Abstract
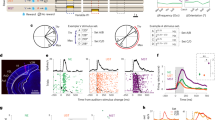
Physiological studies of auditory perception have not yet clearly distinguished sensory from decision processes. In this experiment, human participants identified speech sounds masked by varying levels of noise while blood oxygenation signals in the brain were recorded with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Accuracy and response time were used to characterize the behavior of sensory and decision components of this perceptual system. Oxygenation signals in a cortical subregion just anterior and lateral to primary auditory cortex predicted accuracy of sound identification, whereas signals in an inferior frontal region predicted response time. Our findings provide neurophysiological evidence for a functional distinction between sensory and decision mechanisms underlying auditory object identification. The present results also indicate a link between inferior frontal lobe activation and response-selection processes during auditory perception tasks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zatorre, R.R. & Binder, J.R. The human auditory system. in Brain Mapping: The Systems (eds. Toga, A.W. & Mazziotta, J.C.) 365–402 (Academic, San Diego, 2000).
Näätänen, R. The perception of speech sounds by the human brain as reflected by the mismatch negativity (MMN) and its magnetic equivalent (MMNm). Psychophysiology 38, 1–21 (2001).
Mecklinger, A., Ullsperger, P., Molle, M. & Grune, K. Event-related potentials indicate information extraction in a comparative judgement task. Psychophysiology 31, 23–28 (1994).
Honey, G.D., Bullmore, E.T. & Sharma, T. Prolonged reaction time to a verbal working memory task predicts increased power of posterior parietal cortical activation. NeuroImage 12, 495–503 (2000).
Fiez, J.A. et al. PET studies of auditory and phonological processing: Effects of stimulus characteristics and task demands. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 7, 357–375 (1995).
Price, C.J. et al. Hearing and saying. The functional neuroanatomy of auditory word processing. Brain 119, 919–931 (1996).
Burton, M.W., Small, S. & Blumstein, S.E. The role of segmentation in phonological processing: an fMRI investigation. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 12, 679–690 (2000).
Hall, D.A. et al. Modulation and task effects in auditory processing measured using fMRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 10, 107–119 (2000).
Norris, D. & Wise, R. The study of prelexical and lexical processes in comprehension: Psycholinguistics and functional neuroimaging. in The New Cognitive Neurosciences 2nd edn. (ed. Gazzaniga, M.S.) 867–880 (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2000).
Donders, F.C. On the speed of mental processes. Acta Psychologica, 30, 412–431 (1969).
Yellott, J.I., Jr. Correction for guessing and the speed-accuracy tradeoff in choice reaction time. J. Math. Psychol. 8, 159–199 (1971).
Grice, G.R., Nullmeyer, R. & Spiker, V.A. Human reaction time: toward a general theory. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 111, 135–153 (1982).
Binder, J.R. et al. Human temporal lobe activation by speech and nonspeech sounds. Cereb. Cortex 10, 512–528 (2000).
Scott, S.K., Blank, C., Rosen, S. & Wise, R.J.S. Identification of a pathway for intelligible speech in the left temporal lobe. Brain 123, 2400–2406 (2000).
Belin, P., Zatorre, R.J. & Ahad, P. Human temporal-lobe response to vocal sounds. Cogn. Brain Res. 13, 17–26 (2002).
Liebenthal, E., Binder, J.R., Piorkowski, R.L. & Remez, R.E. Short-term reorganization of auditory analysis induced by phonetic experience. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 15, 549–558 (2003).
Davis, M.H. & Johnsrude, I.S. Hierarchical processing in spoken language comprehension. J. Neurosci. 23, 3423–3431 (2003).
Warren, J.D. & Griffiths, T.D. Distinct mechanisms for processing spatial sequences and pitch sequences in the human auditory brain. J. Neurosci. 23, 5799–5804 (2003).
Meyer, A. The relationship of the auditory center to aphasia. J. Psychol. Neurol. 13, 203–213 (1908).
Kleist, K. Sensory Aphasia and Amusia (Pergamon Press, London, 1962).
Galaburda, A.M., Sanides, F. & Geschwind, N. Human brain. Cytoarchitectonic left-right asymmetries in the temporal speech region. Arch. Neurol. 35, 812–817 (1978).
Rademacher, J., Caviness, V.S., Steinmetz, H. & Galaburda, A.M. Topographical variation of the human primary cortices: Implications for neuroimaging, brain mapping and neurobiology. Cereb. Cortex 3, 313–329 (1993).
Galaburda, A.M. & Pandya, D.N. The intrinsic architectonic and connectional organization of the superior temporal region of the rhesus monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 221, 169–184 (1983).
Kaas, J.H. & Hackett, T.A. Subdivisions of auditory cortex and levels of processing in primates. Audiol. Neurootol. 3, 73–85 (1998).
Romanski, L.M. et al. Dual streams of auditory afferents target multiple domains in the primate prefrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 1131–1136 (1999).
Tian, B., Reser, D., Durham, A., Kustov, A. & Rauschecker, J.P. Functional specialization in the rhesus monkey auditory cortex. Science 292, 290–293 (2001).
