Abstract
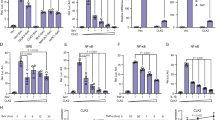
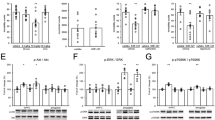
Inhibitor of κB kinase (IκK) has historically been studied in the context of immune response and inflammation, but recent evidence demonstrates that IκK activity is necessary and sufficient for regulation of neuronal function. Chronic social defeat stress of mice increases IκK activity in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and this increase is strongly correlated to depression-like behaviors. Inhibition of IκK signaling results in a reversal of chronic social defeat stress-induced social avoidance behavior. Here, we more completely define the role of IκK in anxiety and depressive-like behaviors. Mice underwent stereotaxic microinjection of a herpes simplex virus expressing either green fluorescent protein, a constitutively active form of IκK (IκKca), or a dominant negative form of IκK into the NAc. Of all three experimental groups, only mice expressing IκKca show a behavioral phenotype. Expression of IκKca results in a decrease in the time spent in the non-periphery zones of an open field arena and increased time spent immobile during a forced swim test. No baseline differences in sucrose preference were observed, but following the acute swim stress we noted a marked reduction in sucrose preference. To determine whether IκK activity alters responses to other acute stressors, we examined behavior and spine morphology in mice undergoing an acute social defeat stress. We found that IκKca enhanced social avoidance behavior and promoted thin spine formation. These data show that IκK in NAc is a critical regulator of both depressive- and anxiety-like states and may do so by promoting the formation of immature excitatory synapses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abbasi SH, Hosseini F, Modabbernia A, Ashrafi M, Akhondzadeh S (2012). Effect of celecoxib add-on treatment on symptoms and serum IL-6 concentrations in patients with major depressive disorder: randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J Affect Disord; e-pud ahead of print 18 April 2012.
Ahn HJ, Hernandez CM, Levenson JM, Lubin FD, Liou HC, Sweatt JD (2008). c-Rel, an NF-kappaB family transcription factor, is required for hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Learn Mem 15: 539–549.
Autry AE, Adachi M, Nosyreva E, Na ES, Los MF, Cheng PF et al (2011). NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses. Nature 475: 91–95.
Berton O, McClung CA, Dileone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ et al (2006). Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 311: 864–868.
Bewernick BH, Hurlemann R, Matusch A, Kayser S, Grubert C, Hadrysiewicz B et al (2010). Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation decreases ratings of depression and anxiety in treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 67: 110–116.
Boersma MC, Dresselhaus EC, De Biase LM, Mihalas AB, Bergles DE, Meffert MK (2011). A requirement for nuclear factor-kappaB in developmental and plasticity-associated synaptogenesis. J Neurosci 31: 5414–5425.
Bourne J, Harris KM (2007). Do thin spines learn to be mushroom spines that remember? Curr Opin Neurobiol 17: 381–386.
Bunting K, Rao S, Hardy K, Woltring D, Denyer GS, Wang J et al (2007). Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in T cells to identify targets of the NF-kappa B transcription factor c-Rel. J Immunol 178: 7097–7109.
Carlezon Jr WA, Neve RL (2003). Viral-mediated gene transfer to study the behavioral correlates of CREB function in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Methods Mol Med 79: 331–350.
Chen LF, Greene WC (2004). Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev 5: 392–401.
Chen YL, Law PY, Loh HH (2006). Nuclear factor kappaB signaling in opioid functions and receptor gene expression. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1: 270–279.
Christoffel DJ, Golden SA, Dumitriu D, Robison AJ, Janssen WG, Ahn HF et al (2011a). IkappaB kinase regulates social defeat stress-induced synaptic and behavioral plasticity. J Neurosci 31: 314–321.
Christoffel DJ, Golden SA, Russo SJ (2011b). Structural and synaptic plasticity in stress-related disorders. Rev Neurosci 22: 535–549.
Covington 3rd HE, Maze I, LaPlant QC, Vialou VF, Ohnishi YN, Berton O et al (2009). Antidepressant actions of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Neurosci 29: 11451–11460.
Frensing T, Kaltschmidt C, Schmitt-John T (2008). Characterization of a neuregulin-1 gene promoter: positive regulation of type I isoforms by NF-kappaB. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779: 139–144.
