Abstract
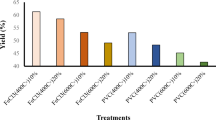
Using a critical solution mixture, into which chelating agents have been dissolved, resulted in the efficient, rapid and simultaneous removal of both heavy metals and organic pollutants from contaminated sediments. Both heating and cooling across the immiscibility curve and isothermal extraction were investigated. In addition, the extraction yields were compared to those obtained with solution mixtures that do not possess a critical point of miscibility. Extraction yields of the former were superior to those of the latter in the range of relevant pressures (1 atm.) and temperatures. Extraction via heating and cooling across the miscibility curve resulted in the removal of close to 90% of the heavy metals and practically all of the organic contaminants, compared to only about 40% when the extraction was performed isothermally at around 20oC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golan, T., Ludmer, Z., Ermolenko, E. et al. The Use of Critical Solution Mixtures for Contaminated Sediments Remediation. Nat Prec (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2007.792.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2007.792.1