Abstract
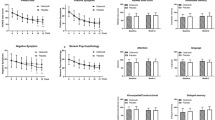
The neurosteroid pregnenolone and its sulfated derivative enhance learning and memory in rodents. Pregnenolone sulfate also positively modulates NMDA receptors and could thus ameliorate hypothesized NMDA receptor hypofunction in schizophrenia. Furthermore, clozapine increases pregnenolone in rodent hippocampus, possibly contributing to its superior efficacy. We therefore investigated adjunctive pregnenolone for cognitive and negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder receiving stable doses of second-generation antipsychotics in a pilot randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Following a 2-week single-blind placebo lead-in, patients were randomized to pregnenolone (fixed escalating doses to 500 mg/day) or placebo, for 8 weeks. Primary end points were changes in BACS and MCCB composite and total SANS scores. Of 21 patients randomized, 18 completed at least 4 weeks of treatment (n=9/group). Pregnenolone was well tolerated. Patients receiving pregnenolone demonstrated significantly greater improvements in SANS scores (mean change=10.38) compared with patients receiving placebo (mean change=2.33), p=0.048. Mean composite changes in BACS and MCCB scores were not significantly different in patients randomized to pregnenolone compared with placebo. However, serum pregnenolone increases predicted BACS composite scores at 8 weeks in the pregnenolone group (rs=0.81, p=0.022). Increases in allopregnanolone, a GABAergic pregnenolone metabolite, also predicted BACS composite scores (rs=0.74, p=0.046). In addition, baseline pregnenolone (rs=−0.76, p=0.037), pregnenolone sulfate (rs=−0.83, p=0.015), and allopregnanolone levels (rs=−0.83, p=0.015) were inversely correlated with improvements in MCCB composite scores, further supporting a possible role for neurosteroids in cognition. Mean BACS and MCCB composite scores were correlated (rs=0.74, p<0.0001). Pregnenolone may be a promising therapeutic agent for negative symptoms and merits further investigation for cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Addington D, Addington J, Schissel B (1990). A depression rating scale for schizophrenics. Schizophr Res 3: 247–251.
Akwa Y, Ladurelle N, Covey DF, Baulieu EE (2001). The synthetic enantiomer of pregnenolone sulfate is very active on memory in rats and mice, even more so than its physiological neurosteroid counterpart: distinct mechanisms? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 14033–14037.
Andreasen N (1983). Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS). University of Iowa: Iowa City.
Azcoitia I, Leonelli E, Magnaghi V, Veiga S, Garcia-Segura LM, Melcangi RC (2003). Progesterone and its derivatives dihydroprogesterone and tetrahydroprogesterone reduce myelin fiber morphological abnormalities and myelin fiber loss in the sciatic nerve of aged rats. Neurobiol Aging 24: 853–860.
Barbaccia ML, Affricano D, Purdy RH, Maciocco E, Spiga F, Biggio G (2001). Clozapine, but not haloperidol, increases brain concentrations of neuroactive steroids in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 25: 489–497.
Barnes TR (1989). A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154: 672–676.
Benes FM, Berretta S (2001). GABAergic interneurons: implications for understanding schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 25: 1–27.
Benes FM, Lim B, Matzilevich D, Walsh JP, Subburaju S, Minns M (2007). Regulation of the GABA cell phenotype in hippocampus of schizophrenics and bipolars. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 10164–10169.
Benitez-King G, Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Ortiz L, Meza I (2004). The neuronal cytoskeleton as a potential therapeutical target in neurodegenerative diseases and schizophrenia. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 3: 515–533.
Bowlby MR (1993). Pregnenolone sulfate potentiation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol 43: 813–819.
Buchanan RW (2006). Important steps in the development of cognitive-enhancing drugs in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 163: 1867–1869.
Buchanan RW (2007). Persistent negative symptoms in schizophrenia: an overview. Schizophr Bull 33: 1013–1022.
Buchanan RW, Davis M, Goff D, Green MF, Keefe RS, Leon AC et al (2005). A summary of the FDA-NIMH-MATRICS workshop on clinical trial design for neurocognitive drugs for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 31: 5–19.
Buchanan RW, Javitt DC, Marder SR, Schooler NR, Gold JM, McMahon RP et al (2007). The Cognitive and Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia Trial (CONSIST): the efficacy of glutamatergic agents for negative symptoms and cognitive impairments. Am J Psychiatry 164: 1593–1602.
