Abstract
Background:
BPR0L075 [6-methoxy-3-(3',4',5'-trimethoxy-benzoyl)-1H-indole] is a novel anti-cancer compound. It inhibits tubulin polymerization and induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in various human cancer cells with different multi-drug resistance (MDR) status. Over-expression of an anti-apoptotic molecule, survivin, causes drug-resistance in various cancers. Survivin inhibits apoptosis by interfering caspase-3 and promotes cell growth by stabilizing microtubule networks. Here, we determined the effects of down-regulation of survivin in BPR0L075 (L075) treatment. Methods: Western blot analysis was used to determine the expression level of survivin in L075-untreated/-treated human oral carcinoma KB and nasopharyngeal carcinoma HONE-1 cancer cells. siRNA was used to down-regulate endogenous survivin. MTT cell viability assay, real-time caspase-3 activity assay and immuno-fluorescence microscopy were used to analyze downstream effects.
Results:
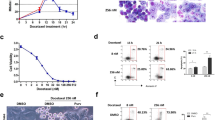
Survivin expression was up-regulated in both KB and HONE-1 cells in response to L075 treatment. Down-regulation of survivin induced hyper-sensitivity to L075 in KB and re-stored sensitivity to L075 in KB-derived L075-resistant KB-L30 cancer cells. At the molecular level, down-regulation of survivin induced changes in microtubule dynamics in both KB and KB-L30 cells. Surprisingly, down-regulation of survivin did not enhance the activity of caspase-3 in L075 therapy. Instead, down-regulation of survivin induced translocation of the apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) from cytoplasm to nucleus. Conclusion: Down-regulation of survivin improved drug sensitivity to L075 in both KB and L075-resistant KB-L30 cancer cells, possibly through a tubulin-dependent and caspase-independent mechanism. We suggest that combining BPR0L075 and survivin inhibitor may give better clinical outcome than the use of BPR0L075 monotherapy in future clinical trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheung, C., Kuo, CC., Chang, CY. et al. Down-regulation of Survivin enhances sensitivity to BPR0L075 in human cancer cells via caspase-independent mechanisms. Nat Prec (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2008.2729.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2008.2729.1