Abstract
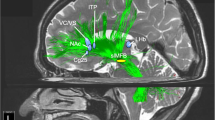
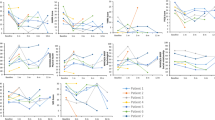
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) as a putative approach for treatment-resistant depression (TRD) has now been researched for about a decade. Several uncontrolled studies—all in relatively small patient populations and different target regions—have shown clinically relevant antidepressant effects in about half of the patients and very recently, DBS to a key structure of the reward system, the medial forebrain bundle, has yielded promising results within few days of stimulation and at much lower stimulation intensities. On the downside, DBS procedures in regions are associated with surgical risks (eg, hemorrhage) and psychiatric complications (suicidal attenuation, hypomania) as well as high costs. This overview summarizes research on the mechanisms of brain networks with respect to psychiatric diseases and—as a novelty—extrapolates to the role of the reward system in DBS for patients with treatment-resistant depression. It further evaluates relevant methodological aspects of today’s research in DBS for TRD. On the scientific side, the reward system has an important yet clearly under-recognized role in both neurobiology and treatment of depression. On the methodological side of DBS research in TRD, better animal models are clearly needed to explain clinical effects of DBS in TRD. Larger sample sizes, long-term follow-up and designs including blinded sham control are required to draw final conclusions on efficacy and side effects. Practical research issues cover study design, patient tracking, and the discussion of meaningful secondary outcome measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aouizerate B, Cuny E, Martin-Guehl C, Guehl D, Amieva H, Benazzouz A et al (2004). Deep brain stimulation of the ventral caudate nucleus in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder and major depression. Case report. J Neurosurg 101: 574–575.
Argyropoulos SV, Nutt DJ (1997). Anhedonia and chronic mild stress model in depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 134: 333–336.
Baumeister AA (2000). The Tulane Electrical Brain Stimulation Program a historical case study in medical ethics. J History Neurosci 9: 262–278.
Berton O, Nestler EJ (2006). New approaches to antidepressant drug discovery: beyond monoamines. Nat Rev Neurosci 7: 137–151.
Bewernick B, Kayser S, Sturm V, Schlaepfer TE (2012). Long-term effects of nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: evidence for sustained efficacy. Neuropschopharmacology 37: 1975–1985.
Bewernick BH, Hurlemann R, Matusch A, Kayser S, Grubert C, Hadrysiewicz B et al (2010). Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation decreases ratings of depression and anxiety in treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 67: 110–116.
Bishop MP, Elder ST, Heath RG (1963). Intracranial self-stimulation in man. Science 140: 394–396.
Blair-West GW, Cantor CH, Mellsop GW, Eyeson-Annan ML (1999). Lifetime suicide risk in major depression: sex and age determinants. J Affect Disord 55: 171–178.
Blumberger DM, Mulsant BH, Daskalakis ZJ (2013). What is the role of brain stimulation therapies in the treatment of depression? Curr Psychiatry Rep 15: 368.
Bourne SK, Eckhardt CA, Sheth SA, Eskandar EN (2012). Mechanisms of deep brain stimulation for obsessive compulsive disorder: effects upon cells and circuits. Front Integr Neurosci 6: 29.
Chang WS, Roh D, Kim CH, Chang JW (2013). Combined bilateral anterior cingulotomy and ventral capsule/ventral striatum deep brain stimulation for refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder with major depression: do combined procedures have a long-term benefit? Restor Neurol Neurosci 31: 723–732.
Chaudhury D, Walsh JJ, Friedman AK, Juarez B, Ku SM, Koo JW et al (2013). Rapid regulation of depression-related behaviours by control of midbrain dopamine neurons. Nature 493: 532–536.
Coenen V, Honey C (2009a). Ablative procedures for depression. In: Lozano A, Gildenberg PL, Tasker RR (eds). Textbook of Stereotatcic and Functional Neurosurgery. Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg. pp 2943–2952.