Carter CS, Barch DM, Buchanan RW, Bullmore E, Krystal JH, Cohen J et al (2008). Identifying cognitive mechanisms targeted for treatment development in schizophrenia: an overview of the first meeting of the Cognitive Neuroscience Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia Initiative. Biol Psychiatry 64: 4–10.
Cascella NG, Macciardi F, Cavallini C, Smeraldi E (1994). D-cycloserine adjuvant therapy to conventional neuroleptic treatment in schizophrenia: an open-label study. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 95: 105–111.
Charalampopoulos I, Alexaki VI, Tsatsanis C, Minas V, Dermitzaki E, Lasaridis I et al (2006). Neurosteroids as endogenous inhibitors of neuronal cell apoptosis in aging. Ann NY Acad Sci 1088: 139–152.
Charalampopoulos I, Tsatsanis C, Dermitzaki E, Alexaki VI, Castanas E, Margioris AN et al (2004). Dehydroepiandrosterone and allopregnanolone protect sympathoadrenal medulla cells against apoptosis via antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 8209–8214.
Cheney DL, Uzunov D, Guidotti A (1995). Pregnenolone sulfate antagonizes dizocilpine amnesia: role for allopregnanolone. Neuroreport 6: 1697–1700.
Coyle JT (2006). Glutamate and schizophrenia: beyond the dopamine hypothesis. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26: 365–384.
Danovich L, Veenman L, Leschiner S, Lahav M, Shuster V, Weizman A et al (2008). The influence of clozapine treatment and other antipsychotics on the 18 kDa translocator protein, formerly named the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor, and steroid production. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18: 24–33.
Darnaudery M, Koehl M, Pallares M, Le Moal M, Mayo W (1998). The neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate increases cortical acetylcholine release: a microdialysis study in freely moving rats. J Neurochem 71: 2018–2022.
Darnaudery M, Pallares M, Piazza PV, Le Moal M, Mayo W (2002). The neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate infused into the medial septum nucleus increases hippocampal acetylcholine and spatial memory in rats. Brain Res 951: 237–242.
Davison R, Koets P, Snow WG, Gabrielson CLG (1950). Effects of delta 5 pregnenolone in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Intern Med 85: 365–389.
Dawson D, Reid K (1997). Fatigue, alcohol and performance impairment. Nature 388: 235.
Dickerson F, Stallings C, Origoni A, Boronow J, Yolken R (2007). C-reactive protein is associated with the severity of cognitive impairment but not of psychiatric symptoms in individuals with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 93: 261–265.
Djebaili M, Guo Q, Pettus EH, Hoffman SW, Stein DG (2005). The neurosteroids progesterone and allopregnanolone reduce cell death, gliosis, and functional deficits after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 22: 106–118.
Djebaili M, Hoffman SW, Stein DG (2004). Allopregnanolone and progesterone decrease cell death and cognitive deficits after a contusion of the rat pre-frontal cortex. Neuroscience 123: 349–359.
Duncan EJ, Szilagyi S, Schwartz MP, Bugarski-Kirola D, Kunzova A, Negi S et al (2004). Effects of D-cycloserine on negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 71: 239–248.
Ebner MJ, Corol DI, Havlikova H, Honour JW, Fry JP (2006). Identification of neuroactive steroids and their precursors and metabolites in adult male rat brain. Endocrinology 147: 179–190.
First M, Spitzer R, Gibbon M, Williams J (1996). Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders-patient edition (SCID-I/P, version 2.0).
Flood JF, Morley JE, Roberts E (1992). Memory-enhancing effects in male mice of pregnenolone and steroids metabolically derived from it. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 1567–1571.
Flood JF, Morley JE, Roberts E (1995). Pregnenolone sulfate enhances post-training memory processes when injected in very low doses into limbic system structures: the amygdala is by far the most sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 10806–10810.
Fontaine-Lenoir V, Chambraud B, Fellous A, David S, Duchossoy Y, Baulieu EE et al (2006). Microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) is a neurosteroid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 4711–4716.
Freeman H, Pincus G, Bachrach S, Johnson CW, McCabe GE, MacGilpin H (1950a). Oral steroid medication in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 10: 1523–1532.
Freeman H, Pincus G, Johnson CW, Bachrach S, McCabe GE, MacGilpin H (1950b). Therapeutic efficacy of delta5-pregnenolone in rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA 142: 1124–1127.
