Abstract
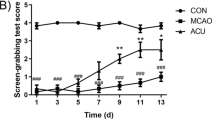
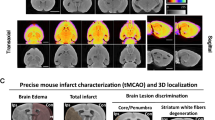
While acupuncture has survived several thousand years’ evolution of medical practice, its function still remains as a myth from the view point of modern medicine. Our goal in this paper is to quantitatively understand the function of acupuncture in ischemia stroke treatment. We carried out a comparative study using the Sprague Dawley rat animal model. We induced the focal cerebral ischemia in the rats using the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) procedure. For each rat from the real acupuncture group (n = 40), sham acupoint treatment group (n = 54), and blank control group (n = 16), we acquired 3-D FDG-microPET images at baseline, after MCAO, and after treatment (i.e., real acupuncture, sham acupoint treatment, or resting according to the group assignment), respectively. After verifying that the injured area is in the right hemisphere of the cerebral cortex in the brain by using magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) and triphenyl tetrazolium cchloride (TTC)-staining, we directly compared the glucose metabolism in the right hemisphere of each rat. We carried out t-test and permutation test on the image data. Both tests demonstrated that acupuncture had a more positive effect than non-acupoint stimulus and blank control (P < 0.025) in increasing the glucose metabolic level in the stroke-injured area in the brain, while there was no statistically significant difference between non-acupoint stimulus and blank control (P>0.15). The immediate positive effect of acupuncture over sham acupoint treatment and blank control is verified using our experiments. The long-term benefit of acupuncture needs to be further studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, X., Tang, H., Li, J. et al. Using MicroPET Imaging in Quantitative Verification of Acupuncture Effect in Ischemia Stroke Treatment. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4128.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4128.1