Abstract
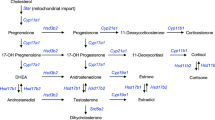
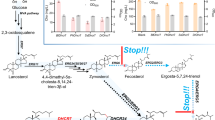
Steroid hormones regulate many physiological processes in vertebrates, nematodes and arthropods through binding to nuclear receptors (NR), a metazoan-specific family of ligand-activated transcription factors. The main steps controlling the diversification of this family are now well understood. In contrast, the origin and evolution of steroid ligands remain mysterious although this is crucial for understanding the emergence of modern endocrine systems. Using a comparative genomic approach, we analyzed complete metazoan genomes to provide a comprehensive view of the evolution of major enzymatic players implicated in steroidogenesis at the whole Metazoan scale. Our analysis reveals that steroidogenesis has been independently elaborated in the three main Bilaterian lineages, and that steroidogenic cytochrome P450 enzymes descended from those that detoxify xenobiotics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markov, G., Tavares, R., Dauphin-Villemant, . et al. Independent elaboration of steroid hormone signaling pathways in Metazoans. Nat Prec (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.3374.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.3374.1