Abstract
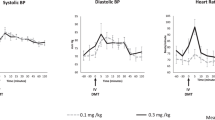
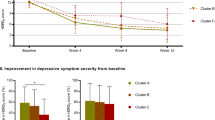
Thiazolidinediones have shown antidepressant effect in animal studies, as well as in some uncontrolled studies evaluating human subjects with concurrent major depressive disorder (MDD) and metabolic syndrome. Although these drugs are insulin sensitizers, they also have important anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-excitotoxic properties. Thus, we hypothesized that they would show antidepressant effect in patients with MDD even if it was not accompanied by metabolic disturbances. In this double-blind placebo-controlled study, 40 patients with MDD (DSM-IV-TR) and Hamilton depression rating scale-17 (Ham-D) score ⩾22 were randomized to citalopram plus pioglitazone (15 mg every 12 h) (n=20) or citalopram plus placebo (n=20) for 6 weeks. Patients were evaluated using Ham-D (weeks 0, 2, 4, 6). Repeated-measure analysis of variance (ANOVA) and analysis of covariance were used for comparison of scores between the two groups. Treatment response (⩾50% reduction in Ham-D score), remission (Ham-D score⩽7), and early improvement (⩾20% reduction in Ham-D score within the first 2 weeks) were compared between the two groups using Fisher's exact test. Pioglitazone showed superiority over placebo during the course of the trial (F(1, 38)=9.483, p=0.004). Patients in the pioglitazone group had significantly lower scores at all time points than the placebo group (P<0.01). Frequency of early improvement, response (week 6), and remission was significantly higher in the pioglitazone group (95%, 95%, 45%, respectively) than in the placebo (30%, 40%, 15% respectively) group (P<0.001, <0.001, 0.04, respectively). Frequency of side effects was similar between the two groups. Pioglitazone is a safe and effective adjunctive short-term treatment in patients with moderate-to-severe MDD even in the absence of metabolic syndrome and diabetes (http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01109030).
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abolfazli R, Hosseini M, Ghanizadeh A, Ghaleiha A, Tabrizi M, Raznahan M et al (2011). Double-blind randomized parallel-group clinical trial of efficacy of the combination fluoxetine plus modafinil versus fluoxetine plus placebo in the treatment of major depression. Depress Anxiety 28: 297–302.
Akhondzadeh S, Jafari S, Raisi F, Nasehi AA, Ghoreishi A, Salehi B et al (2009). Clinical trial of adjunctive celecoxib treatment in patients with major depression: a double blind and placebo controlled trial. Depress Anxiety 26: 607–611.
Apler A (2011). Citalopram for major depressive disorder in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published placebo-controlled trials. BMJ Open 1: e000106.
Berlie HD, Kalus JS, Jaber LA (2007). Thiazolidinediones and the risk of edema: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 76: 279–289.
Blier P, Gobbi G, Turcotte JE, De Montigny C, Boucher N, Hebert C et al (2009). Mirtazapine and paroxetine in major depression: a comparison of mono-therapy versus their combination from treatment initiation. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 19: 457–465.
Blier P, Ward HE, Tremblay P, Laberge L, Hebert C, Bergeron R (2010). Combination of antidepressant medications from treatment initiation for major depressive disorder: a double-blind randomized study. Am J Psychiatry 167: 281–288.
Budni J, Lobato KR, Binfare RW, Freitas AE, Costa AP, Saavedra MD et al (2011). Involvement of PI3K, GSK-3beta and PPARgamma in the antidepressant-like effect of folic acid in the forced swimming test in mice. J Psychopharmacol (in press).
Chen CY, Tzeng NS, Chen YC (2010). Maintenance therapy of celecoxib for major depression with mimicking neuropsychological dysfunction. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 32: 647 e7-9.
Eissa Ahmed AA, Al-Rasheed NM (2009). Antidepressant-like effects of rosiglitazone, a PPARgamma agonist, in the rat forced swim and mouse tail suspension tests. Behav Pharmacol 20: 635–642.
Fava M, Rush AJ (2006). Current status of augmentation and combination treatments for major depressive disorder: a literature review and a proposal for a novel approach to improve practice. Psychother Psychosom 75: 139–153.
Garcia-Bueno B, Caso JR, Perez-Nievas BG, Lorenzo P, Leza JC (2007). Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists on brain glucose and glutamate transporters after stress in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 32: 1251–1260.
