Abstract
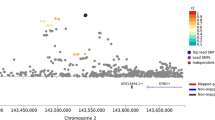
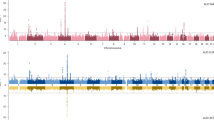
Several genome scans on alcohol dependence (AD) and AD-related traits have been published. In this article, we present the results of a genome-wide linkage scan on AD and several related traits in 322 European-American (EA) families, and results of additional analysis in 335 African-American (AA) families that were the subject of a previous report. All families were initially ascertained for cocaine and/or opioid dependence. Non-parametric linkage analysis in the EA sample revealed suggestive linkages on chromosomes 7 (LOD=2.1 at 82.8 cM, p=0.0009) and 10 (LOD=3.0 at 137.7 cM, p=0.0001). The chromosome 10 linkage peak is 20 cM distal from a genome-wide significant linkage peak we observed previously in the AA sample. Parametric linkage analysis on chromosome 10 (assuming a recessive model, 80% penetrance, disease allele frequency=0.3) resulted in LOD scores of 2.7 at 136.7 cM and 1.9 at 121.7 cM in the EA and AA samples, respectively, with a combined sample genome-wide significant LOD score of 4.1 at 131.7 cM. To reduce heterogeneity of the AD phenotype, we also assessed linkage of chromosome 10 markers with the presence of alcohol withdrawal symptoms, one of the seven components of the DSM-IV diagnosis of AD. Suggestive evidence for linkage was observed in both populations with only 5 cM separating the location of the peak LOD scores despite a loss of power due to a smaller number of families informative for this trait. Results of our study confirm a chromosome 10 risk locus for AD in two genetically distinct populations and suggest that this locus may correspond more precisely to a specific component of the disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2002). Merlin—rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30: 97–101.
Abecasis GR, Wigginton JE (2005). Handling marker-marker linkage disequilibrium: pedigree analysis with clustered markers. Am J Hum Genet 77: 754–767.
Agrawal A, Hinrichs AL, Dunn G, Bertelsen S, Dick DM, Saccone SF et al. (2008). Linkage scan for quantitative traits identifies new regions of interest for substance dependence in the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) sample. Drug Alcohol Depend 93: 12–20.
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC.
Bautista JF, Quade SR, Parrado AR, Goddard KA (2005). Linkage analysis of alcoholism-related electrophysiological phenotypes: genome scans with microsatellites compared to single-nucleotide polymorphisms. BMC Genet 6 (Suppl 1): S156.
Erdmann J, Nothen MM, Shimron-Abarbanell D, Rietschel M, Albus M, Borrmann M et al. (1996). The human serotonin 7 (5-HT7) receptor gene: genomic organization and systematic mutation screening in schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder. Mol Psychiatry 1: 392–397.
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003). Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164: 1567–1587.
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2007). Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: dominant markers and null alleles. Mol Ecol Notes 7: 574–578.
Fowler T, Shelton K, Lifford K, Rice F, McBride A, Nikolov I et al. (2007). Genetic and environmental influences on the relationship between peer alcohol use and own alcohol use in adolescents. Addiction 102: 894–903.
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Panhuysen C, Weiss RD, Brady K, Poling J et al. (2009). Dense genomewide linkage scan for alcohol dependence in African Americans: significant linkage on chromosome 10. Biol Psychiatry 65: 111–115.
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR (2009). Genetics of alcohol dependence. Hum Genet 126: 91–99.
Gelernter J, Panhuysen C, Weiss R, Brady K, Hesselbrock V, Rounsaville B et al. (2005). Genomewide linkage scan for cocaine dependence and related traits: significant linkages for a cocaine-related trait and cocaine-induced paranoia. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 136B: 45–52.
Gelernter J, Panhuysen C, Weiss R, Brady K, Poling J, Krauthammer M et al. (2007). Genomewide linkage scan for nicotine dependence: identification of a chromosome 5 risk locus. Biol Psychiatry 61: 119–126.
Gelernter J, Panhuysen C, Wilcox M, Hesselbrock V, Rounsaville B, Poling J et al. (2006). Genomewide linkage scan for opioid dependence and related traits. Am J Hum Genet 78: 759–769.
Harwood H (2000). Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. National Institutes of Health, Rockville, MD.
Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Ogburn E, Grant BF (2007). Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64: 830–842.
Hopfer CJ, Crowley TJ, Hewitt JK (2003). Review of twin and adoption studies of adolescent substance use. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42: 710–719.
Ikeda M, Iwata N, Kitajima T, Suzuki T, Yamanouchi Y, Kinoshita Y et al. (2006). Positive association of the serotonin 5-HT7 receptor gene with schizophrenia in a Japanese population. Neuropsychopharmacology 31: 866–871.
Kang TS, Woo SW, Park HJ, Lee Y, Roh J (2009). Comparison of genetic polymorphisms of CYP2E1, ADH2, and ALDH2 genes involved in alcohol metabolism in Koreans and four other ethnic groups. J Clin Pharm Ther 34: 225–230.
Keyes KM, Geier T, Grant BF, Hasin DS (2009). Influence of a drinking quantity and frequency measure on the prevalence and demographic correlates of DSM-IV alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33: 761–771.
Kong A, Cox N (1997). Allele-sharing models: LOD scores and accurate linkage tests. Am J Hum Genet 61: 1179–1188.
Kuo PH, Neale MC, Riley BP, Webb BT, Sullivan PF, Vittum J et al. (2006). Identification of susceptibility loci for alcohol-related traits in the Irish Affected Sib Pair Study of Alcohol Dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30: 1807–1816.