George MS, Guidotti A, Rubinow D, Pan B, Mikalauskas K, Post RM (1994). CSF neuroactive steroids in affective disorders: pregnenolone, progesterone, and DBI. Biol Psychiatry 35: 775–780.
Ghoumari AM, Ibanez C, El-Etr M, Leclerc P, Eychenne B, O'Malley BW et al (2003). Progesterone and its metabolites increase myelin basic protein expression in organotypic slice cultures of rat cerebellum. J Neurochem 86: 848–859.
Glantz LA, Gilmore JH, Lieberman JA, Jarskog LF (2006). Apoptotic mechanisms and the synaptic pathology of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 81: 47–63.
Glantz LA, Lewis DA (2000). Decreased dendritic spine density on prefrontal cortical pyramidal neurons in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57: 65–73.
Goff DC, Henderson DC, Evins AE, Amico E (1999a). A placebo-controlled crossover trial of D-cycloserine added to clozapine in patients with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 45: 512–514.
Goff DC, Tsai G, Levitt J, Amico E, Manoach D, Schoenfeld DA et al (1999b). A placebo-controlled trial of D-cycloserine added to conventional neuroleptics in patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56: 21–27.
Goff DC, Tsai G, Manoach DS, Coyle JT (1995). Dose-finding trial of D-cycloserine added to neuroleptics for negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 152: 1213–1215.
Goff DC, Tsai G, Manoach DS, Flood J, Darby DG, Coyle JT (1996). D-cycloserine added to clozapine for patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 153: 1628–1630.
Green MF (2006). Cognitive impairment and functional outcome in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 67: e12.
Green MF, Kern RS, Braff DL, Mintz J (2000). Neurocognitive deficits and functional outcome in schizophrenia: are we measuring the ‘right stuff’? Schizophr Bull 26: 119–136.
Griffin LD, Gong W, Verot L, Mellon SH (2004). Niemann-Pick type C disease involves disrupted neurosteroidogenesis and responds to allopregnanolone. Nat Med 10: 704–711.
Guest CM, Kammerer WH, Cecil RL, Berson SA (1950). Epinephrine, pregnenolone and testosterone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA 143: 338–344.
Guidotti A, Auta J, Davis JM, Dong E, Grayson DR, Veldic M et al (2005). GABAergic dysfunction in schizophrenia: new treatment strategies on the horizon. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 180: 191–205.
Hakak Y, Walker JR, Li C, Wong WH, Davis KL, Buxbaum JD et al (2001). Genome-wide expression analysis reveals dysregulation of myelination-related genes in chronic schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 4746–4751.
Harvey PD, Green MF, Keefe RS, Velligan DI (2004). Cognitive functioning in schizophrenia: a consensus statement on its role in the definition and evaluation of effective treatments for the illness. J Clin Psychiatry 65: 361–372.
He J, Evans CO, Hoffman SW, Oyesiku NM, Stein DG (2004). Progesterone and allopregnanolone reduce inflammatory cytokines after traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 189: 404–412.
Heinrichs DW, Hanlon TE, Carpenter Jr WT (1984). The Quality of Life Scale: an instrument for rating the schizophrenic deficit syndrome. Schizophr Bull 10: 388–398.
Henderson E, Weinberg M, Wright WA (1950). Pregnenolone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 10: 455–474.
Heresco-Levy U, Ermilov M, Lichtenberg P, Bar G, Javitt DC (2004). High-dose glycine added to olanzapine and risperidone for the treatment of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 55: 165–171.
Heresco-Levy U, Javitt DC, Ebstein R, Vass A, Lichtenberg P, Bar G et al (2005). D-serine efficacy as add-on pharmacotherapy to risperidone and olanzapine for treatment-refractory schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 57: 577–585.
Heresco-Levy U, Javitt DC, Ermilov M, Mordel C, Horowitz A, Kelly D (1996). Double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of glycine adjuvant therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 169: 610–617.
Heresco-Levy U, Javitt DC, Ermilov M, Mordel C, Silipo G, Lichtenstein M (1999). Efficacy of high-dose glycine in the treatment of enduring negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56: 29–36.
Higashi T, Daifu Y, Ikeshima T, Yagi T, Shimada K (2003a). Studies on neurosteroids XV. Development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for examining whether pregnenolone sulfate is a veritable neurosteroid. J Pharm Biomed Anal 30: 1907–1917.