Garcia-Bueno B, Madrigal JL, Lizasoain I, Moro MA, Lorenzo P, Leza JC (2005). The anti-inflammatory prostaglandin 15d-PGJ2 decreases oxidative/nitrosative mediators in brain after acute stress in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 180: 513–522.
Garcia-Bueno B, Perez-Nievas BG, Leza JC (2010). Is there a role for the nuclear receptor PPARgamma in neuropsychiatric diseases? Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13: 1411–1429.
Geldmacher DS, Fritsch T, Mcclendon MJ, Landreth G (2011). A randomized pilot clinical trial of the safety of pioglitazone in treatment of patients with Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 68: 45–50.
Heneka MT, Landreth GE (2007). PPARs in the brain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1771: 1031–1045.
Henkel V, Seemuller F, Obermeier M, Adli M, Bauer M, Mundt C et al (2009). Does early improvement triggered by antidepressants predict response/remission? Analysis of data from a naturalistic study on a large sample of inpatients with major depression. J Affect Disord 115: 439–449.
Jeong EA, Jeon BT, Shin HJ, Kim N, Lee DH, Kim HJ et al (2011). Ketogenic diet-induced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation decreases neuroinflammation in the mouse hippocampus after kainic acid-induced seizures. Exp Neurol 232: 195–202.
Jope RS (2011). Glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the etiology and treatment of mood disorders. Front Mol Neurosci 4: 16.
Joyce PR, Mulder RT, Luty SE, Sullivan PF, Mckenzie JM, Abbott RM et al (2002). Patterns and predictors of remission, response and recovery in major depression treated with fluoxetine or nortriptyline. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 36: 384–391.
Kaiser CC, Shukla DK, Stebbins GT, Skias DD, Jeffery DR, Stefoski D et al (2009). A pilot test of pioglitazone as an add-on in patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 211: 124–130.
Karege F, Perroud N, Burkhardt S, Fernandez R, Ballmann E, La Harpe R et al (2012). Protein levels of beta-catenin and activation state of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in major depression. A study with postmortem prefrontal cortex. J Affect Disord 136: 185–188.
Kemp DE, Ismail-Beigi F, Calabrese JR (2009). Antidepressant response associated with pioglitazone: support for an overlapping pathophysiology between major depression and metabolic syndrome. Am J Psychiatry 166: 619.
Kemp DE, Ismail-Beigi F, Ganocy SJ, Conroy C, Gao K, Obral S et al (2012). Use of insulin sensitizers for the treatment of major depressive disorder: a pilot study of pioglitazone for major depression accompanied by abdominal obesity. J Affect Disord 136: 1164–1173.
Kim EJ, Kwon KJ, Park JY, Lee SH, Moon CH, Baik EJ (2002). Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists on LPS-induced neuronal death in mixed cortical neurons: associated with iNOS and COX-2. Brain Res 941: 1–10.
Kim JM, Kim SY, Stewart R, Yoo JA, Bae KY, Jung SW et al (2011). Improvement within 2 weeks and later treatment outcomes in patients with depressive disorders: the CRESCEND study. J Affect Disord 129: 183–190.
Maes M, Libbrecht I, Van Hunsel F, Campens D, Meltzer HY (1999). Pindolol and mianserin augment the antidepressant activity of fluoxetine in hospitalized major depressed patients, including those with treatment resistance. J Clin Psychopharmacol 19: 177–182.
Marcus RN, Mcquade RD, Carson WH, Hennicken D, Fava M, Simon JS et al (2008). The efficacy and safety of aripiprazole as adjunctive therapy in major depressive disorder: a second multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28: 156–165.
Miller BW, Willett KC, Desilets AR (2011). Rosiglitazone and pioglitazone for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Ann Pharmacother 45: 1416–1424.
Muller N, Schwarz MJ, Dehning S, Douhe A, Cerovecki A, Goldstein-Muller B et al (2006). The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib has therapeutic effects in major depression: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, add-on pilot study to reboxetine. Mol Psychiatry 11: 680–684.
Munhoz CD, Garcia-Bueno B, Madrigal JL, Lepsch LB, Scavone C, Leza JC (2008). Stress-induced neuroinflammation: mechanisms and new pharmacological targets. Braz J Med Biol Res 41: 1037–1046.
Nelson JC, Mazure CM, Jatlow PI, Bowers Jr MB, Price LH (2004). Combining norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake inhibition mechanisms for treatment of depression: a double-blind, randomized study. Biol Psychiatry 55: 296–300.
