Abstract
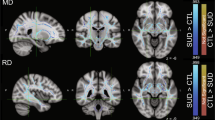
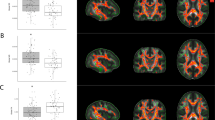
Cocaine dependence is associated with white matter impairments that may compromise cognitive function and hence drug users’ abilities to engage in and benefit from treatment. The main aim of this study was to assess whether white matter integrity correlates with treatment outcome measures in cocaine dependence. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) was used to assess the white matter (WM) of 16 treatment-seeking cocaine-dependent patients before 8 weeks of therapy. The measures for treatment outcome were longest self-reported duration of continuous cocaine abstinence, percent of urine screens negative for cocaine, and duration (weeks) of treatment retention. Correlations between treatment outcome measures and DTI parameters (fractional anisotropy (FA), longitudinal eigenvalue (λ1), perpendicular eigenvalue (λT), and mean diffusivity (MD)) were analyzed. Longest self-reported abstinence from cocaine and percent of cocaine-negative urine samples during treatment positively correlated with FA values and negatively correlated with λ1, λT, and MD values across extensive brain regions including the corpus callosum, frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes, and cerebellum. The findings of an association between better WM integrity at treatment onset and longer abstinence suggest that strategies for improving WM integrity warrant consideration in developing new interventions for cocaine dependence.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aharonovich E, Hasin DS, Brooks AC, Liu X, Bisaga A, Nunes EV (2006). Cognitive deficits predict low treatment retention in cocaine dependent patients. Drug Alcohol Depend 81: 313–322.
Ahmadi J, Kampman K, Dackis C (2006). Outcome predictors in cocaine dependence treatment trials. Am J Addict 15: 434–439.
Alexander AL, Lee JE, Lazar M, Field AS (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 4: 316–329.
Arnone D, Barrick TR, Chengappa S, Mackay CE, Clark CA, Abou-Saleh MT (2008). Corpus callosum damage in heavy marijuana use: preliminary evidence from diffusion tensor tractography and tract-based spatial statistics. Neuroimage 41: 1067–1074.
Bartzokis G, Beckson M, Lu PH, Edwards N, Bridge P, Mintz J (2002). Brain maturation may be arrested in chronic cocaine addicts. Biol Psychiatry 51: 605–611.
Bhagat YA, Hussain MS, Stobbe RW, Butcher KS, Emery DJ, Shuaib A et al (2008). Elevations of diffusion anisotropy are associated with hyper-acute stroke: a serial imaging study. Magn Reson Imaging 26: 683–693.
Bleiberg JL, Devlin P, Croan J, Briscoe R (1994). Relationship between treatment length and outcome in a therapeutic community. Int J Addict 29: 729–740.
Brewer JA, Worhunsky PD, Carroll KM, Rounsaville BJ, Potenza MN (2008). Pretreatment brain activation during stroop task is associated with outcomes in cocaine-dependent patients. Biol Psychiatry 64: 998–1004.
Budde MD, Xie M, Cross AH, Song SK (2009). Axial diffusivity is the primary correlate of axonal injury in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis spinal cord: a quantitative pixelwise analysis. J Neurosci 29: 2805–2813.
Carroll KM (1997). Integrating psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy to improve drug abuse outcomes. Addict Behav 22: 233–245.
Carroll KM, Ball SA, Martino S, Nich C, Babuscio TA, Nuro KF et al (2008). Computer-assisted delivery of cognitive-behavioral therapy for addiction: a randomized trial of CBT4CBT. Am J Psychiatry 165: 881–888.
Carroll KM, Kiluk BD, Nich C, Babuscio TA, Brewer JA, Potenza MN et al. Cognitive function and treatment response in a randomized clinical trial of computer-based training in cognitive-behavioral therapy. Substance Use Misuse (in press).
Chung A, Lyoo IK, Kim SJ, Hwang J, Bae SC, Sung YH et al (2007). Decreased frontal white-matter integrity in abstinent methamphetamine abusers. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10: 765–775.
Concha L, Gross DW, Wheatley BM, Beaulieu C (2006). Diffusion tensor imaging of time-dependent axonal and myelin degradation after corpus callosotomy in epilepsy patients. Neuroimage 32: 1090–1099.
Dutra L, Stathopoulou G, Basden SL, Leyro TM, Powers MB, Otto MW (2008). A meta-analytic review of psychosocial interventions for substance use disorders. Am J Psychiatry 165: 179–187.
Elkashef A, Biswas J, Acri JB, Vocci F (2007). Biotechnology and the treatment of addictive disorders: new opportunities. BioDrugs 21: 259–267.
Fals-Stewart W, O’Farrell TJ, Freitas TT, McFarlin SK, Rutigliano P (2000). The timeline followback reports of psychoactive substance use by drug-abusing patients: Psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 68: 134–144.