Higashi T, Sugitani H, Yagi T, Shimada K (2003b). Studies on neurosteroids XVI. Levels of pregnenolone sulfate in rat brains determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay not requiring solvolysis. Biol Pharm Bull 26: 709–711.
Hsu HJ, Liang MR, Chen CT, Chung BC (2006). Pregnenolone stabilizes microtubules and promotes zebrafish embryonic cell movement. Nature 439: 480–483.
Ibanez C, Shields SA, El-Etr M, Leonelli E, Magnaghi V, Li WW et al (2003). Steroids and the reversal of age-associated changes in myelination and remyelination. Prog Neurobiol 71: 49–56.
Irwin RP, Lin SZ, Rogawski MA, Purdy RH, Paul SM (1994). Steroid potentiation and inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated intracellular Ca++ responses: structure-activity studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271: 677–682.
Jarskog LF, Glantz LA, Gilmore JH, Lieberman JA (2005). Apoptotic mechanisms in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29: 846–858.
Javitt DC (2004). Glutamate as a therapeutic target in psychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry 9: 984–997.
Javitt DC (2007). Glutamate and schizophrenia: phencyclidine, N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors, and dopamine-glutamate interactions. Int Rev Neurobiol 78: 69–108.
Javitt DC, Silipo G, Cienfuegos A, Shelley AM, Bark N, Park M et al (2001). Adjunctive high-dose glycine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 4: 385–391.
Johansson T, Frandberg PA, Nyberg F, Le Greves P (2008). Molecular mechanisms for nanomolar concentrations of neurosteroids at NR1/NR2B receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324: 759–768.
Jones NC, Constantin D, Prior MJ, Morris PG, Marsden CA, Murphy S (2005). The neuroprotective effect of progesterone after traumatic brain injury in male mice is independent of both the inflammatory response and growth factor expression. Eur J Neurosci 21: 1547–1554.
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987). The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13: 261–276.
Keefe RS, Bilder RM, Davis SM, Harvey PD, Palmer BW, Gold JM et al (2007). Neurocognitive effects of antipsychotic medications in patients with chronic schizophrenia in the CATIE Trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64: 633–647.
Keefe RS, Goldberg TE, Harvey PD, Gold JM, Poe MP, Coughenour L (2004). The Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia: reliability, sensitivity, and comparison with a standard neurocognitive battery. Schizophr Res 68: 283–297.
Keefe RS, Harvey PD, Goldberg TE, Gold JM, Walker TM, Kennel C et al (2008). Norms and standardization of the Brief Assessment of Cognition in Schizophrenia (BACS). Schizophr Res 102: 108–115.
Kirkpatrick B, Fenton WS, Carpenter Jr WT, Marder SR (2006). The NIMH-MATRICS consensus statement on negative symptoms. Schizophr Bull 32: 214–219.
Knight JG, Menkes DB, Highton J, Adams DD (2007). Rationale for a trial of immunosuppressive therapy in acute schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 12: 424–431.
Koenig HL, Schumacher M, Ferzaz B, Thi AN, Ressouches A, Guennoun R et al (1995). Progesterone synthesis and myelin formation by Schwann cells. Science 268: 1500–1503.
Kokate TG, Banks MK, Magee T, Yamaguchi S, Rogawski MA (1999). Finasteride, a 5alpha-reductase inhibitor, blocks the anticonvulsant activity of progesterone in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288: 679–684.
Kokate TG, Cohen AL, Karp E, Rogawski MA (1996). Neuroactive steroids protect against pilocarpine- and kainic acid-induced limbic seizures and status epilepticus in mice. Neuropharmacology 35: 1049–1056.
Kokate TG, Svensson BE, Rogawski MA (1994). Anticonvulsant activity of neurosteroids: correlation with gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked chloride current potentiation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270: 1223–1229.
Lacapere JJ, Papadopoulos V (2003). Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor: structure and function of a cholesterol-binding protein in steroid and bile acid biosynthesis. Steroids 68: 569–585.
Lacroix C, Fiet J, Benais JP, Gueux B, Bonete R, Villette JM et al (1987). Simultaneous radioimmunoassay of progesterone, androst-4-enedione, pregnenolone, dehydroepiandrosterone and 17-hydroxyprogesterone in specific regions of human brain. J Steroid Biochem 28: 317–325.