Coenen VA, Honey CR, Hurwitz T, Rahman AA, McMaster J, Burgel U et al (2009b). Medial forebrain bundle stimulation as a pathophysiological mechanism for hypomania in subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Neurosurgery 64: 1106–1114.
Coenen VA, Mädler B, Schlaepfer TE (2013). Reply to: medial forebrain bundle stimulation-speed access to an old or entry into a new depression neurocircuit? Biol Psychiatry 74: e45–e46.
Coenen VA, Panksepp J, Hurwitz TA, Urbach H, Madler B (2012). Human medial forebrain bundle (MFB) and anterior thalamic radiation (ATR): imaging of two major subcortical pathways and the dynamic balance of opposite affects in understanding depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 24: 223–236.
Coenen VA, Schlaepfer TE, Maedler B, Panksepp J (2011). Cross-species affective functions of the medial forebrain bundle-implications for the treatment of affective pain and depression in humans. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35: 1971–1981.
Crupi R, Marino A, Cuzzocrea S (2011). New therapeutic strategy for mood disorders. Curr Med Chem 18: 4284–4298.
Daniels C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Raethjen J, Pinsker MO, Kloss M et al (2011). Is improvement in the quality of life after subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease predictable? Mov Disord 26: 2516–2521.
Delgado JMR (1971) Physical Control of the Mind — Toward a Psychocivilized Society. Harper Colophon books: New York.
Doshi PK (2011). Long-term surgical and hardware-related complications of deep brain stimulation. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 89: 89–95.
Dougherty D, Carpenter L, Bhati M, Howland R, O’Reardon J, Denko T et al (2012). A Randomized Sham-Controlled Trial of DBS of the VC/VS for Treatment-Resistant Depression. Society of Biological Psychiatry 67th Annual Scientific Convention. 071-Late Breaking Oral Session #2—Mixed Topics http://goo.gl/PGTpo.
Famm K, Litt B, Tracey KJ, Boyden ES, Slaoui M (2013). Drug discovery: a jump-start for electroceuticals. Nature 496: 159–161.
Farah MJ, Illes J, Cook-Deegan R, Gardner H, Kandel E, King P et al (2004). Neurocognitive enhancement: what can we do and what should we do? Nat Rev Neurosci 5: 421–425.
Figee M, de Koning P, Klaassen S, Vulink N, Mantione M, van den Munckhof P et al (2013). Deep brain stimulation induces striatal dopamine release in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry S0006-3223: 00631–00638.
Fily F, Haegelen C, Tattevin P, Buffet-Bataillon S, Revest M, Cady A et al (2011). Deep brain stimulation hardware-related infections: a report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis 52: 1020–1023.
Gale JT, Lee KH, Amirnovin R, Roberts DW, Williams ZM, Blaha CD et al (2013). Electrical stimulation-evoked dopamine release in the primate striatum. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 91: 355–363.
Goodman WK, Foote KD, Greenberg BD, Ricciuti N, Bauer R, Ward H et al (2010). Deep brain stimulation for intractable obsessive compulsive disorder: pilot study using a blinded, staggered-onset design. Biol Psychiatry 67: 535–542.
Gradinaru V, Mogri M, Thompson KR, Henderson JM, Deisseroth K (2009). Optical deconstruction of parkinsonian neural circuitry. Science 324: 354–359.
Greenberg BD, Askland KD, Carpenter LL (2008). The evolution of deep brain stimulation for neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Biosci 13: 4638–4648.
Grubert C, Hurlemann R, Bewernick BH, Kayser S, Hadrysiewicz B, Axmacher N et al (2011). Neuropsychological safety of nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation for major depression: effects of 12-month stimulation. World J Biol Psychiatry 12: 516–527.
Hariz MI, Blomstedt P, Zrinzo L (2010). Deep brain stimulation between 1947 and 1987: the untold story. Neurosurg Focus 29: E1.
Heath RG (1954) Studies In Schizophrenia. Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA. pp 46–47.
Holtzheimer PE 3rd, Kosel M, Schlaepfer T (2012a). Brain stimulation therapies for neuropsychiatric disease. Handb Clin Neurol 106: 681–695.
