Abstract
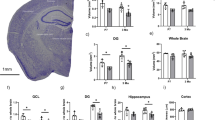
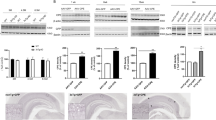
Ample evidence implicates neuroinflammatory processes in the etiology and progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). To assess the specific role of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 (IL-1) in AD we examined the effects of intra-hippocampal transplantation of neural precursor cells (NPCs) with transgenic over-expression of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1raTG) on memory functioning and neurogenesis in a murine model of AD (Tg2576 mice). WT NPCs- or sham-transplanted Tg2576 mice, as well as naive Tg2576 and WT mice served as controls. To assess the net effect of IL-1 blockade (not in the context of NPCs transplantation), we also examined the effects of chronic (4 weeks) intra-cerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of IL-1ra. We report that 12-month-old Tg2576 mice exhibited increased mRNA expression of hippocampal IL-1β, along with severe disturbances in hippocampal-dependent contextual and spatial memory as well as in neurogenesis. Transplantation of IL-1raTG NPCs 1 month before the neurobehavioral testing completely rescued these disturbances and significantly increased the number of endogenous hippocampal cells expressing the plasticity-related molecule BDNF. Similar, but less-robust effects were also produced by transplantation of WT NPCs and by i.c.v. IL-1ra administration. NPCs transplantation produced alterations in hippocampal plaque formation and microglial status, which were not clearly correlated with the cognitive effects of this procedure. The results indicate that elevated levels of hippocampal IL-1 are causally related to some AD-associated memory disturbances, and provide the first example for the potential use of genetically manipulated NPCs with anti-inflammatory properties in the treatment of AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM et al (2000). Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 21: 383–421.
Allan SM, Tyrrell PJ, Rothwell NJ (2005). Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury. Nat Rev Immunol 5: 629–640.
Avital A, Goshen I, Kamsler A, Segal M, Iverfeldt K, Richter-Levin G et al (2003). Impaired interleukin-1 signaling is associated with deficits in hippocampal memory processes and neural plasticity. Hippocampus 13: 826–834.
Barrientos RM, Sprunger DB, Campeau S, Higgins EA, Watkins LR, Rudy JW et al (2003). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA downregulation produced by social isolation is blocked by intrahippocampal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Neuroscience 121: 847–853.
Barrientos RM, Sprunger DB, Campeau S, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF (2004). BDNF mRNA expression in rat hippocampus following contextual learning is blocked by intrahippocampal IL-1beta administration. J Neuroimmunol 155: 119–126.
Ben Menachem-Zidon O, Avital A, Ben-Menahem Y, Goshen I, Kreisel T, Shmueli EM et al (2011). Astrocytes support hippocampal-dependent memory and long-term potentiation via interleukin-1 signaling. Brain Behav Immun 25: 1008–1016.
Ben Menachem-Zidon O, Goshen I, Kreisel T, Ben Menahem Y, Reinhartz E, Ben Hur T et al (2008). Intrahippocampal transplantation of transgenic neural precursor cells overexpressing interleukin-1 receptor antagonist blocks chronic isolation-induced impairment in memory and neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 33: 2251–2262.
Ben-Hur T, Ben-Menachem O, Furer V, Einstein O, Mizrachi-Kol R, Grigoriadis N (2003). Effects of proinflammatory cytokines on the growth, fate, and motility of multipotential neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 24: 623–631.
Blank T, Prinz M (2013). Microglia as modulators of cognition and neuropsychiatric disorders. Glia 61: 62–70.
Blurton-Jones M, Kitazawa M, Martinez-Coria H, Castello NA, Muller FJ, Loring JF et al (2009). Neural stem cells improve cognition via BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 13594–13599.
Chen WW, Blurton-Jones M (2012). Concise review: can stem cells be used to treat or model Alzheimer's disease? Stem Cells 30: 2612–2618.