Lander E, Kruglyak L (1995). Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat Genet 11: 241–247.
Leo D, Adriani W, Cavaliere C, Cirillo G, Marco EM, Romano E et al. (2009). Methylphenidate to adolescent rats drives enduring changes of accumbal Htr7 expression: implications for impulsive behavior and neuronal morphology. Genes Brain Behav 8: 356–368.
Lin Z, Walther D, Yu XY, Li S, Drgon T, Uhl GR (2005). SLC18A2 promoter haplotypes and identification of a novel protective factor against alcoholism. Hum Mol Genet 14: 1393–1404.
Loukola A, Broms U, Maunu H, Widen E, Heikkila K, Siivola M et al. (2008). Linkage of nicotine dependence and smoking behavior on 10q, 7q and 11p in twins with homogeneous genetic background. Pharmacogenomics J 8: 209–219.
Martin GE, Hendrickson LM, Penta KL, Friesen RM, Pietrzykowski AZ, Tapper AR et al. (2008). Identification of a BK channel auxiliary protein controlling molecular and behavioral tolerance to alcohol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 17543–17548.
Mukhopadhyay N, Almasy L, Schroeder M, Mulvihill WP, Weeks DE (2005). Mega2: data-handling for facilitating genetic linkage and association analyses. Bioinformatics 21: 2556–2557.
McPeek MS, Sun L (2000). Statistical tests for detection of misspecified relationships by use of genome-screen data. Am J Hum Genet 66: 1076–1094.
O’Connell JR, Weeks DE (1998). PedCheck: a program for identification of genotype incompatibilities in linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet 63: 259–266.
Pagan JL, Rose RJ, Viken RJ, Pulkkinen L, Kaprio J, Dick DM (2006). Genetic and environmental influences on stages of alcohol use across adolescence and into young adulthood. Behav Genet 36: 483–497.
Peter D, Finn JP, Klisak I, Liu Y, Kojis T, Heinzmann C et al. (1993). Chromosomal localization of the human vesicular amine transporter genes. Genomics 18: 720–723.
Pierucci-Lagha A, Gelernter J, Feinn R, Cubells JF, Pearson D, Pollastri A et al. (2005). Diagnostic reliability of the Semi-structured Assessment for Drug Dependence and Alcoholism (SSADDA). Drug and Alcohol Dependence 80: 303–312.
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000). Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155: 945–959.
Scott DM, Taylor RE (2007). Health-related effects of genetic variations of alcohol-metabolizing enzymes in African Americans. Alcohol Res Health 30: 18–21.
Scott DM, Williams CD, Cain GE, Kwagyan J, Kalu N, Ehlers CL et al. (2008). Clinical course of alcohol dependence in African Americans. J Addict Dis 27: 43–50.
Schuckit MA, Wilhelmsen K, Smith TL, Feiler HS, Lind P, Lange LA et al. (2005). Autosomal linkage analysis for the level of response to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29: 1976–1982.
Viel K, Charlesworth J, Tejero E, Dyer T, Cole S, Haack K et al. (2008). A linkage analysis of cigarette and alcohol consumption in an unselected Mexican American population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B: 983–986.
Warren JI, Stein JA, Grella CE (2007). Role of social support and self-efficacy in treatment outcomes among clients with co-occurring disorders. Drug Alcohol Depend 89: 267–274.
Wei Z, Wang L, Xuan J, Che R, Du J, Qin S et al. (2009). Association analysis of serotonin receptor 7 gene (HTR7) and risperidone response in Chinese schizophrenia patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33: 547–551.
Yu Y, Kranzler HR, Panhuysen C, Weiss RD, Poling J, Farrer LA et al. (2008). Substance dependence low-density whole genome association study in two distinct American populations. Hum Genet 123: 495–506.
Zhang C, Cawley S, Liu G, Cao M, Gorrell H, Kennedy GC (2005). A genomewide linkage analysis of alcoholism on microsatellite and single-nucleotide polymorphism data, using alcohol dependence phenotypes and electroencephalogram measures. BMC Genet 6 (Suppl 1): S17.
Acknowledgements
We thank John Farrell and Michael Jervis for database management support. This work was supported by NIDA grants R01 DA12690, R01 DA12849, R01 AA11330, K24 DA15105, and K24 DA022288 and NIAAA grant K24 AA013736. Genotyping services were provided by the Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR). CIDR is fully funded through a federal contract from the National Institutes of Health to The Johns Hopkins University contract number N01-HG-65403.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Kranzler has received consulting fees from Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceuticals, H. Lundbeck A/S, Forest Pharmaceuticals, elbion NV, Sanofi-Aventis, Solvay Pharmaceuticals, and Alkermes, Inc. He has received research support from Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, and Merck & Co., Inc. and honoraria from Forest Pharmaceuticals, Alkermes, Inc., and the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. Dr Farrer has received consulting fees from Novartis Pharmaceuticals and research support from Eisai Pharmaceuticals. Dr Gelernter reports that he has received compensation for professional services in the previous 3 years from the following entities: Yale University School of Medicine, Veterans Affairs Healthcare System (VA) and the National Institutes of Health (NIAAA, NIDA, and NIMH) and related to academic lectures and editorial functions in various scientific venues (including the ACNP). None of the other authors has anything to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panhuysen, C., Kranzler, H., Yu, Y. et al. Confirmation and Generalization of an Alcohol-Dependence Locus on Chromosome 10q. Neuropsychopharmacol 35, 1325–1332 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.1