Holtzheimer PE, Kelley ME, Gross RE, Filkowski MM, Garlow SJ, Barrocas A et al (2012b). Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant unipolar and bipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69: 150–158.
Holtzheimer PE, Kelley ME, Gross RE, Filkowski MM, Garlow SJ, Barrocas A et al (2012c). Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant unipolar and bipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69: 150–158.
Howe MW, Tierney PL, Sandberg SG, Phillips PE, Graybiel AM (2013). Prolonged dopamine signalling in striatum signals proximity and value of distant rewards. Nature 500: 575–579.
Hurwitz TA, Honey CR, Allen J, Gosselin C, Hewko R, Martzke J et al (2012). Bilateral anterior capsulotomy for intractable depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 24: 176–182.
Ikemoto S (2010). Brain reward circuitry beyond the mesolimbic dopamine system: a neurobiological theory. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35: 129–150.
Insel TR (2010). Faulty circuits. Scientific American 302: 44–51.
Ishak WW, Greenberg JM, Balayan K, Kapitanski N, Jeffrey J, Fathy H et al (2011a). Quality of life: the ultimate outcome measure of interventions in major depressive disorder. Harv Rev Psychiatry 19: 229–239.
Ishak WW, Ha K, Kapitanski N, Bagot K, Fathy H, Swanson B et al (2011b). The impact of psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy, and their combination on quality of life in depression. Harv Rev Psychiatry 19: 277–289.
Isometsa ET, Henriksson MM, Aro HM, Heikkinen ME, Kuoppasalmi KI, Lonnqvist JK (1994). Suicide in major depression. Am J Psychiatry 151: 530–536.
Jiménez F, Velasco F, Salin-Pascual R, Hernández JA, Velasco M, Criales JL et al (2005). A patient with a resistant major depression disorder treated with deep brain stimulation in the inferior thalamic peduncle. J Neurosurg 57: 585–593.
Kelley ME, Franco AR, Mayberg HS, Holtzheimer PE (2012). The Illness Density Index (IDI): a longitudinal measure of treatment efficacy. Clin Trials 9: 596–604.
Kennedy SH, Eisfeld BS, Cooke RG (2001). Quality of life: an important dimension in assessing the treatment of depression? J Psychiatry Neurosci 26 Suppl: S23–S28.
Kennedy SH, Giacobbe P, Rizvi SJ, Placenza FM, Nishikawa Y, Mayberg HS et al (2011). Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: follow-up after 3 to 6 years. Am J Psychiatry 168: 502–510.
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ (2008). The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature 455: 894–902.
Lammel S, Lim BK, Malenka RC (2014). Reward and aversion in a heterogeneous midbrain dopamine system. Neuropharmacology 76 Pt B: 351–359.
Lammel S, Tye KM, Warden MR (2013). Progress in understanding mood disorders: optogenetic dissection of neural circuits. Genes Brain Behav 13: 38–51.
Lippitz BE, Mindus P, Meyerson BA, Kihlstrom L, Lindquist C (1999). Lesion topography and outcome after thermocapsulotomy or gamma knife capsulotomy for obsessive-compulsive disorder: relevance of the right hemisphere. Neurosurgery 44: 452–458.
Lipsman N, Neimat JS, Lozano AM (2007). Deep brain stimulation for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder: the search for a valid target. Neurosurgery 61: 1–11.
Lisanby SH (2007). Electroconvulsive therapy for depression. N Engl J Med 357: 1939–1945.
Lozano AM, Giacobbe P, Hamani C, Rizvi SJ, Kennedy SH, Kolivakis TT et al (2012). A multicenter pilot study of subcallosal cingulate area deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. J Neurosurg 116: 315–322.
Lozano AM, Lipsman N (2013). Probing and regulating dysfunctional circuits using deep brain stimulation. Neuron 77: 406–424.
Lozano AM, Mayberg HS, Giacobbe P, Hamani C, Craddock RC, Kennedy SH (2008). Subcallosal cingulate gyrus deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 64: 461–467.