De Feo D, Merlini A, Laterza C, Martino G (2012). Neural stem cell transplantation in central nervous system disorders: from cell replacement to neuroprotection. Curr Opin Neurol 25: 322–333.
Ekdahl CT, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2009). Brain inflammation and adult neurogenesis: the dual role of microglia. Neuroscience 158: 1021–1029.
Fainstein N, Einstein O, Cohen ME, Brill L, Lavon I, Ben-Hur T (2013). Time limited immunomodulatory functions of transplanted neural precursor cells. Glia 61: 140–149.
Farfara D, Lifshitz V, Frenkel D (2008). Neuroprotective and neurotoxic properties of glial cells in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Mol Med 12: 762–780.
Ghosh S, Wu MD, Shaftel SS, Kyrkanides S, LaFerla FM, Olschowka JA et al (2013). Sustained interleukin-1β overexpression exacerbates tau pathology despite reduced amyloid burden in an Alzheimer's mouse model. J Neurosci 33: 5053–5064.
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC, Gage FH (2010). Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140: 918–934.
Golde TE, Schneider LS, Koo EH (2011). Anti-aβ therapeutics in Alzheimer's disease: the need for a paradigm shift. Neuron 69: 203–213.
Goldgaber D, Harris HW, Hla T, Maciag T, Donnelly RJ, Jacobsen JS et al (1989). Interleukin 1 regulates synthesis of amyloid beta-protein precursor mRNA in human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 7606–7610.
Goshen I, Avital A, Kreisel T, Licht T, Segal M, Yirmiya R (2009a). Environmental enrichment restores memory functioning in mice with impaired IL-1 signaling via reinstatement of long-term potentiation and spine size enlargement. J Neurosci 29: 3395–3403.
Goshen I, Kreisel T, Ben-Menachem-Zidon O, Licht T, Weidenfeld J, Ben-Hur T et al (2008). Brain interleukin-1 mediates chronic stress-induced depression in mice via adrenocortical activation and hippocampal neurogenesis suppression. Mol Psychiatry 13: 717–728.
Goshen I, Yirmiya R (2009b). Interleukin-1 (IL-1): a central regulator of stress responses. Front Neuroendocrinol 30: 30–45.
Griffin WS (2011). Alzheimer's—looking beyond plaques. F1000 Med Rep 3: 24.
Griffin WS, Stanley LC, Ling C, White L, MacLeod V, Perrot LJ et al (1989). Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 7611–7615.
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Stutz A, Delekate A, Schwartz S, Vieira-Saecker A et al (2013). NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer's disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 493: 674–678.
Heneka MT, Nadrigny F, Regen T, Martinez-Hernandez A, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L, Terwel D et al (2010a). Locus ceruleus controls Alzheimer's disease pathology by modulating microglial functions through norepinephrine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 6058–6063.
Heneka MT, O'Banion MK, Terwel D, Kummer MP (2010b). Neuroinflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm 117: 919–947.
Hernández-Rabaza V, Llorens-Martín M, Velázquez-Sánchez C, Ferragud A, Arcusa A, Gumus HG et al (2009). Inhibition of adult hippocampal neurogenesis disrupts contextual learning but spares spatial working memory, long-term conditional rule retention and spatial reversal. Neuroscience 159: 59–68.
Hsiao K, Chapman P, Nilsen S, Eckman C, Harigaya Y, Younkin S et al (1996). Correlative memory deficits, Abeta elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science 274: 99–102.
Irizarry MC, McNamara M, Fedorchak K, Hsiao K, Hyman BT (1997). APPSw transgenic mice develop age-related A beta deposits and neuropil abnormalities, but no neuronal loss in CA1. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56: 965–973.
Karran E, Mercken M, De Strooper B (2011). The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease: an appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10: 698–712.
Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH (1997). Genetic influence on neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 10409–10414.
Kim TK, Lee JE, Park SK, Lee KW, Seo JS, Im JY et al (2012). Analysis of differential plaque depositions in the brains of Tg2576 and Tg-APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer disease. Exp Mol Med 44: 492–502.