First MB, Gibbon M, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Benjamin LS (1997). Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis II personality disorders (SCID-II): user's guide. American Psychiatric Press: Washington, DC.
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams J (1996). Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders- patient edition (SCID-IP, Version 2.0). Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute: New York, NY.
Harsan LA, Steibel J, Zaremba A, Agin A, Sapin R, Poulet P et al (2008). Recovery from chronic demyelination by thyroid hormone therapy: myelinogenesis induction and assessment by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci 28: 14189–14201.
Hersh D, Mulgrew CL, Van Kirk J, Kranzler HR (1999). The validity of self-reported cocaine use in two groups of cocaine abusers. J Consulting Clin Psychol 67: 37–42.
Jentsch JD, Taylor JR (1999). Impulsivity resulting from frontostriatal dysfunction in drug abuse: Implications for the control of behavior by reward-related stimuli. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 146: 373.
Johnson BA, Devous Sr MD, Ruiz P, Ait-Daoud N (2001). Treatment advances for cocaine-induced ischemic stroke: focus on dihydropyridine-class calcium channel antagonists. Am J Psychiatry 158: 1191–1198.
Kalivas PW, Volkow ND (2005). The neural basis of addiction: a pathology of motivation and choice. Am J Psychiatry 162: 1403–1413.
Kaufman MJ, Levin JM, Ross MH, Lange N, Rose SL, Kukes TJ et al (1998). Cocaine-induced cerebral vasoconstriction detected in humans with magnetic resonance angiography. JAMA 279: 376–380.
Knapp WP, Soares BG, Farrel M, Lima MS (2007). Psychosocial interventions for cocaine and psychostimulant amphetamines related disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD003023.
Koob GF (2004). Allostatic view of motivation: implications for psychopathology. Nebr Symp Motiv 50: 1–18.
Koob GF (2006). The neurobiology of addiction: a neuroadaptational view relevant for diagnosis. Addiction 101 (Suppl 1): 23–30.
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2008). Addiction and the brain antireward system. Annu Rev Psychol 59: 29–53.
Lim KO, Choi SJ, Pomara N, Wolkin A, Rotrosen JP (2002). Reduced frontal white matter integrity in cocaine dependence: a controlled diffusion tensor imaging study. Biol Psychiatry 51: 890–895.
Lim KO, Wozniak JR, Mueller BA, Franc DT, Specker SM, Rodriguez CP et al (2008). Brain macrostructural and microstructural abnormalities in cocaine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 92: 164–172.
Ma L, Hasan KM, Steinberg JL, Narayana PA, Lane SD, Zuniga EA et al (2009). Diffusion tensor imaging in cocaine dependence: regional effects of cocaine on corpus callosum and effect of cocaine administration route. Drug Alcohol Depend 104: 262–267.
McLellan AT, Kushner H, Metzger D, Peters R, Smith I, Grissom G et al (1992). The fifth edition of the addiction severity index. J Subst Abuse Treat 9: 199–213.
Moeller FG, Dougherty DM, Barratt ES, Schmitz JM, Swann AC, Grabowski J (2001). The impact of impulsivity on cocaine use and retention in treatment. J Subst Abuse Treat 21: 193–198.
Moeller FG, Hasan KM, Steinberg JL, Kramer LA, Dougherty DM, Santos RM et al (2005). Reduced anterior corpus callosum white matter integrity is related to increased impulsivity and reduced discriminability in cocaine-dependent subjects: diffusion tensor imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology 30: 610–617.
Moeller FG, Hasan KM, Steinberg JL, Kramer LA, Valdes I, Lai LY et al (2007a). Diffusion tensor imaging eigenvalues: preliminary evidence for altered myelin in cocaine dependence. Psychiatry Res 154: 253–258.
Moeller FG, Steinberg JL, Lane SD, Buzby M, Swann AC, Hasan KM et al (2007b). Diffusion tensor imaging in MDMA users and controls: association with decision making. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 33: 777–789.
Nichols TE, Holmes AP (2002). Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Hum Brain Mapp 15: 1–25.
Patkar AA, Murray HW, Mannelli P, Gottheil E, Weinstein SP, Vergare MJ (2004). Pre-treatment measures of impulsivity, aggression and sensation seeking are associated with treatment outcome for African-American cocaine-dependent patients. J Addict Dis 23: 109–122.
Potenza MN (2007). To do or not to do? The complexities of addiction, motivation, self-control, and impulsivity. Am J Psychiatry 164: 4–6.
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (2008). Review. The incentive sensitization theory of addiction: some current issues. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363: 3137–3146.
Romero MJ, Asensio S, Palau C, Sanchez A, Romero FJ (2010). Cocaine addiction: diffusion tensor imaging study of the inferior frontal and anterior cingulate white matter. Psychiatry Res 181: 57–63.