Ladurelle N, Eychenne B, Denton D, Blair-West J, Schumacher M, Robel P et al (2000). Prolonged intracerebroventricular infusion of neurosteroids affects cognitive performances in the mouse. Brain Res 858: 371–379.
Lamond N, Dawson D (1999). Quantifying the performance impairment associated with fatigue. J Sleep Res 8: 255–262.
Lanthier A, Patwardhan VV (1986). Sex steroids and 5-en-3 β-hydroxysteroids in specific regions of the human brain and cranial nerves. J Steroid Biochem 25: 445–449.
Lencz T, Morgan TV, Athanasiou M, Dain B, Reed CR, Kane JM et al (2007). Converging evidence for a pseudoautosomal cytokine receptor gene locus in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 12: 572–580.
Lewis DA, Glantz LA, Pierri JN, Sweet RA (2003). Altered cortical glutamate neurotransmission in schizophrenia: evidence from morphological studies of pyramidal neurons. Ann NY Acad Sci 1003: 102–112.
Lewis DA, Hashimoto T, Volk DW (2005). Cortical inhibitory neurons and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 6: 312–324.
Lewis DA, Volk DW, Hashimoto T (2004). Selective alterations in prefrontal cortical GABA neurotransmission in schizophrenia: a novel target for the treatment of working memory dysfunction. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174: 143–150.
Liere P, Pianos A, Eychenne B, Cambourg A, Liu S, Griffiths W et al (2004). Novel lipoidal derivatives of pregnenolone and dehydroepiandrosterone and absence of their sulfated counterparts in rodent brain. J Lipid Res 45: 2287–2302.
Liu S, Sjovall J, Griffiths WJ (2003). Neurosteroids in rat brain: extraction, isolation, and analysis by nanoscale liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 75: 5835–5846.
Lockhart EM, Warner DS, Pearlstein RD, Penning DH, Mehrabani S, Boustany RM (2002). Allopregnanolone attenuates N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced excitotoxicity and apoptosis in the human NT2 cell line in culture. Neurosci Lett 328: 33–36.
Majewska MD, Harrison NL, Schwartz RD, Barker JL, Paul SM (1986). Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science 232: 1004–1007.
Marder SR (2006). Drug initiatives to improve cognitive function. J Clin Psychiatry 67 (Suppl 9): 31–35; discussion 36–42.
Marder SR, Fenton W (2004). Measurement and Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia: NIMH MATRICS initiative to support the development of agents for improving cognition in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 72: 5–9.
Marx CE, Shampine LJ, Duncan GE, VanDoren MJ, Grobin AC, Massing MW et al (2006a). Clozapine markedly elevates pregnenolone in rat hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and serum: candidate mechanism for superior efficacy? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84: 598–608.
Marx CE, Shampine LJ, Khisti RT, Trost WT, Bradford DW, Grobin AC et al (2006b). Olanzapine and fluoxetine administration and coadministration increase rat hippocampal pregnenolone, allopregnanolone and peripheral deoxycorticosterone: implications for therapeutic actions. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84: 609–617.
Marx CE, Stevens RD, Shampine LJ, Uzunova V, Trost WT, Butterfield MI et al (2006c). Neuroactive steroids are altered in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: relevance to pathophysiology and therapeutics. Neuropsychopharmacology 31: 1249–1263.
Marx CE, Trost WT, Shampine L, Behm FM, Giordano LA, Massing MW et al (2006d). Neuroactive steroids, negative affect, and nicotine dependence severity in male smokers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 186: 462–472.
Marx CE, Trost WT, Shampine LJ, Stevens RD, Hulette CM, Steffens DC et al (2006e). The neurosteroid allopregnanolone is reduced in prefrontal cortex in Alzheimer's disease. Biol Psychiatry 60: 1287–1294.
Marx CE, VanDoren MJ, Duncan GE, Lieberman JA, Morrow AL (2003). Olanzapine and clozapine increase the GABAergic neuroactive steroid allopregnanolone in rodents. Neuropsychopharmacology 28: 1–13.
Mathis C, Paul SM, Crawley JN (1994). The neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate blocks NMDA antagonist-induced deficits in a passive avoidance memory task. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 116: 201–206.
Mathis C, Vogel E, Cagniard B, Criscuolo F, Ungerer A (1996). The neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate blocks deficits induced by a competitive NMDA antagonist in active avoidance and lever-press learning tasks in mice. Neuropharmacology 35: 1057–1064.
