Abstract
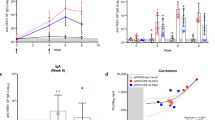
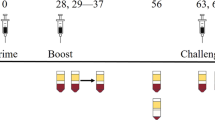
Eight different protocols were compared for their ability to raise protection against immunodeficiency virus challenges in rhesus macaques. The most promising containment of challenge infections was achieved by intradermal DNA priming followed by recombinant fowl pox virus booster immunizations. This containment did not require neutralizing antibody and was active for a series of challenges ending with a highly virulent virus with a primary isolate envelope heterologous to the immunizing strain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
The World Health Organization in AIDS Epidemic Update (Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS and the World Health Organization, Geneva, 1998).
Moore, J.P. & Ho, D.D. HIV-1 neutralization: the consequences of viral adaptation to growth on transformed T cells. AIDS 9, S117–136 (1995).
Burton, D.R. & Moore, J.P. Why do we not have an HIV vaccine and how can we make one? Nature Med. 4, 495–498 (1998).
Rosenberg, E.S. et al. Vigorous HIV-1-specific CD4+ T cell responses associated with control of viremia. Science 278, 1447– 1450 (1997).
Schacker, T.W., Hughes, J.P., Shea, T., Coombs, R.W. & Corey, L. Biological and virologic characteristics of primary HIV infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 128, 613 –620 (1998).
Finzi, D. & Silliciano, R.F. Viral dynamics in HIV-1 infection. Cell 93, 665–671 (1998).
Daniel, M.D., Kirchhoff, F., Czajak, S.C., Sehgal, P.K. & Desrosiers, R.C. Protective effects of a live attenuated SIV vaccine with a deletion in the nef gene. Science 258, 1938–1941 ( 1992).
Baba, T.W. et al. Pathogenicity of live, attenuated SIV after mucosal infection of neonatal macaques. Science 267, 1820– 1825 (1995).
Ruprecht, R.M., Baba, T.W. & Liska, V. Attenuated HIV vaccine: caveats. Science 271, 1790–1792 (1996).
Mascola, J.R. et al. Immunization with envelope subunit vaccine products elicits neutralizing antibodies against laboratory-adapted but not primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases AIDS Vaccine Evaluation Group. J. Infect. Dis. 173, 340–348 ( 1996).
Connor, R.I. et al. Immunological and virological analyses of persons infected by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 while participating in trials of recombinant gp120 subunit vaccines. J. Virol. 72, 1552 –1576 (1998).
Graham, B.S. et al. Analysis of intercurrent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infections in phase I and II trials of candidate AIDS vaccines. AIDS Vaccine Evaluation Group, and the Correlates of HIV Immune Protection Group. J. Infect. Dis. 177, 310–319 (1998).
Moss, B. Recombinant DNA virus vectors for vaccination. Semin. Immunol. 2, 317–327 ( 1990).
Tartaglia, J. et al. Canarypox virus-based vaccines: prime-boost strategies to induce cell- mediated and humoral immunity against HIV. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 14 Suppl 3, S291– 298 (1998).
Stott, J. & Hu, S.L. AIDS 1998. Vaccines and immunology: overview. AIDS 12, S95– 96 (1998).
Hu, S.-L. et al. in Transmembrane Protein and Core Antigens in Protection against SIV Infection (eds. Chanock, R.M., Brown, F., Ginsberg, H.S. & Norrby, E.) 167–173 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1995).
Robinson, H.L. & Torres, C.A. DNA vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 9, 271– 283 (1997).
Donnelly, J.J., Ulmer, J.B., Shiver, J.W. & Liu, M.A. DNA vaccines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 617 –648 (1997).
Boyer, J.D. et al. Protection of chimpanzees from high-dose heterologous HIV-1 challenge by DNA vaccination. Nature Med. 3, 526–532 (1997).
Letvin, N.L. et al. Potent, protective anti-HIV immune responses generated by bimodal HIV envelope DNA plus protein vaccination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 9378–9383 (1997).
Li, J., Lord, C.I., Haseltine, W., Letvin, N.L. & Sodroski, J. Infection of cynomolgus monkeys with a chimeric HIV-1/SIVmac virus that expresses the HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 5, 639– 646 (1992).
Li, J.T. et al. Persistent infection of macaques with simian-human immunodeficiency viruses. J. Virol. 69, 7061– 7067 (1995).
Reimann, K.A. et al. A chimeric simian/human immunodeficiency virus expressing a primary patient human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate env causes an AIDS-like disease after in vivo passage in rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 70, 6922–6928 ( 1996).
Lu, S. et al. Simian immunodeficiency virus DNA vaccine trial in macaques. J. Virol. 70, 3978–3991 (1996).
Fynan, E.F. et al. DNA vaccines: protective immunizations by parenteral, mucosal, and gene-gun inoculations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 11478–11482 (1993).
Pertmer, T.M. et al. Gene gun-based nucleic acid immunization: elicitation of humoral and cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses following epidermal delivery of nanogram quantities of DNA. Vaccine 13, 1427– 1430 (1995).
Klaniecki, J. et al. Cross-neutralizing antibodies in rabbits immunized with HIV-1 gp160 purified from simian cells infected with a recombinant vaccinia virus. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 7, 791– 798 (1991).
Jenkins, S. et al. Formation of lentivirus particles by mammalian cells infected with recombinant fowlpox virus. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 7, 991–998 (1991).
