Abstract
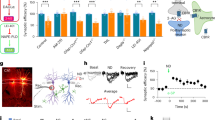
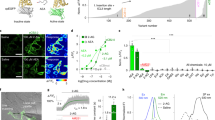
The central amygdala (CeA) has a major role in alcohol dependence and reinforcement, and behavioral and neurochemical evidence suggests a role for the endocannabinoid (eCB) system in ethanol binging and dependence. We used a slice preparation to investigate the physiological role of cannabinoids and their interaction with ethanol on inhibitory synaptic transmission in CeA. Superfusion of the cannabinoid receptor (CB1) agonist WIN55212-2 (WIN2) onto CeA neurons decreased evoked GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) in a concentration-dependent manner, an effect prevented by the CB1 antagonists Rimonabant (SR141716, SR1) and AM251. SR1 or AM251 applied alone augmented IPSPs, revealing a tonic eCB activity that decreased inhibitory transmission in CeA. Paired-pulse analysis suggested a presynaptic CB1 mechanism. Intracellular BAPTA abolished the ability of AM251 to augment IPSPs, demonstrating the eCB-driven nature and postsynaptic origin of the tonic CB1-dependent control of GABA release. Superfusion of ethanol increased IPSPs and addition of WIN2 reversed the ethanol effect. Similarly, previous superfusion of WIN2 prevented subsequent ethanol effects on GABAergic transmission. The ethanol-induced augmentation of IPSPs was additive to CB1 blockade, ruling out a participation of CB1 in the action of acute ethanol. Our study points to an important role of CB1 in CeA in which the eCBs tonically regulate neuronal activity, and suggests a potent mechanism for modulating CeA tone during challenge with ethanol.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adermark L, Lovinger DM (2009). Frequency-dependent inversion of net striatal output by endocannabinoid-dependent plasticity at different synaptic inputs. J Neurosci 29: 1375–1380.
Andreasen M, Hablitz JJ (1994). Paired-pulse facilitation in the dentate gyrus: a patch-clamp study in rat hippocampus in vitro. J Neurophysiol 72: 326–336.
Azad SC, Eder M, Marsicano G, Lutz B, Zieglgänsberger W, Rammes G (2003). Activation of the cannabinoid receptor type 1 decreases glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic transmission in the lateral amygdala of the mouse. Learn Mem 10: 116–128.
Bajo M, Cruz MT, Siggins GR, Messing RO, Roberto M (2008). Protein kinase Ce mediation of CRF- and ethanol-induced GABA release in central amygdala. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 8410–8415.
Bajo M, Roberto M, Schweitzer P (2009). Differential alteration of hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission by cannabinoid ligands. J Neurosci Res 87: 766–775.
Basavarajappa BS, Hungund BL (2005). Role of the endocannabinoid system in the development of tolerance to alcohol. Alcohol Alcohol 40: 15–24.
Basavarajappa BS, Ninan I, Arancio O (2008). Acute ethanol suppresses glutamatergic neurotransmission through endocannabinoids in hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem 107: 1001–1013.
Bonci A, Williams JT (1997). Increased probability of GABA release during withdrawal from morphine. J Neurosci 17: 796–803.
Cassell MD, Freedman LJ, Shi C (1999). The intrinsic organization of the central extended amygdala. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877: 217–241.
Colombo G, Orru A, Lai P, Cabras C, Maccioni P, Rubio M et al (2007). The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, rimonabant, as a promising pharmacotherapy for alcohol dependence: preclinical evidence. Mol Neurobiol 36: 102–112.
Colombo G, Serra S, Brunetti G, Gomez R, Melis S, Vacca G et al (2002). Stimulation of voluntary ethanol intake by cannabinoid receptor agonists in ethanol-preferring sP rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 159: 181–187.
Colombo G, Serra S, Vacca G, Carai MAM, Gessa GL (2005). Endocannabinoid system and alcohol addiction: pharmacological studies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81: 369–380.
Davis M, Rainnie DG, Cassell MD (1994). Neurotransmission in the rat amygdala related to fear and anxiety. Trends Neurosci 17: 208–214.
Gerdeman GL, Ronesi J, Lovinger DM (2002). Postsynaptic endocannabinoid release is critical to long-term depression in the striatum. Nat Neurosci 5: 446–451.