Mayo W, Dellu F, Robel P, Cherkaoui J, Le Moal M, Baulieu EE et al (1993). Infusion of neurosteroids into the nucleus basalis magnocellularis affects cognitive processes in the rat. Brain Res 607: 324–328.
Mayo W, Lemaire V, Malaterre J, Rodriguez JJ, Cayre M, Stewart MG et al (2005). Pregnenolone sulfate enhances neurogenesis and PSA-NCAM in young and aged hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 26: 103–114.
McGavack TH, Chevalley J, Weissberg J (1951). The use of delta 5-pregnenolone in various clinical disorders. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 11: 559–577.
Meieran SE, Reus VI, Webster R, Shafton R, Wolkowitz OM (2004). Chronic pregnenolone effects in normal humans: attenuation of benzodiazepine-induced sedation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29: 486–500.
Mellon SH, Gong W, Schonemann MD (2008). Endogenous and synthetic neurosteroids in treatment of Niemann-Pick Type C disease. Brain Res Rev 57: 410–420.
Meziane H, Mathis C, Paul SM, Ungerer A (1996). The neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate reduces learning deficits induced by scopolamine and has promnestic effects in mice performing an appetitive learning task. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 126: 323–330.
Millan MJ (2005). N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors as a target for improved antipsychotic agents: novel insights and clinical perspectives. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179: 30–53.
Morley JE, Kaiser F, Raum WJ, Perry III HM, Flood JF, Jensen J et al (1997). Potentially predictive and manipulable blood serum correlates of aging in the healthy human male: progressive decreases in bioavailable testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, and the ratio of insulin-like growth factor 1 to growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 7537–7542.
Morrow AL, Pace JR, Purdy RH, Paul SM (1990). Characterization of steroid interactions with gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-gated chloride ion channels: evidence for multiple steroid recognition sites. Mol Pharmacol 37: 263–270.
Morrow AL, Suzdak PD, Paul SM (1987). Steroid hormone metabolites potentiate GABA receptor-mediated chloride ion flux with nanomolar potency. Eur J Pharmacol 142: 483–485.
Mtchedlishvili Z, Kapur J (2003). A presynaptic action of the neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate on GABAergic synaptic transmission. Mol Pharmacol 64: 857–864.
Murakami K, Fellous A, Baulieu EE, Robel P (2000). Pregnenolone binds to microtubule-associated protein 2 and stimulates microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 3579–3584.
Naylor JC, Hulette CM, Steffens DC, Shampine LJ, Ervin JF, Payne VM et al (2008). Cerebrospinal fluid dehydroepiandrosterone levels are correlated with brain dehydroepiandrosterone levels, elevated in Alzheimer's disease, and related to neuropathological disease stage. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93: 3173–3178.
Nuechterlein K, Green MF (2006). MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery (MCCB). MATRICS Assessments Inc.: Los Angeles.
Nuechterlein KH, Green MF, Kern RS, Baade LE, Barch DM, Cohen JD et al (2008). The MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery, part 1: test selection, reliability, and validity. Am J Psychiatry 165: 203–213.
Pallares M, Darnaudery M, Day J, Le Moal M, Mayo W (1998). The neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate infused into the nucleus basalis increases both acetylcholine release in the frontal cortex or amygdala and spatial memory. Neuroscience 87: 551–558.
Pincus G, Hoagland H (1944). Effects of administered pregnenolone on fatiguing psychomotor performance. J Aviation Med 15: 98–115.
Pincus G, Hoagland H (1945a). Effects on industrial production of the administration of Δ5 pregnenolone to factory workers, I. Psychosomatic Medicine 7: 342–346.
Pincus G, Hoagland H (1945b). Effects on industrial production of the administration of Δ5 pregnenolone to factory workers, II. Psychosomatic Medicine 7: 347–352.
Porcu P, O'Buckley TK, Morrow AL, Adinoff B (2008). Differential hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activation of the neuroactive steroids pregnenolone sulfate and deoxycorticosterone in healthy controls and alcohol-dependent subjects. Psychoneuroendocrinology 33: 214–226.
Roberts E (1995). Pregnenolone—from Selye to Alzheimer and a model of the pregnenolone sulfate binding site on the GABAA receptor. Biochem Pharmacol 49: 1–16.
