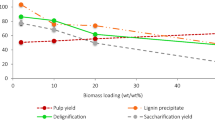
Abstract
Concerns regarding the non-renewable nature of, and pollution from, petroleum derived energy and commercial products has led to the concept of a biomass economy. As part of this vision for a society based on sustainable biomaterials, proposed biorefineries need to tackle the challenges of taking a wide diversity of raw biomass and rapidly and effectively transforming it into functionalizable platform molecules that can be derivatized into industrial and consumer products, or converted into biofuels. A substantial research effort is underway focussed on degrading biomass into smaller constituents using a variety of physical, chemical, and biological processes. One promising technology for the solubilization of biomass is ionic liquids (ILs), which has received considerable attention as a medium for efficient solubilization of a variety of materials. ILs also allow fractional separation when combined with solvent extraction (conventional, and green technologies such as supercritical CO2), precipitation, and adsorption/absorption methods, and to conduct a wide range of chemical reactions using thermal, electrochemical, photochemical, and biocatalytic processes. As a potential pretreatment technology for the biorefineries of the future, we report herein the first rapid dissolution of a range of coniferous and deciduous woods and grassy lignocellulosic plant materials in an IL using microwave radiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rayne, S., Mazza, G. Rapid Dissolution of Lignocellulosic Plant Materials in an Ionic Liquid. Nat Prec (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2007.637.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2007.637.1