Gibson HE, Edwards JG, Page RS, Van Hook MJ, Kauer JA (2008). TRPV1 channels mediate long-term depression at synapses on hippocampal interneurons. Neuron 57: 746–759.
Hájos N, Freund TF (2002). Pharmacological separation of cannabinoid sensitive receptors on hippocampal excitatory and inhibitory fibers. Neuropharmacology 43: 503–510.
Hentges ST, Low MJ, Williams JT (2005). Differential regulation of synaptic inputs by constitutively released endocannabinoids and exogenous cannabinoids. J Neurosci 25: 9746–9751.
Hermann H, Lutz B (2005). Coexpression of the cannabinoid receptor type 1 with the corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1 in distinct regions of the adult mouse forebrain. Neurosci Lett 375: 13–18.
Hoffman AF, Lupica CR (2001). Direct actions of cannabinoids on synaptic transmission in the nucleus accumbens: a comparison with opioids. J Neurophysiol 85: 72–83.
Hungund BL, Szakall I, Adam A, Basavarajappa BS, Vadasz C (2003). Cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice exhibit markedly reduced voluntary alcohol consumption and lack alcohol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 84: 698–704.
Hyytia P, Koob GF (1995). GABAA receptor antagonism in the extended amygdala decreases ethanol self-administration in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 283: 151–159.
Katona I, Rancz EA, Acsády L, Ledent C, Mackie K, Hájos N et al (2001). Distribution of CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the amygdala and their role in the control of GABAergic transmission. J Neurosci 21: 9506–9518.
Kelm MK, Criswell HE, Breese GR (2008). The role of protein kinase A in the ethanol-induced increase in spontaneous GABA release onto cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurophysiol 100: 3417–3428.
Koob GF (2003). Neuroadaptive mechanisms of addiction: studies on the extended amygdala. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 13: 442–452.
Koob GF, Roberts AJ, Schulteis G, Parsons LH, Heyser CJ, Hyytia P et al (1998). Neurocircuitry targets in ethanol reward and dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22: 3–9.
Losonczy A, Biró AA, Nusser Z (2004). Persistently active cannabinoid receptors mute a subpopulation of hippocampal interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 1362–1367.
Maldonado R, Valverde O, Berrendero F (2006). Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction. Trends Neurosci 29: 225–232.
Marsicano G, Lutz B (1999). Expression of the cannabinoid receptor CB1 in distinct neuronal subpopulations in the adult mouse forebrain. Eur J Neurosci 11: 4213–4225.
Marsicano G, Wotjak CT, Azad SC, Bisogno T, Rammes G, Cascio MG et al (2002). The endogenous cannabinoid system controls extinction of aversive memories. Nature 418: 530–534.
Massi L, Elezgarai I, Puente N, Reguero L, Grandes P, Manzoni OJ et al (2008). Cannabinoid receptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis control cortical excitation of midbrain dopamine cells in vivo. J Neurosci 28: 10496–10508.
McDonald AJ, Mascagni F (2001). Localization of the CB1 type cannabinoid receptor in the rat basolateral amygdala: high concentrations in a subpopulation of cholecystokinin-containing interneurons. Neuroscience 107: 641–652.
Neu A, Foldy C, Soltesz I (2007). Postsynaptic origin of CB1-dependent tonic inhibition of GABA release at cholecystokinin-positive basket cell to pyramidal cell synapses in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol 578: 233–247.
Nie ZG, Schweitzer P, Roberts AJ, Madamba SG, Moore SD, Siggins GR (2004). Ethanol augments GABAergic transmission in the central amygdala via CRF1 receptors. Science 303: 1512–1514.
Parolaro D, Rubino T (2008). The role of the endogenous cannabinoid system in drug addiction. Drug News Perspect 21: 149–157.
Patel S, Cravatt BF, Hillard CJ (2005). Synergistic interactions between cannabinoids and environmental stress in the activation of the central amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology 30: 497–507.
Perra S, Pillolla G, Luchicchi A, Pistis M (2008). Alcohol inhibits spontaneous activity of basolateral amygdala projection neurons in the rat: involvement of the endocannabinoid system. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32: 443–449.