Ponce-Lopez T, Liy-Salmeron G, Hong E, Meneses A (2011). Lithium, phenserine, memantine and pioglitazone reverse memory deficit and restore phospho-GSK3beta decreased in hippocampus in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced memory deficit model. Brain Res 1426: 73–85.
Rasgon NL, Kenna HA, Williams KE, Powers B, Wroolie T, Schatzberg AF (2010). Rosiglitazone add-on in treatment of depressed patients with insulin resistance: a pilot study. ScientificWorld J 10: 321–328.
Rosa AO, Kaster MP, Binfare RW, Morales S, Martin-Aparicio E, Navarro-Rico ML et al (2008). Antidepressant-like effect of the novel thiadiazolidinone NP031115 in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32: 1549–1556.
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Stewart JW, Nierenberg AA, Fava M, Kurian BT et al (2011). Combining medications to enhance depression outcomes (CO-MED): acute and long-term outcomes of a single-blind randomized study. Am J Psychiatry 168: 689–701.
Sadaghiani MS, Javadi-Paydar M, Gharedaghi MH, Fard YY, Dehpour AR (2011). Antidepressant-like effect of pioglitazone in the forced swimming test in mice: the role of PPAR-gamma receptor and nitric oxide pathway. Behav Brain Res 224: 336–343.
Schatzberg AF (2008). Achieving remission and favorable outcomes in patients with depression/anxiety and substance use disorders. CNS Spectr 13: 10–12.
Spiegelman BM (1998). PPAR-gamma: adipogenic regulator and thiazolidinedione receptor. Diabetes 47: 507–514.
Toyomoto M, Ohta M, Okumura K, Yano H, Matsumoto K, Inoue S et al (2004). Prostaglandins are powerful inducers of NGF and BDNF production in mouse astrocyte cultures. FEBS Lett 562: 211–215.
Trivedi MH, Greer TL, Church TS, Carmody TJ, Grannemann BD, Galper DI et al (2011). Exercise as an augmentation treatment for nonremitted major depressive disorder: a randomized, parallel dose comparison. J Clin Psychiatry 72: 677–684.
Trivedi MH, Greer TL, Grannemann BD, Chambliss HO, Jordan AN (2006a). Exercise as an augmentation strategy for treatment of major depression. J Psychiatr Pract 12: 205–213.
Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Warden D, Ritz L et al (2006b). Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: implications for clinical practice. Am J Psychiatry 163: 28–40.
Van Calker D, Zobel I, Dykierek P, Deimel CM, Kech S, Lieb K et al (2009). Time course of response to antidepressants: predictive value of early improvement and effect of additional psychotherapy. J Affect Disord 114: 243–253.
Vlckova V, Cornelius V, Kasliwal R, Wilton L, Shakir S (2010). Hypoglycaemia with pioglitazone: analysis of data from the Prescription-Event Monitoring study. J Eval Clin Pract 16: 1124–1128.
Warden D, Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Fava M, Wisniewski SR (2007). The STAR*D Project results: a comprehensive review of findings. Curr Psychiatry Rep 9: 449–459.
Acknowledgements
This study was Dr Khatereh Sepanjnia's postgraduate thesis toward qualification for the Iranian Board of Psychiatry under the supervision of Prof. Shahin Akhondzadeh. This study was supported by a grant from Tehran University of Medical Sciences to Prof. Shahin Akhondzadeh (Grant No. 9476).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The abstract of this work was submitted to CINP 2012.
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sepanjnia, K., Modabbernia, A., Ashrafi, M. et al. Pioglitazone Adjunctive Therapy for Moderate-to-Severe Major Depressive Disorder: Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Neuropsychopharmacol 37, 2093–2100 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.58
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.58
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the neurobiology of major depressive disorder and suicide risk
Molecular Psychiatry (2024)
-
Emerging Perspectives on the Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Anti-Diabetic Drugs on Premenstrual Syndrome. A Narrative Review
Diabetes Therapy (2024)
-
Major depressive disorder
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2023)
-
The Relationships Among Metal Homeostasis, Mitochondria, and Locus Coeruleus in Psychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders: Potential Pathogenetic Mechanism and Therapeutic Implications
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Neuronally-enriched exosomal microRNA-27b mediates acute effects of ibuprofen on reward-related brain activity in healthy adults: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial
Scientific Reports (2022)