Grabowski, T.J. & Damasio, A.R. Investigating language with functional neuroimaging. in Brain Mapping: The Systems (eds. Toga, A.W. & Mazziotta, J.C.) 425–461 (Academic, San Diego, 2000).
Binder, J.R. & Price, C.J. Functional imaging of language. in Handbook of Functional Neuroimaging of Cognition (eds. Cabeza, R. & Kingstone, A.) 187–251 (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2001).
Tallal, P., Miller, S. & Fitch, R. Neurobiological basis of speech: a case for the preeminence of temporal processing. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 682, 27–47 (1993).
Johnsrude, I.S., Zatorre, R.J., Milner, B.A. & Evans, A.C. Left-hemisphere specialization for the processing of acoustic transients. Neuroreport 8, 61–65 (1997).
Poeppel, D. The analysis of speech in different temporal integration windows: cerebral lateralization as 'asymmetric sampling in time'. Speech Commun. 41, 245–255 (2003).
Zatorre, R.J., Belin, P. & Penhune, V.B. Structure and function of auditory cortex: music and speech. Trends Cogn. Sci. 6, 37–46 (2002).
Démonet, J.-F. et al. The anatomy of phonological and semantic processing in normal subjects. Brain 115, 1753–1768 (1992).
Zatorre, R.J., Evans, A.C., Meyer, E. & Gjedde, A. Lateralization of phonetic and pitch discrimination in speech processing. Science 256, 846–849 (1992).
Green, D.M. & Swets, J.A. Signal Detection Theory (Wiley, New York, 1966).
Krawczyk, D.C. Contributions of the prefrontal cortex to the neural basis of human decision making. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 26, 631–664 (2002).
Binder, J.R. et al. Human brain language areas identified by functional MRI. J. Neurosci. 17, 353–362 (1997).
Lewis, J.W., Beauchamp, M.S. & DeYoe, E.A. A comparison of visual and auditory motion processing in human cerebral cortex. Cereb. Cortex 10, 873–888 (2000).
Adler, C.M. et al. Changes in neuronal activation with increasing attention demand in healthy volunteers: an fMRI study. Synapse 42, 266–272 (2001).
Menon, V., Adleman, N.E., White, C.D., Glover, G.H. & Reiss, A.L. Error-related brain activation during a Go/NoGo response inhibition task. Hum. Brain Mapp. 12, 131–143 (2001).
Taylor, S.F., Kornblum, S., Minoshima, S., Oliver, L.M. & Koeppe, R.A. Changes in medial cortical blood flow with a stimulus-response compatibility task. Neuropsychologia 32, 249–255 (1994).
Braver, T.S., Barch, D.M., Gray, J.R., Molfese, D.L. & Snyder, A. Anterior cingulate cortex and response conflict: Effects of frequency, inhibition and errors. Cereb. Cortex 11, 825–836 (2001).
Ullsperger, M. & von Cramon, D.Y. Subprocesses of performance monitoring: A dissociation of error processing and response competition revealed by event-related fMRI and ERPs. Neuroimage 14, 1387–1401 (2001).
Horovitz, S.G., Skudlarski, P. & Gore, J.C. Correlations and dissociations between BOLD signal and p300 amplitude in an auditory oddball task: a parametric approach to combining fMRI and ERP. Magn. Reson. Imaging 20, 319–325 (2002).
Ito, S.-I., Ohgushi, M., Ifuku, H. & Ogawa, H. Neuronal activity in the monkey fronto-opercular and adjacent insular/prefrontal cortices during a taste discrimination GO/NOGO task: response to cues. Neurosci. Res. 41, 257–266 (2001).
Scott, S.K. & Johnsrude, I.S. The neuroanatomical and functional organization of speech perception. Trends Neurosci. 26, 100–107 (2003).
Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9, 97–113 (1971).
Fant, G. Speech Sounds and Features (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1973).
Cox, R.W. AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput. Biomed. Res. 29, 162–173 (1996).
Talairach, J. & Tournoux, P. Co-Planar Stereotaxic Atlas of the Human Brain (Thieme Medical Publishers, New York, 1998).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank J.N. Kaufman, R. Tong, A. Jesmanowicz and R.W. Cox for technical assistance. Supported by National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke grant R01 NS33576, National Institute of Mental Health grant P01 MH51358 and National Institutes of Health General Clinical Research Center grant M01 RR00058.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binder, J., Liebenthal, E., Possing, E. et al. Neural correlates of sensory and decision processes in auditory object identification. Nat Neurosci 7, 295–301 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1198
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1198
This article is cited by
-
Auditory-cognitive training for adult cochlear implant recipients: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial
Trials (2021)
-
Motor engagement relates to accurate perception of phonemes and audiovisual words, but not auditory words
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Investigating Cortical Responses to Noise-Vocoded Speech in Children with Normal Hearing Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS)
Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology (2021)
-
Repetition enhancement to voice identities in the dog brain
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Effects of genetic variability of CYP2D6 on neural substrates of sustained attention during on-task activity
Translational Psychiatry (2020)