Kitazawa M, Cheng D, Tsukamoto MR, Koike MA, Wes PD, Vasilevko V et al (2011). Blocking IL-1 Signaling rescues cognition, attenuates tau pathology, and restores neuronal beta-catenin pathway function in an Alzheimer's disease model. J Immunol 187: 6539–6549.
Koo JW, Duman RS (2008). IL-1beta is an essential mediator of the antineurogenic and anhedonic effects of stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 751–756.
Lee CY, Landreth GE (2010). The role of microglia in amyloid clearance from the AD brain. J Neural Transm 117: 949–960.
Li Y, Liu L, Barger SW, Griffin WS (2003). Interleukin-1 mediates pathological effects of microglia on tau phosphorylation and on synaptophysin synthesis in cortical neurons through a p38-MAPK pathway. J Neurosci 23: 1605–1611.
Li Y, Liu L, Kang J, Sheng JG, Barger SW, Mrak RE et al (2000). Neuronal-glial interactions mediated by interleukin-1 enhance neuronal acetylcholinesterase activity and mRNA expression. J Neurosci 20: 149–155.
Lu Y, Wu X, Dong Y, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Xie Z (2010). Anesthetic sevoflurane causes neurotoxicity differently in neonatal naive and Alzheimer disease transgenic mice. Anesthesiology 112: 1404–1416.
Lundkvist J, Sundgren-Andersson AK, Tingsborg S, Ostlund P, Engfors C, Alheim K et al (1999). Acute-phase responses in transgenic mice with CNS overexpression of IL-1 receptor antagonist. Am J Physiol 276 (3 Pt 2): R644–R651.
Lynch MA (2009). The multifaceted profile of activated microglia. Mol Neurobiol 40: 139–156.
Matousek SB, Ghosh S, Shaftel SS, Kyrkanides S, Olschowka JA, O'Banion MK (2012). Chronic IL-1β-mediated neuroinflammation mitigates amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease without inducing overt neurodegeneration. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7: 156–164.
McAfoose J, Baune BT (2009). Evidence for a cytokine model of cognitive function. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33: 355–366.
McGeer EG, McGeer PL (2003). Inflammatory processes in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27: 741–749.
Medeiros R, Kitazawa M, Passos GF, Baglietto-Vargas D, Cheng D, Cribbs DH et al (2013). Aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 stimulates alternative activation of microglia and reduces Alzheimer disease-like pathology in mice. Am J Pathol 182: 1780–1789.
Meshi D, Drew MR, Saxe M, Ansorge MS, David D, Santarelli L et al (2006). Hippocampal neurogenesis is not required for behavioral effects of environmental enrichment. Nat Neurosci 9: 729–731.
Mu Y, Gage FH (2011). Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and its role in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener 6: 85.
Nagahara AH, Tuszynski MH (2011). Potential therapeutic uses of BDNF in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10: 209–219.
Oprica M, Hjorth E, Spulber S, Popescu BO, Ankarcrona M, Winblad B et al (2007). Studies on brain volume, Alzheimer-related proteins and cytokines in mice with chronic overexpression of IL-1 receptor antagonist. J Cell Mol Med 11: 810–825.
Pollak Y, Gilboa A, Ben-Menachem O, Ben-Hur T, Soreq H, Yirmiya R (2005). Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors reduce brain and blood interleukin-1beta production. Ann Neurol 57: 741–745.
Rachal Pugh C, Fleshner M, Watkins LR, Maier SF, Rudy JW (2001). The immune system and memory consolidation: a role for the cytokine IL-1beta. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25: 29–41.
Rainero I, Bo M, Ferrero M, Valfre W, Vaula G, Pinessi L (2004). Association between the interleukin-1alpha gene and Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis. Neurobiol Aging 25: 1293–1298.