Perra S, Pillolla G, Melis M, Muntoni AL, Gessa GL, Pistis M (2005). Involvement of the endogenous cannabinoid system in the effects of alcohol in the mesolimbic reward circuit: electrophysiological evidence in vivo. Psychopharmacology 183: 368–377.
Pistis M, Perra S, Pillolla G, Melis M, Gessa GL, Muntoni AL (2004). Cannabinoids modulate neuronal firing in the rat basolateral amygdala: evidence for CB1-and non-CB1-mediated actions. Neuropharmacology 46: 115–125.
Roberto M, Madamba SG, Moore SD, Tallent MK, Siggins GR (2003). Ethanol increases GABAergic transmission at both pre- and postsynaptic sites in rat central amygdala neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 2053–2058.
Roberto M, Madamba SG, Stouffer DG, Parsons LH, Siggins GR (2004). Increased GABA release in the central amygdala of ethanol-dependent rats. J Neurosci 24: 10159–10166.
Sah P, Faber ES, Lopez de AM, Power J (2003). The amygdaloid complex: anatomy and physiology. Physiol Rev 83: 803–834.
Schiess MC, Callahan PM, Zheng H (1999). Characterization of the electrophysiological and morphological properties of rat central amygdala neurons in vitro. J Neurosci Res 58: 663–673.
Siggins GR, Roberto M, Nie Z (2005). The tipsy terminal: presynaptic effects of ethanol. Pharmacol Ther 107: 80–98.
Tsou K, Brown S, Sañudo-Peña MC, Mackie K, Walker JM (1998). Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83: 393–411.
Wallace MJ, Newton PM, McMahon T, Connolly J, Huibers A, Whistler J et al (2009). PKCe regulates behavioral sensitivity, binding and tolerance to the CB1 receptor agonist WIN55,212-2. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 1733–1742.
Wang L, Liu H, Harvey-White J, Zimmer A, Kunos G (2003). Endocannabinoid signaling via cannabinoid receptor 1 is involved in ethanol preference and its age-dependent decline in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 1393–1398.
Weiner JL, Valenzuela CF (2006). Ethanol modulation of GABAergic transmission: the view from the slice. Pharmacol Ther 111: 533–554.
Wilson RI, Nicoll RA (2001). Endogenous cannabinoids mediate retrograde signalling at hippocampal synapses. Nature 410: 588–592.
Zarrindast MR, Sarahroodi S, Arzi A, Khodayar MJ, Taheri-Shalmani S, Rezayof A (2008). Cannabinoid CB1 receptors of the rat central amygdala mediate anxiety-like behavior: interaction with the opioid system. Behav Pharmacol 19: 716–723.
Zhu PJ, Lovinger DM (2005). Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling in a postsynaptic neuron/synaptic bouton preparation from basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci 25: 6199–6207.
Zhu W, Pan ZZ (2004). Synaptic properties and postsynaptic opioid effects in rat central amygdala neurons. Neuroscience 127: 871–879.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health funding from NIAAA (AA06420, AA007456, AA014619, AA016985, A013498, AA015566). We thank the Helen Doris Research Center, Samuel Madamba for technical support, and George Koob for helpful discussions. This is publication number 20070 from The Scripps Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberto, M., Cruz, M., Bajo, M. et al. The Endocannabinoid System Tonically Regulates Inhibitory Transmission and Depresses the Effect of Ethanol in Central Amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacol 35, 1962–1972 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.70
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.70
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of fatty acid binding protein-5 in the basolateral amygdala induces anxiolytic effects and accelerates fear memory extinction
Psychopharmacology (2024)
-
Deficient endocannabinoid signaling in the central amygdala contributes to alcohol dependence-related anxiety-like behavior and excessive alcohol intake
Neuropsychopharmacology (2018)
-
Opposing actions of CRF-R1 and CB1 receptors on VTA-GABAergic plasticity following chronic exposure to ethanol
Neuropsychopharmacology (2018)
-
Exploring the communication effects of message framing of smoking cessation advertising on smokers’ mental processes
International Review on Public and Nonprofit Marketing (2018)
-
Ethanol modulates facial stimulation-evoked outward currents in cerebellar Purkinje cells in vivo in mice
Scientific Reports (2016)