Abstract
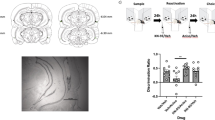
The mammalian basolateral amygdala (BLA) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) comprise a functionally interconnected circuit that is critical for processing opiate-related associative memories. In the opiate-naïve state, reward memory formation in the BLA involves a functional link between dopamine (DA) D1 receptor (D1R) and extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling substrates, but switches to a DA D2 (D2R)/Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIα (CaMKIIα)-dependent memory substrate following chronic opiate exposure and spontaneous withdrawal. Using conditioned place preference (CPP) in rats paired with molecular analyses, we examined the role of intra-mPFC CaMKII, ERK and DAergic activity during the formation of opiate associative memories, and how opiate exposure state may regulate the functions of these molecular memory pathways. We report that the role of CaMKIIα signaling is functionally reversed within the BLA-mPFC pathway depending on opiate exposure state. Thus, in the opiate-naïve state, intra-mPFC but not intra-BLA blockade of CaMKII signaling prevents formation of opiate reward memory. However, following chronic opiate exposure and spontaneous withdrawal, the role of CaMKII signaling in the BLA-mPFC is functionally reversed. This behavioral memory switch corresponds to a selective increase in the expression of D2R and CaMKIIα, but not other calcium/calmodulin-related molecules, nor D1R expression levels within the mPFC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Achterberg KG, Buitendijk GHS, Kool MJ, Goorden SMI, Post L, Slump DE et al (2014). Temporal and region-specific requirements of αCaMKII in spatial and contextual learning. J Neurosci 34: 11180–11187.
Andersen JM, Klykken C, Mørland J (2012). Long-term methadone treatment reduces phosphorylation of CaMKII in rat brain. J Pharm Pharmacol 64: 843–847.
Bechara A, Nader K, van der Kooy D (1995). Neurobiology of withdrawal motivation: evidence for two separate aversive effects produced in morphine-naïve versus morphine-dependent rats by both naloxone and spontaneous withdrawal. Behav Neurosci 109: 91–105.
Bilecki W, Zapart G, Ligeza A, Wawrzczak-Bargiela A, Urbański MJ, Przewłocki R (2005). Regulation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases following acute and chronic opioid treatment. Cell Mol Life Sci 62: 2369–2375.
Bishop SF, Lauzon NM, Bechard MA, Gholizadeh S, Laviolette SR (2011). NMDA receptor hypofunction in the prelimbic cortex increases sensitivity to the rewarding properties of opiates via dopaminergic and amygdalar substrates. Cereb cortex 21: 68–80.
Bossert JM, Stern AL, Theberge FRM, Marchant NJ, Wang H-L, Morales M et al (2012). Role of projections from ventral medial prefrontal cortex to nucleus accumbens shell in context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. J Neurosci 32: 4982–4991.
Cardinal RN, Parkinson JA, Hall J, Everitt BJ (2002). Emotion and motivation: the role of the amygdala, ventral striatum, and prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26: 321–352.
Chen Y, Jiang Y, Yue W, Zhou Y, Lu L, Ma L (2008). Chronic, but not acute morphine treatment, up-regulates alpha-Ca2+/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II gene expression in rat brain. Neurochem Res 33: 2092–2098.
Divsalar K, Meymandi MS, Afarinesh M, Zarandi MM, Haghpanah T, Keyhanfar F et al (2014). Serum biochemical parameters following heroin withdrawal: an exploratory study. Am J Addict 23: 48–52.
Doherty JM, Cooke BM, Frantz KJ (2013). A role for the prefrontal cortex in heroin-seeking after forced abstinence by adult male rats but not adolescents. Neuropsychopharmacology 38: 446–454.
Edwards S, Graham DL, Whisler KN, Self DW (2009). Phosphorylation of GluR1, ERK, and CREB during spontaneous withdrawal from chronic heroin self-administration. Synapse 63: 224–235.
Frankland P, O’Brien C, Ohno M (2001). α-CaMKII-dependent plasticity in the cortex is required for permanent memory. Nature 309–313.
Fricks-Gleason AN, Marshall JF (2011). Role of dopamine D1 receptors in the activation of nucleus accumbens extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) by cocaine-paired contextual cues. Neuropsychopharmacology 36: 434–444.
Gholizadeh S, Sun N, De Jaeger X, Bechard MA, Coolen L, Laviolette SR (2013). Early versus late-phase consolidation of opiate reward memories requires distinct molecular and temporal mechanisms in the amygdala-prefrontal cortical pathway. PLoS One 8: e63612.
De Jaeger X, Bishop SF, Ahmad T, Lyons D, Ng GA, Laviolette SR (2013). The effects of AMPA receptor blockade in the prelimbic cortex on systemic and ventral tegmental area opiate reward sensitivity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 225: 687–695.
Lai Y-T, Fan H-Y, Cherng CG, Chiang C-Y, Kao G-S, Yu L (2008). Activation of amygdaloid PKC pathway is necessary for conditioned cues-provoked cocaine memory performance. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90: 164–170.
Lauzon NM, Ahmad T, Laviolette SR (2012). Dopamine D4 receptor transmission in the prefrontal cortex controls the salience of emotional memory via modulation of calcium calmodulin-dependent kinase II. Cereb cortex 22: 2486–2494.
Laviolette SR, van der Kooy D (2003). Blockade of mesolimbic dopamine transmission dramatically increases sensitivity to the rewarding effects of nicotine in the ventral tegmental area. Mol Psychiatry 8: 50–59 9.