Golden SA, Covington 3rd HE, Berton O, Russo SJ (2011). A standardized protocol for repeated social defeat stress in mice. Nat Protoc 6: 1183–1191.
Häcker H, Karin M (2006). Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases. Sci STKE 2006: re13.
Israel A (2010). The IKK complex, a central regulator of NF-kappaB activation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2: a000158.
Kaltschmidt B, Ndiaye D, Korte M, Pothion S, Arbibe L, Prullage M et al (2006). NF-kappaB regulates spatial memory formation and synaptic plasticity through protein kinase A/CREB signaling. Mol Cell Biol 26: 2936–2946.
Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Baeuerle P (1993). Brain synapses contain inducible forms of the transcription factor NF-κB. Mech Dev 43: 135–147.
Koo JW, Duman RS (2008). IL-1beta is an essential mediator of the antineurogenic and anhedonic effects of stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 751–756.
Koo JW, Russo SJ, Ferguson D, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (2010). Nuclear factor-kappaB is a critical mediator of stress-impaired neurogenesis and depressive behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 2669–2674.
Krishnan V, Han MH, Graham DL, Berton O, Renthal W, Russo SJ et al (2007). Molecular adaptations underlying susceptibility and resistance to social defeat in brain reward regions. Cell 131: 391–404.
LaPlant Q, Chakravarty S, Vialou V, Mukherjee S, Koo JW, Kalahasti G et al (2009). Role of nuclear factor kappaB in ovarian hormone-mediated stress hypersensitivity in female mice. Biol Psychiatry 65: 874–880.
Lee DF, Kuo HP, Chen CT, Hsu JM, Chou CK, Wei Y et al (2007). IKK beta suppression of TSC1 links inflammation and tumor angiogenesis via the mTOR pathway. Cell 130: 440–455.
Lee KW, Kim Y, Kim AM, Helmin K, Nairn AC, Greengard P (2006). Cocaine-induced dendritic spine formation in D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-containing medium spiny neurons in nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 3399–3404.
Lehmann ML, Brachman RA, Listwak SJ, Herkenham M (2010). NF-kappaB activity affects learning in aversive tasks: possible actions via modulation of the stress axis. Brain Behav Immun 24: 1008–1017.
Li N, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M et al (2010). mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 329: 959–964.
Liu Y, Ho RC, Mak A (2011). Interleukin (IL)-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and soluble interleukin-2 receptors (sIL-2R) are elevated in patients with major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. J Affect Disord 139: 230–239.
Lobo MK, Covington 3rd HE, Chaudhury D, Friedman AK, Sun H, Damez-Werno D et al (2010). Cell type-specific loss of BDNF signaling mimics optogenetic control of cocaine reward. Science 330: 385–390.
Lubin FD, Sweatt JD (2007). The IkappaB kinase regulates chromatin structure during reconsolidation of conditioned fear memories. Neuron 55: 942–957.
Meffert MK, Chang JM, Wiltgen BJ, Fanselow MS, Baltimore D (2003). NF-kappa B functions in synaptic signaling and behavior. Nat Neurosci 6: 1072–1078.
Mercurio F, Murray BW, Shevchenko A, Bennett BL, Young DB, Li JW et al (1999). IkappaB kinase (IKK)-associated protein 1, a common component of the heterogeneous IKK complex. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1526–1538.
Mercurio F, Zhu H, Murray BW, Shevchenko A, Bennett BL, Li J et al (1997). IKK-1 and IKK-2: cytokine-activated IkappaB kinases essential for NF-kappaB activation. Science 278: 860–866.
Mogenson GJ, Jones DL, Yim CY (1980). From motivation to action: functional interface between the limbic system and the motor system. Prog Neurobiol 14: 69–97.
Monteggia LM, Luikart B, Barrot M, Theobold D, Malkovska I, Nef S et al (2007). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor conditional knockouts show gender differences in depression-related behaviors. Biol Psychiatry 61: 187–197.
Nakamori Y, Emoto M, Fukuda N, Taguchi A, Okuya S, Tajiri M et al (2006). Myosin motor Myo1c and its receptor NEMO/IKK-gamma promote TNF-alpha-induced serine307 phosphorylation of IRS-1. J Cell Biol 173: 665–671.