Robertson CL, Puskar A, Hoffman GE, Murphy AZ, Saraswati M, Fiskum G (2006). Physiologic progesterone reduces mitochondrial dysfunction and hippocampal cell loss after traumatic brain injury in female rats. Exp Neurol 197: 235–243.
Romeo E, Cheney DL, Zivkovic I, Costa E, Guidotti A (1994). Mitochondrial diazepam-binding inhibitor receptor complex agonists antagonize dizocilpine amnesia: putative role for allopregnanolone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270: 89–96.
Roof RL, Hoffman SW, Stein DG (1997). Progesterone protects against lipid peroxidation following traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Chem Neuropathol 31: 1–11.
Rosse RB, Fay-McCarthy M, Kendrick K, Davis RE, Deutsch SI (1996). D-cycloserine adjuvant therapy to molindone in the treatment of schizophrenia. Clin Neuropharmacol 19: 444–450.
Rujescu D, Bender A, Keck M, Hartmann AM, Ohl F, Raeder H et al (2006). A pharmacological model for psychosis based on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor hypofunction: molecular, cellular, functional and behavioral abnormalities. Biol Psychiatry 59: 721–729.
Sakamoto H, Ukena K, Tsutsui K (2001). Effects of progesterone synthesized de novo in the developing Purkinje cell on its dendritic growth and synaptogenesis. J Neurosci 21: 6221–6232.
Sayeed I, Guo Q, Hoffman SW, Stein DG (2006). Allopregnanolone, a progesterone metabolite, is more effective than progesterone in reducing cortical infarct volume after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Ann Emerg Med 47: 381–389.
Schumacher M, Akwa Y, Guennoun R, Robert F, Labombarda F, Desarnaud F et al (2000). Steroid synthesis and metabolism in the nervous system: trophic and protective effects. J Neurocytol 29: 307–326.
Schumacher M, Liere P, Akwa Y, Rajkowski K, Griffiths W, Bodin K et al (2008). Pregnenolone sulfate in the brain: a controversial neurosteroid. Neurochem Int 52: 522–540.
Simpson GM, Angus JW (1970). A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 212: 11–19.
Sliwinski A, Monnet FP, Schumacher M, Morin-Surun MP (2004). Pregnenolone sulfate enhances long-term potentiation in CA1 in rat hippocampus slices through the modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Neurosci Res 78: 691–701.
Stein DG (2008). Progesterone exerts neuroprotective effects after brain injury. Brain Res Rev 57: 386–397.
Strous RD, Maayan R, Lapidus R, Stryjer R, Lustig M, Kotler M et al (2003). Dehydroepiandrosterone augmentation in the management of negative, depressive, and anxiety symptoms in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60: 133–141.
Tkachev D, Mimmack ML, Huffaker SJ, Ryan M, Bahn S (2007). Further evidence for altered myelin biosynthesis and glutamatergic dysfunction in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10: 557–563.
Tsai G, Yang P, Chung LC, Lange N, Coyle JT (1998). D-serine added to antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 44: 1081–1089.
Tsai GE, Yang P, Chung LC, Tsai IC, Tsai CW, Coyle JT (1999). D-serine added to clozapine for the treatment of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156: 1822–1825.
Vallee M, Mayo W, Darnaudery M, Corpechot C, Young J, Koehl M et al (1997). Neurosteroids: deficient cognitive performance in aged rats depends on low pregnenolone sulfate levels in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 14865–14870.
Vallee M, Shen W, Heinrichs SC, Zorumski CF, Covey DF, Koob GF et al (2001). Steroid structure and pharmacological properties determine the anti-amnesic effects of pregnenolone sulphate in the passive avoidance task in rats. Eur J Neurosci 14: 2003–2010.
van Berckel BN, Hijman R, van der Linden JA, Westenberg HG, van Ree JM, Kahn RS (1996). Efficacy and tolerance of D-cycloserine in drug-free schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 40: 1298–1300.
VanLandingham JW, Cekic M, Cutler S, Hoffman SW, Stein DG (2007). Neurosteroids reduce inflammation after TBI through CD55 induction. Neurosci Lett 425: 94–98.
Wang JM, Johnston PB, Ball BG, Brinton RD (2005). The neurosteroid allopregnanolone promotes proliferation of rodent and human neural progenitor cells and regulates cell-cycle gene and protein expression. J Neurosci 25: 4706–4718.
