Abstract
Background.
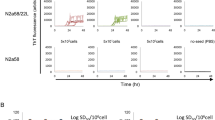
Our studies on the role of cholesterol in prion infection/replication showed that brains and peripheral cells of sheep susceptible to or suffering from Scrapie were characterized by an altered cholesterol homeostasis compared to animals with a scrapie-resistant genotype, and that drugs influencing cholesterol esterification were endowed with selective anti-prion activity in N2a cell lines infected with the 22L and RML prion strains. Results. In prion-infected N2a cell lines we now report increased anti-prion activity of dual-drug combinations consisting of cholesterol ester modulators associated with prion inhibitors Synergism was obtained with the cholesterol ester modulators everolimus, pioglitazone, progesterone, and verapamil associated with the anti-prion chlorpromazine, and with everolimus and pioglitazone associated with the anti-prion quinacrine. Comparative lipid analyses in prion-infected and non-infected N2a cells by colorimetric, enzymatic, and chemical means, clearly demonstrated a derangement of type and distribution of cholesterol esters, free cholesterol, and triglycerides in the infected N2a cells. Although single-drug treatments influenced lipid syntheses, only the combined-drug treatments appeared to restore a lipid profile similar to that of untreated-uninfected cells.
Conclusions.
We conclude that the anti-prion synergistic effect of cholesterol ester modulators with the cholesterol metabolism interfering anti-prion drugs chlorpromazine and quinacrine may arise from the ability of combined drugs to re-establish the intracellular lipid profile of untreated-uninfected cells. Overall, these data suggest that inhibition of prion replication can be readily potentiated by combinatorial drug treatments, and that steps of cholesterol/cholesterol ester metabolism may represent suitable targets.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orrù, C., Cannas, M., Vascellari, S. et al. In vitro synergistic anti-prion effect of cholesterol ester modulators . Nat Prec (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.3883.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2009.3883.1