro experiments. A.S.R. was involved in in vitro assay design, execution and interpretation and produced recombinant proteins as well as RiboMAB supernatants. R.P.R. performed in vivo experiments and supported the design of the studies. Ö.T., C.R.S., H.B.-M., K.K. and U.S. drafted the manuscript. All authors discussed the results, assisted in the preparation of the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
C.R.S. is Head of Bispecific Antibodies at BioNTech and has ownership interest in patent applications. H.B.-M. is Deputy Head of Bispecific Antibodies at BioNTech and has ownership interest in a patent application. L.C. is a member of Bispecific Antibodies at BioNTech and has ownership interest in a patent application. K.K. is Vice President of BioNTech RNA and has ownership interest in patent applications. Ö.T. has ownership interest in patent applications. U.S. is cofounder of BioNTech and has ownership interest (including patents) in TRON and BioNTech.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5 (PDF 1012 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stadler, C., Bähr-Mahmud, H., Celik, L. et al. Elimination of large tumors in mice by mRNA-encoded bispecific antibodies. Nat Med 23, 815–817 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4356
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4356
This article is cited by
-
mRNA-Encoded antibodies as a next-generation therapeutic paradigm: a rapid and adaptive platform for the prevention and treatment of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases — A critical review
Immunologic Research (2026)
-
Spleen-targeted NeoPol-mL242 mRNA vaccine induces robust T-cell responses in a hepatocellular carcinoma model
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2025)
-
Bispecific antibodies and nanotechnology: a strategic alliance in cancer immunotherapy
Molecular Cancer (2025)
-
mRNA vaccines in the context of cancer treatment: from concept to application
Journal of Translational Medicine (2025)
-
Technological advancements in antibody-based therapeutics for treatment of diseases
Journal of Biomedical Science (2025)