Malone DA (2011). Use of deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression. Cleve Clin J Med 77: 77.
Malone DA Jr., Dougherty DD, Rezai AR, Carpenter LL, Friehs GM, Eskandar EN et al (2009). Deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 65: 267–275.
Mayberg HS (1997). Limbic-cortical dysregulation: a proposed model of depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9: 471–481.
Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, McNeely HE, Seminowicz D, Hamani C et al (2005). Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron 45: 651–660.
McNeely HE, Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Kennedy SH (2008). Neuropsychological impact of Cg25 deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: preliminary results over 12 months. J Nerv Ment Dis 196: 405–410.
Mercado R, Constantoyannis C, Mandat T, Kumar A, Schulzer M, Stoessl AJ et al (2006). Expectation and the placebo effect in Parkinson’s disease patients with subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation. Mov Disord 21: 1457–1461.
Meyer A, Beck E, Mc LT (1947). Prefrontal leucotomy; a neuro-anatomical report. Brain 70: 18–49.
Miller IW, Keitner GI, Schatzberg AF, Klein DN, Thase ME, Rush AJ et al (1998). The treatment of chronic depression, part 3: psychosocial functioning before and after treatment with sertraline or imipramine. J Clin Psychiatry 59: 608–619.
Miocinovic S, Somayajula S, Chitnis S, Vitek JL (2013). History, applications, and mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. JAMA Neurol 70: 163–171.
Moniz E (1994). Prefrontal leucotomy in the treatment of mental disorders. 1937. Am J Psychiatry 151 (Suppl 6): 236–239.
Nuttin B, Cosyns P, Demeulemeester H, Gybels J, Meyerson B (1999). Electrical stimulation in anterior limbs of internal capsules in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Lancet 354: 1526.
Olds J, Milner P (1954). Positive reinforcement produced by electrical stimulation of septal area and other regions of rat brain. J Comp Physiol Psychol 47: 419–427.
Papez JW (1995). A proposed mechanism of emotion. 1937. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 7: 103–112.
Pizzagalli DA, Holmes AJ, Dillon DG, Goetz EL, Birk JL, Bogdan R et al (2009). Reduced caudate and nucleus accumbens response to rewards in unmedicated individuals with major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry 166: 702–710.
Pizzagalli DA, Iosifescu D, Hallett LA, Ratner KG, Fava M (2008). Reduced hedonic capacity in major depressive disorder: evidence from a probabilistic reward task. J Psychiatr Res 43: 76–87.
Puigdemont D, Perez-Egea R, Portella MJ, Molet J, de Diego-Adelino J, Gironell A et al (2011). Deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate gyrus: further evidence in treatment-resistant major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15: 121–133.
Riva-Posse P, Holtzheimer PE, Garlow SJ, Mayberg HS (2013). Practical considerations in the development and refinement of subcallosal cingulate white matter deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. World Neurosurg 80: S27 e25–S27.
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D et al (2006). Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry 163: 1905–1917.
Rush AJ, Weissenburger JE (1994). Melancholic symptom features and DSM-IV. Am J Psychiatry 151: 489–498.
Russo SJ, Nestler EJ (2013). The brain reward circuitry in mood disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 14: 609–625.
Sartorius A, Henn FA (2007). Deep brain stimulation of the lateral habenula in treatment resistant major depression. Med Hypotheses 69: 1305–1308.
Sartorius A, Kiening KL, Kirsch P, von Gall CC, Haberkorn U, Unterberg AW et al (2010). Remission of major depression under deep brain stimulation of the lateral habenula in a therapy-refractory patient. Biol Psychiatry 67: e9–e11.
Schatzberg AF, Kraemer HC (2000). Use of placebo control groups in evaluating efficacy of treatment of unipolar major depression. Biol Psychiatry 47: 736–744.
Schlaepfer TE, Bewernick BH, Kayser S, Madler B, Coenen VA (2013). Rapid effects of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant major depression. Biol Psychiatry 73: 1204–1212.
