Abstract
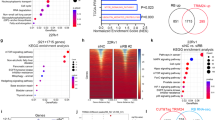
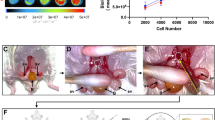
We introduce a new effective method to control hormone refractory prostate cancer cells by using an activated rubber/resin form (RB), far-infrared ray emitter, with or without sodium butyrate (SB). The growth of three human prostate cancer cell lines (Du145, PC-3 and LNCaP) was suppressed in vitro and in vivo by using RB, and the cells were eradicated with RB + 3 mM SB. G1 arrest and apoptotic pathway proteins were induced by RB with intensified expressions of apoptosis - related mRNA on cDNA microarray. RB radiates far-infrared rays of the 4 to 25 [mu]m wavelengths to an object which exert a favorable influence on a cancer control. These results may render us a new therapeutic modality in hormone refractory prostate cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shima, H., Yamamoto, S., Qiu, J. et al. Far-infrared rays control prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Nat Prec (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.1980.2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.1980.2