O’Mahony A, Raber J, Montano M, Foehr E, Han V, Lu SM et al (2006). NF-kappaB/Rel regulates inhibitory and excitatory neuronal function and synaptic plasticity. Mol Cell Biol 26: 7283–7298.
O’Neill LA, Kaltschmidt C (1997). NF-kappa B: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci 20: 252–258.
Papp M, Willner P, Muscat R (1991). An animal model of anhedonia: attenuation of sucrose consumption and place preference conditioning by chronic unpredictable mild stress. Psychopharmacology 104: 255–259.
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978). Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47: 379–391.
Radley JJ, Rocher AB, Miller M, Janssen WG, Liston C, Hof PR et al (2006). Repeated stress induces dendritic spine loss in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 16: 313–320.
Radley JJ, Rocher AB, Rodriguez A, Ehlenberger DB, Dammann M, McEwen BS et al (2008). Repeated stress alters dendritic spine morphology in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. J Comp Neurol 507: 1141–1150.
Richter M, Suau P, Ponte I (2002). Sequence and analysis of the 5′ flanking and 5′ untranslated regions of the rat N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 2A gene. Gene 295: 135–142.
Rodriguez A, Ehlenberger DB, Dickstein DL, Hof PR, Wearne SL (2008). Automated three-dimensional detection and shape classification of dendritic spines from fluorescence microscopy images. PLoS One 3: e1997.
Russo SJ, Dietz DM, Dumitriu D, Morrison JH, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ (2010). The addicted synapse: mechanisms of synaptic and structural plasticity in nucleus accumbens. Trends Neurosci 2: 1–10.
Russo SJ, Wilkinson MB, Mazei-Robison MS, Dietz DM, Maze I, Krishnan V et al (2009). Nuclear factor kappa B signaling regulates neuronal morphology and cocaine reward. J Neurosci 29: 3529–3537.
Saha RN, Liu X, Pahan K (2006). Up-regulation of BDNF in astrocytes by TNF-alpha: a case for the neuroprotective role of cytokine. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1: 212–222.
Schmeisser MJ, Baumann B, Johannsen S, Vindedal GF, Jensen V, Hvalby OC et al (2012). IkappaB kinase/nuclear factor kappaB-dependent insulin-like growth factor 2 (Igf2) expression regulates synapse formation and spine maturation via Igf2 receptor signaling. J Neurosci 32: 5688–5703.
Schölzke MN, Potrovita I, Subramaniam S, Prinz S, Schwaninger M (2003). Glutamate activates NF-kappaB through calpain in neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18: 3305–3310.
Sheng M, Cummings J, Roldan LA, Jan YN, Jan LY (1994). Changing subunit composition of heteromeric NMDA receptors during development of rat cortex. Nature 368: 144–147.
Vialou V, Robison AJ, Laplant QC, Covington 3rd HE, Dietz DM, Ohnishi YN et al (2010). DeltaFosB in brain reward circuits mediates resilience to stress and antidepressant responses. Nat Neurosci 13: 745–752.
Vyas A, Jadhav S, Chattarji S (2006). Prolonged behavioral stress enhances synaptic connectivity in the basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience 143: 387–393.
Acknowledgements
We thank Kevin Guise for his assistance in performing the cumulative frequency plots of average spine head volume. This work was supported by funding from the US National Institute of Mental Health (R01MH090264-01) and the National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression (SJR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christoffel, D., Golden, S., Heshmati, M. et al. Effects of Inhibitor of κB Kinase Activity in the Nucleus Accumbens on Emotional Behavior. Neuropsychopharmacol 37, 2615–2623 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.121
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.121
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prokineticin-2 Participates in Chronic Constriction Injury-Triggered Neuropathic Pain and Anxiety via Regulated by NF-κB in Nucleus Accumbens Shell in Rats
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Dendritic remodeling of D1 neurons by RhoA/Rho-kinase mediates depression-like behavior
Molecular Psychiatry (2020)
-
Dendritic spine density is increased on nucleus accumbens D2 neurons after chronic social defeat
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
The molecular and cellular mechanisms of depression: a focus on reward circuitry
Molecular Psychiatry (2019)
-
A diet enriched with curcumin promotes resilience to chronic social defeat stress
Neuropsychopharmacology (2019)