Abstract
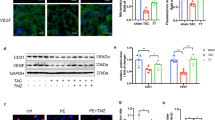
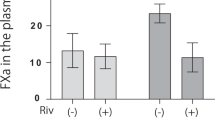
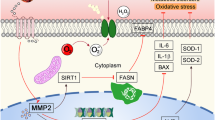
To examine how heat shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1) protects against maladaptive hypertrophy during pressure overload, we subjected HSF1 transgenic (TG), knockout (KO) and wild type (WT) mice to a constriction of transverse aorta (TAC), and found that cardiac hypertrophy, functions and angiogenesis were well preserved in TG mice but were decreased in KO mice compared to WT ones at 4 weeks, which was related to HIF-1 and p53 expression. Inhibition of angiogenesis suppressed cardiac adaptation in TG mice while overexpression of angiogenesis factors improved maladaptive hypertrophy in KO mice. In vitro formation of vasculatures by microvascular endothelial cells was higher in TG mice but lower in KO mice than in WT ones. A siRNA of p53 but not a HIF-1 gene significantly reversed maladaptive hypertrophy in KO mice whereas a siRNA of HIF-1 but not a p53 gene induced maladaptive hypertrophy in TG mice. Heart microRNA analysis showed that miR-378 and miR-379 were differently changed among the three mice after TAC, and miR-378 or siRNA of miR-379 could maintain cardiac adaptation in WT mice. These results indicate that HSF1 preserves cardiac adaptation during pressure overload through p53-HIF-1-associated angiogenesis, which is controlled by miR-378 and miR-379.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Ge, J., Yuan, J. et al. Heat shock transcription factor 1 preserves cardiac angiogenesis and adaptation during pressure overload. Nat Prec (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2008.2716.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2008.2716.1