Wang MD, Wahlstrom G, Backstrom T (1997). The regional brain distribution of the neurosteroids pregnenolone and pregnenolone sulfate following intravenous infusion. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 62: 299–306.
Weill-Engerer S, David JP, Sazdovitch V, Liere P, Eychenne B, Pianos A et al (2002). Neurosteroid quantification in human brain regions: comparison between Alzheimer's and nondemented patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87: 5138–5143.
Wright DW, Kellermann AL, Hertzberg VS, Clark PL, Frankel M, Goldstein FC et al (2007). ProTECT: a randomized clinical trial of progesterone for acute traumatic brain injury. Ann Emerg Med 49: 391–402.
Wu FS, Gibbs TT, Farb DH (1991). Pregnenolone sulfate: a positive allosteric modulator at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Mol Pharmacol 40: 333–336.
Xiao G, Wei J, Yan W, Wang W, Lu Z (2008). Improved outcomes from the administration of progesterone for patients with acute severe traumatic brain injury: a randomized controlled trial. Crit Care 12: R61.
Xilouri M, Papazafiri P (2006). Anti-apoptotic effects of allopregnanolone on P19 neurons. Eur J Neurosci 23: 43–54.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the following sources: The VA Mid-Atlantic Mental Illness, Research, Education, and Clinical Center, VA Advanced Research Career Development Award (CEM), K23 MH65080 (CEM), National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Affective Disorders (CEM), Durham VA REAP (PI Roger D. Madison, PhD), R37AA10564 (ALM), VA Career Development Award (JLS). We thank Gillian Parke for her excellent assistance with this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
DISCLOSURE OF COMPENSATION OVER THE LAST 3 YEARS/CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Dr Marx has no compensation to disclose over the last 3 years. Dr Marx is a co-applicant on a pending US patent application on the use of neurosteroids for the treatment of central nervous system disorders. She is an unpaid scientific advisor and board member of NeuroScience Pharmaceuticals. Dr Keefe has received compensation from the following sources: Astra-Zeneca, Cyberonics, Gabriel Pharmaceuticals, Organon Pharmaceuticals, Otsuka, Pfizer, Saegis, Abbott, Acadia, BiolineRx, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cephalo, Cortex, Dainippon Sumitomo Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson, Lundbeck, Memory Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Orexigen, Sanofi/Aventis, Shering-Plough, Wyeth, and Xenoport. Dr Keefe is a contributor to a pending US patent application on the use of neurosteroids for the treatment of central nervous system disorders. Dr Keefe receives royalties for two of the cognitive test batteries used in this study, the BACS and the MATRICS Consensus Cognitive Battery. Dr Buchanan has received compensation from the following sources: Astra-Zeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Natixis Bleichroeder, Organon, Ortho-McNeil, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, Solvay Pharmaceuticals, and Wyeth. Dr Hamer has received compensation from the following sources: Acadia, Allergan, Alpharma, Astra-Zeneca, Cenerx, Corcept, EnabledMD, Epix, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Schwartz, Solvay Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi-Aventis, Takeda, and Wyeth. Dr Kilts, Dr Bradford, Dr Strauss, Dr Naylor, Dr Payne, Ms Leimone, Dr Dunn, Dr Porcu, Dr Morrow, and Mr Shampine have no compensation to disclose over the last 3 years. Dr Lieberman has received compensation from the following sources: Astra-Zeneca, Eli Lilly, Forest Laboratories, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Wyeth, Solvay Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, and Repligen. Dr Savitz has received compensation from the following sources: Astra-Zeneca, Sanofi-Aventis, Janssen, and Pfizer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marx, C., Keefe, R., Buchanan, R. et al. Proof-of-Concept Trial with the Neurosteroid Pregnenolone Targeting Cognitive and Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol 34, 1885–1903 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.26
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Novel neurosteroid therapeutics for post-partum depression: perspectives on clinical trials, program development, active research, and future directions
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Negative symptoms and neurocognition in drug-naïve schizophrenia: moderating role of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and interferon-gamma (INF-γ)
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2023)
-
Effects of Blockade of Cholinesterase on Negative Disorders in Schizophrenia
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2022)
-
Alteration of the steroidogenesis in boys with autism spectrum disorders
Translational Psychiatry (2020)
-
Biomarker screening for antenatal depression in women who underwent caesarean section: a matched observational study with plasma Lipidomics
BMC Psychiatry (2019)