Abstract
Objective:
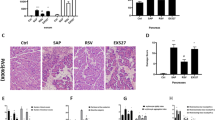
To investigate the effect of Bacailin on inflammatory mediator levels and microcirculation disturbance in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) rats and explore its therapeutic mechanism on this disease. Methods: SAP model rats were randomly divided into model control group and Baicalin treated group, 45 rats in each group. The same number of normal rats were included in sham-operated group. These groups were further subdivided into 3 h, 6 h and 12 h subgroups, respectively (15 rats in each subgroup). At 3, 6 and 12 hours after operation, rats were killed to conduct the following experiments: (1) to examine the mortality rates of rats, the ascites volume and pancreatic pathological changes in each group; (2) to determine the contents of amylase, PLA~2~, TXB~2~, PGE~2~, PAF and IL-1[beta]; in blood as well as the changes in blood viscosity.
Results:
(1) Compared to model control group, treatment with Baicalin is able to improve the pathological damage of the pancreas, lower the contents of amylase and multiple inflammatory mediators in blood, decrease the amount of ascitic fluid and reduce the mortality rates of SAP rats; (2) at 3 hours after operation, the low-shear whole blood viscosity in Baicalin treated group was significantly lower than that in model control group;at 12 hours after operation, both the high-shear and low-shear whole blood viscosity in Baicalin treated group were also significantly lower than those in model control group.
Conclusion:
Baicalin, as a new drug, has good prospects in the treatment of SAP since it can exert therapeutic effects on this disease through inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators, lowering blood viscosity, improving microcirculation and mitigating the pathological damage of the pancreas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Tian, H., Wu, CJ. et al. Effect of Baicalin on inflammatory mediator levels and microcirculation disturbance in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Nat Prec (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2008.1968.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2008.1968.1