Laviolette SR, van der Kooy D (2004). GABAA receptors signal bidirectional reward transmission from the ventral tegmental area to the tegmental pedunculopontine nucleus as a function of opiate state. Eur J Neurosci 20: 2179–2187.
Lintas A, Chi N, Lauzon NM, Bishop SF, Gholizadeh S, Sun N et al (2011). Identification of a dopamine receptor-mediated opiate reward memory switch in the basolateral amygdala-nucleus accumbens circuit. J Neurosci 31: 11172–11183.
Lintas A, Chi N, Lauzon NM, Bishop SF, Sun N, Tan H et al (2012). Inputs from the basolateral amygdala to the nucleus accumbens shell control opiate reward magnitude via differential dopamine D1 or D2 receptor transmission. Eur J Neurosci 35: 279–290.
Liu X-Y, Mao L-M, Zhang G-C, Papasian CJ, Fibuch EE, Lan H-X et al (2009). Activity-dependent modulation of limbic dopamine D3 receptors by CaMKII. Neuron 61: 425–438.
Liu Z, Liu X-D, Zhang J-J, Yu L-C (2012a). Increases in αCaMKII phosphorylated on Thr286 in the nucleus accumbens shell but not the core during priming-induced reinstatement of morphine-seeking in rats. Neurosci Lett 526: 39–44.
Liu Z, Zhang J-J, Liu X-D, Yu L-C (2012b). Inhibition of CaMKII activity in the nucleus accumbens shell blocks the reinstatement of morphine-seeking behavior in rats. Neurosci Lett 518: 167–171.
Lu L, Zeng S, Liu D, Ceng X (2000). Inhibition of the amygdala and hippocampal calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II attenuates the dependence and relapse to morphine differently in rats. Neurosci Lett 291: 191–195.
Lucas M, Frenois F, Cador M, Le Moine C (2012). Remodeling of the neuronal circuits underlying opiate-withdrawal memories following remote retrieval. Neurobiol Learn Mem 97: 47–53.
Lyons D, de Jaeger X, Rosen LG, Ahmad T, Lauzon NM, Zunder J et al (2013). Opiate exposure and withdrawal induces a molecular memory switch in the basolateral amygdala between ERK1/2 and CaMKIIα-dependent signaling substrates. J Neurosci 33: 14693–14704.
Martinez D, Saccone PA, Liu F, Slifstein M, Orlowska D, Grassetti A et al (2012). Deficits in dopamine D(2) receptors and presynaptic dopamine in heroin dependence: commonalities and differences with other types of addiction. Biol Psychiatry 71: 192–198.
Morón JA, Gullapalli S, Taylor C, Gupta A, Gomes I, Devi LA (2010). Modulation of opiate-related signaling molecules in morphine-dependent conditioned behavior: conditioned place preference to morphine induces CREB phosphorylation. Neuropsychopharmacology 35: 955–966.
Nader K, Harrington F, Bechara A, van der Kooy D (1994). Neuroleptics block high but not low dose heroin place preferences: further evidence for a two system model of motivation. Behav Neurosci 108: 1128–1138.
Narita M, Matsumura Y, Ozaki S, Ise Y, Yajima Y, Suzuki T (2004). Role of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ii (CaMKII) in the morphine-induced pharmacological effects in the mouse. Neuroscience 126: 415–421.
Naskar S, Wan H, Kemenes G (2014). pT305-CaMKII stabilizes a learning-induced increase in AMPA receptors for ongoing memory consolidation after classical conditioning. Nat Commun 5: 3967.
Papaleo F, Yang F, Garcia S, Chen J, Lu B, Crawley JN et al (2012). Dysbindin-1 modulates prefrontal cortical activity and schizophrenia-like behaviors via dopamine/D2 pathways. Mol Psychiatry 17: 85–98.
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Elsevier Academic Press: : Amsterdam.
Pelloux Y, Murray JE, Everitt BJ (2013). Differential roles of the prefrontal cortical subregions and basolateral amygdala in compulsive cocaine seeking and relapse after voluntary abstinence in rats. Eur J Neurosci 38: 3018–3026.
Sun N, Chi N, Lauzon N, Bishop S, Tan H, Laviolette SR (2011). Acquisition, extinction, and recall of opiate reward memory are signaled by dynamic neuronal activity patterns in the prefrontal cortex. Cereb cortex 21: 2665–2680.
Sun N, Laviolette SR (2012). Inactivation of the basolateral amygdala during opiate reward learning disinhibits prelimbic cortical neurons and modulates associative memory extinction. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 222: 645–661.
Valjent E, Pagès C, Hervé D, Girault J-A, Caboche J (2004). Addictive and non-addictive drugs induce distinct and specific patterns of ERK activation in mouse brain. Eur J Neurosci 19: 1826–1836.
Wang G, Volkow N, Fowler J (1997). Dopamine D 2 receptor availability in opiate-dependent subjects before and after naloxone-precipitated withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 16: 174–182.
Zhang S, Xie C, Wang Q, Liu Z (2014). Interactions of CaMKII with dopamine D2 receptors: roles in levodopa-induced dyskinesia in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned Parkinson’s rats. Sci Rep 4: 6811.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP 123378), the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), and an Ontario Graduate Scholarship to LGR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosen, L., Zunder, J., Renard, J. et al. Opiate Exposure State Controls a D2-CaMKIIα-Dependent Memory Switch in the Amygdala-Prefrontal Cortical Circuit. Neuropsychopharmacol 41, 847–857 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.211
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.211
This article is cited by
-
Cannabidiol Modulates Fear Memory Formation Through Interactions with Serotonergic Transmission in the Mesolimbic System
Neuropsychopharmacology (2016)