Johnson, R.P. et al. Induction of vigorous cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses by live attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus. J. Virol. 71, 7711–8 (1997).
Richmond, J.F. et al. Studies of the neutralizing activity and avidity of anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env antibody elicited by DNA priming and protein boosting. J. Virol. 72, 9092– 9100 (1998).
Suryanarayana, K., Wiltrout, T.A., Vasquez, G.M., Hirsch, V.M. & Lifson, J.D. Plasma SIV RNA viral load determination by real-time quantification of product generation in reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 14, 183–189 (1998).
Wyand, M.S., Manson, K.H., Garcia-Moll, M., Montefiori, D. & Desrosiers, R.C. Vaccine protection by a triple deletion mutant of simian immunodeficiency virus. J. Virol. 70, 3724–3733 (1996).
Montefiori, D.C. & Evans, T.G. Toward an HIV-type 1 vaccine that generates potent, broadly cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies. AIDS Res. and Hum. Retroviruses 15, 689 –698 (1999).
Yang, O.O. et al. Lysis of HIV-1-infected cells and inhibition of viral replication by universal receptor T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 11478–11483 (1997).
Levy, J.A., Mackewicz, C.E. & Barker, E. Controlling HIV pathogenesis: the role of the noncytotoxic anti-HIV response of CD8+ T cells. Immunol. Today 17 , 217–224 (1996).
Feltquate, D.M., Heaney, S., Webster, R.G. & Robinson, H.L. Different T helper cell types and antibody isotypes generated by saline and gene gun DNA immunization. J. Immunol. 158, 2278–84 (1997).
O'Garra, A. & Murphy, K. Role of cytokines in determining T-lymphocyte function. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 6, 458–66 (1994).
Seder, R.A. & Paul, W.E. Acquisition of lymphokine-producing phenotype by CD4+ T cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12, 635–673 (1994).
Dittmer, U., Brooks, D.M. & Hasenkrug, K.J. Requirement for multiple lymphocyte subsets in protection by a live attenuated vaccine against retroviral infection. Nature Med. 5, 189–193 ( 1999).
Johnson, R.P. Live attenuated AIDS vaccines: hazards and hopes. Nature Med 5, 154–155 (1999).
Schneider, J. et al. Enhanced immunogenicity for CD8+ T cell induction and complete protective efficacy of malaria DNA vaccination by boosting with modified vaccinia virus Ankara. Nature Med. 4, 397– 402 (1998).
Sedegah, M. et al. Boosting with recombinant vaccinia increases immunogenicity and protective efficacy of malaria DNA vaccine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7648–7653 ( 1998).
Kent, S.J. et al. Enhanced T-cell immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vaccine regimen consisting of consecutive priming with DNA and boosting with recombinant fowlpox virus. J. Virol. 72, 10180–10188 (1998).
Polacino, P. et al. Limited breadth of the protective immunity elicited by simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmne gp160 vaccines in a combination immunization regimen. J. Virol. 73, 618– 630 (1999).
Gritz, L. et al. Generation of hybrid genes and proteins by vaccinia virus-mediated recombination: application to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env. J. Virol. 64, 5948–5957 (1990).
Andersson, S., Davis, D.L., Dahlback, H., Jornvall, H. & Russell, D.W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P- 450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 8222–8229 (1989).
Earl, P.L. et al. Native oligomeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein elicits diverse monoclonal antibody reactivities. J. Virol. 68, 3015–3026 (1994).
Schochetman, G., Subbarao, S. & Kalish, M.L. in Viral Genome Methods (ed. K.W. Adolph) 25–41 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1996 ).
Montefiori, D.C., Robinson, W.E. Jr., Schuffman, S.S. & Mitchell, W.M. Evaluation of antiviral drugs and neutralizing antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus by a rapid and sensitive microtiter infection assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 26, 231– 235 (1988).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Feinberg and J. Safrit for critical comments on the manuscript. We are indebted to H. Drake-Perrow for administrative assistance. We thank M. Piatak, L. Li, and T. Parks for assistance with SIV RNA viral load analysis; J. Yang for assistance with T-cell assays; R. Schmidt for help in construction of pRS102; and A. Saekhou for assistance with analyses of transferred virus. This research was supported by NIH grants R01-AI-34241 and P01-AI-43045 (H.L.R.); R01-AI-40334 (S.L.); P01-AI-26503 (S.-L.H.) R01 AI 52634, RR 000138 (R. P. Johnson) and U01 AI 26507 (D.L.P.); by the Yerkes Primate Research Center Base Grant, RR-00165; and by contracts NCI-6S-1649 (D.C.M.) and NO1-CO-56000 (J.D.L.). The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, H., Montefiori, D., Johnson, R. et al. Neutralizing antibody-independent containment of immunodeficiency virus challenges by DNA priming and recombinant pox virus booster immunizations . Nat Med 5, 526–534 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/8406
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/8406
This article is cited by
-
Construction and purification of ANK gene deleted recombinant goatpox virus
VirusDisease (2020)
-
Combination DNA plus protein HIV vaccines
Springer Seminars in Immunopathology (2006)
-
Prime-boost vaccination with plasmid DNA and a chimeric adenovirus type 5 vector with type 35 fiber induces protective immunity against HIV
Gene Therapy (2005)
-
New hope for an aids vaccine
Nature Reviews Immunology (2002)
-
HIV vaccines: Biological and clinical considerations
Current Infectious Disease Reports (2002)