Shaftel SS, Griffin WS, O'Banion MK (2008). The role of interleukin-1 in neuroinflammation and Alzheimer disease: an evolving perspective. J Neuroinflammation 5: 7.
Shaftel SS, Kyrkanides S, Olschowka JA, Miller JN, Johnson RE, O'Banion MK (2007). Sustained hippocampal IL-1 beta overexpression mediates chronic neuroinflammation and ameliorates Alzheimer plaque pathology. J Clin Invest 117: 1595–1604.
Sheng JG, Ito K, Skinner RD, Mrak RE, Rovnaghi CR, Van Eldik LJ et al (1996). In vivo and in vitro evidence supporting a role for the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1 as a driving force in Alzheimer pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging 17: 761–766.
Shruster A, Melamed E, Offen D (2010). Neurogenesis in the aged and neurodegenerative brain. Apoptosis 15: 1415–1421.
Tachida Y, Nakagawa K, Saito T, Saido TC, Honda T, Saito Y et al (2008). Interleukin-1 beta up-regulates TACE to enhance alpha-cleavage of APP in neurons: resulting decrease in Abeta production. J Neurochem 104: 1387–1393.
Tang JX, Mardini F, Janik LS, Garrity ST, Li RQ, Bachlani G et al (2013). Modulation of murine Alzheimer pathogenesis and behavior by surgery. Ann Surg 257: 439–448.
Tong L, Balazs R, Soiampornkul R, Thangnipon W, Cotman CW (2008). Interleukin-1 beta impairs brain derived neurotrophic factor-induced signal transduction. Neurobiol Aging 29: 1380–1393.
Weitz TM, Town T (2012). Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease: It's All About Context. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012: 314185.
Wu MD, Hein AM, Moravan MJ, Shaftel SS, Olschowka JA, O'Banion MK (2012). Adult murine hippocampal neurogenesis is inhibited by sustained IL-1β and not rescued by voluntary running. Brain Behav Immun 26: 292–300.
Yirmiya R, Goshen I (2011). Immune modulation of learning, memory, neural plasticity and neurogenesis. Brain Behav Immun 25: 181–213.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by The Legacy Heritage Bio-Medical Program of the Israel Science Foundation (grant no. 430/09), and in part by grants from the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation (grant number 270804), the Israel Ministry of Health (grant number 2985) and Cure Alzheimer’s Fund. We thank Dr Mikhal Cohen, Sys Kochavi and Erez Yirmiya for help with specific technical aspects of the study.
Author contributions
Dr Ofra Ben Menachem-Zidon designed the work that led to the submission, acquired data, had an important role in interpreting the results, drafted the manuscript and approved the final version. Mr Yair Ben Menahem acquired data and approved the final version. Dr Tamir Ben-Hur had an important role in interpreting the results, revised the manuscript and approved the final version. Dr Raz Yirmiya conceived and designed the work that led to the submission, had an important role in interpreting the results, drafted the manuscript and approved the final version.
Disclaimer
The corresponding author confirms that he has had full access to the data in the study and final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben-Menachem-Zidon, O., Ben-Menahem, Y., Ben-Hur, T. et al. Intra-Hippocampal Transplantation of Neural Precursor Cells with Transgenic Over-Expression of IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Rescues Memory and Neurogenesis Impairments in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Neuropsychopharmacol 39, 401–414 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.208
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.208
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neural stem/progenitor cell therapy for Alzheimer disease in preclinical rodent models: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2023)
-
Stem cell therapy in Alzheimer’s disease: possible benefits and limiting drawbacks
Molecular Biology Reports (2019)
-
Astrocytes decrease adult neurogenesis during virus-induced memory dysfunction via IL-1
Nature Immunology (2018)
-
Lentivirus-mediated interleukin-1β (IL-1β) knock-down in the hippocampus alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced memory deficits and anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2017)
-
Effects of COX1-2/5-LOX blockade in Alzheimer transgenic 3xTg-AD mice
Inflammation Research (2017)