Schlaepfer TE, Cohen MX, Frick C, Kosel M, Brodesser D, Axmacher N et al (2008). Deep brain stimulation to reward circuitry alleviates anhedonia in refractory major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 33: 368–377.
Schlaepfer TE, George MS, Mayberg H (2010). WFSBP Guidelines on brain stimulation treatments in psychiatry. World J Biol Psychiatry 11: 2–18.
Schoene-Bake JC, Parpaley Y, Weber B, Panksepp J, Hurwitz TA, Coenen VA (2010). Tractographic analysis of historical lesion surgery for depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 35: 2553–2563.
Shorter E, Healy D (2007) Shock Therapy: A History of Electroconvulsive Treatment in Mental Illness. University of Toronto Press: Toronto.
Spiegel EA, Wycis HT, Marks M, Lee AJ (1947). Stereotaxic apparatus for operations on the human brain. Science 106: 349–350.
Thomas L (1971). The technology of medicine. N Engl J Med 285: 1366–1368.
Tremblay LK, Naranjo CA, Graham SJ, Herrmann N, Mayberg HS, Hevenor S et al (2005). Functional neuroanatomical substrates of altered reward processing in major depressive disorder revealed by a dopaminergic probe. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62: 1228–1236.
Tye KM, Mirzabekov JJ, Warden MR, Ferenczi EA, Tsai HC, Finkelstein J et al (2012). Dopamine neurons modulate neural encoding and expression of depression-related behaviour. Nature 493: 537–541.
van Dijk A, Klompmakers AA, Feenstra MG, Denys D (2012). Deep brain stimulation of the accumbens increases dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline in the prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem 123: 897–903.
Ware JE Jr., Kosinski M, Gandek B, Aaronson NK, Apolone G, Bech P et al (1998). The factor structure of the SF-36 Health Survey in 10 countries: results from the IQOLA Project. International Quality of Life Assessment. J Clin Epidemiol 51: 1159–1165.
Whiteford HA, Degenhardt L, Rehm J, Baxter AJ, Ferrari AJ, Erskine HE et al (2013). Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 382: 1575–1586.
Wulsin LR, Vaillant GE, Wells VE (1999). A systematic review of the mortality of depression. Psychosom Med 61: 6–17.
Zrinzo L, Foltynie T, Limousin P, Hariz MI (2012). Reducing hemorrhagic complications in functional neurosurgery: a large case series and systematic literature review. J Neurosurg 116: 84–94.
Acknowledgements
TES and VAC received partial funding for two investigator-initiated studies on DBS for major depression from Medtronic Inc. and the Hope for Depression Research Foundation (HDRF) and the Institute for Affective Neuroscience (ISAN). VAC is consultant for Medtronic Europe and occasionally received honoraria for talks. TS is chair of the project group, ‘Deep Brain Stimulation in Psychiatry: Guidance for Responsible Research and Application’, funded by the Volkswagen Foundation (Hanover, Germany). TS and BB are members of the working Group Neuromodulation of the German Research Foundation. RH was supported by a Starting Independent Researcher Grant (NEMO—Neuromodulation of Emotion) jointly provided by the Ministry of Innovation, Science, Research and Technology of the German State of North Rhine-Westphalia (MIWFT) and the University of Bonn.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlaepfer, T., Bewernick, B., Kayser, S. et al. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Human Reward System for Major Depression—Rationale, Outcomes and Outlook. Neuropsychopharmacol 39, 1303–1314 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.28
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.28
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Accelerated TMS - moving quickly into the future of depression treatment
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Normalized affective responsiveness following deep brain stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle in depression
Translational Psychiatry (2024)
-
Linking connectivity of deep brain stimulation of nucleus accumbens area with clinical depression improvements: a retrospective longitudinal case series
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2024)
-
Deep brain stimulation of the “medial forebrain bundle”: a strategy to modulate the reward system and manage treatment-resistant depression
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
Dysregulation of adult hippocampal neuroplasticity in major depression: pathogenesis and therapeutic implications
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)