Salo R, Nordahl TE, Buonocore MH, Natsuaki Y, Waters C, Moore CD et al (2009). Cognitive control and white matter callosal microstructure in methamphetamine-dependent subjects: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Biol Psychiatry 65: 122–128.
Schlaug G, Marchina S, Norton A (2009). Evidence for plasticity in white-matter tracts of patients with chronic Broca's aphasia undergoing intense intonation-based speech therapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1169: 385–394.
Shearer J (2007). Psychosocial approaches to psychostimulant dependence: a systematic review. J Subst Abuse Treat 32: 41–52.
Sidaros A, Engberg AW, Sidaros K, Liptrot MG, Herning M, Petersen P et al (2008). Diffusion tensor imaging during recovery from severe traumatic brain injury and relation to clinical outcome: a longitudinal study. Brain 131 (Part 2): 559–572.
Simpson DD, Joe GW, Broome KM (2002). A national 5-year follow-up of treatment outcomes for cocaine dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59: 538–544.
Simpson DD, Joe GW, Fletcher BW, Hubbard RL, Anglin MD (1999). A national evaluation of treatment outcomes for cocaine dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56: 507–514.
Smith S, Jenkinson M, Beckmann C, Miller K, Woolrich M (2007). Meaningful design and contrast estimability in FMRI. Neuroimage 34: 127–136.
Smith SM (2004). Overview of fMRI analysis. Br J Radiol 77 Spec No 2: S167–S175.
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE et al (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31: 1487–1505.
Song SK, Sun SW, Ramsbottom MJ, Chang C, Russell J, Cross AH (2002). Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. Neuroimage 17: 1429–1436.
Stotts AL, Mooney ME, Sayre SL, Novy M, Schmitz JM, Grabowski J (2007). Illusory predictors: generalizability of findings in cocaine treatment retention research. Addict Behav 32: 2819–2836.
Streeter CC, Terhune DB, Whitfield TH, Gruber S, Sarid-Segal O, Silveri MM et al (2008). Performance on the Stroop predicts treatment compliance in cocaine-dependent individuals. Neuropsychopharmacology 33: 827–836.
Vocci FJ (2008). Cognitive remediation in the treatment of stimulant abuse disorders: a research agenda. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 16: 484–497.
Volkow ND, Hitzemann R, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Wolf AP, Dewey SL et al (1992). Long-term frontal brain metabolic changes in cocaine abusers. Synapse 11: 184.
Wang F, Kalmar JH, Edmiston E, Chepenik LG, Bhagwagar Z, Spencer L et al (2008). Abnormal corpus callosum integrity in bipolar disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Biol Psychiatry 64: 730–733.
Weiss F (2005). Neurobiology of craving, conditioned reward and relapse. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5: 9–19.
Wozniak JR, Lim KO (2006). Advances in white matter imaging: a review of in vivo magnetic resonance methodologies and their applicability to the study of development and aging. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30: 762–774.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the following grants: NIDA P50-DA09241, RO1-DA020908, R37-DA15969, K05-DA00457, K05-DA00089, T32-AA015496 and the VISN 1 Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Center (MIRECC). We thank Charla Nich, Hedy Sarofin, and Karen Martin for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors reported no conflict of interest in the content of this paper. Dr Potenza has received financial support or compensation for the following: Dr Potenza consults for and is an advisor to Boehringer Ingelheim; has financial interests in Somaxon; has received research support from the National Institutes of Health, Veteran's Administration, Mohegan Sun Casino, the National Center for Responsible Gaming and its affiliated Institute for Research on Gambling Disorders, and Forest Laboratories pharmaceuticals; has participated in surveys, mailings or telephone consultations related to drug addiction, impulse control disorders or other health topics; has consulted for law offices on issues related to addictions or impulse control disorders; has provided clinical care in the Connecticut Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services Problem Gambling Services Program; has performed grant reviews for the National Institutes of Health and other agencies; has guest-edited journal sections; has given academic lectures in grand rounds, CME events and other clinical or scientific venues; and has generated books or book chapters for publishers of mental health texts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., DeVito, E., Worhunsky, P. et al. White Matter Integrity is Associated with Treatment Outcome Measures in Cocaine Dependence. Neuropsychopharmacol 35, 1541–1549 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.25
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.25
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
White matter deficits in cocaine use disorder: convergent evidence from in vivo diffusion tensor imaging and ex vivo proteomic analysis
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Potential of Glial Cell Modulators in the Management of Substance Use Disorders
CNS Drugs (2020)
-
Intertemporal choice behavior is constrained by brain structure in healthy participants and pathological gamblers
Brain Structure and Function (2016)
-
White matter integrity in polydrug users in relation to attachment and personality: a controlled diffusion tensor imaging study
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2016)
-
A Molecular Profile of Cocaine Abuse Includes the Differential Expression of Genes that Regulate Transcription, Chromatin, and Dopamine Cell Phenotype
Neuropsychopharmacology (2014)