Abstract
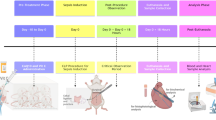
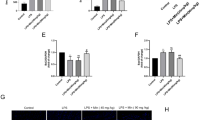
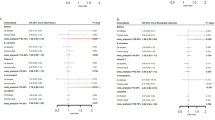
Vitamin C scavenges toxic free radicals as an antioxidant, and oxidative stress is considered as a major contributor inducing damage to cardiomyocytes in heart diseases. Also, it is well-known that stress provokes oxidative stress and induces cardiac sudden death. Here we show the effects of vitamin C on the prevention of cardiac damage by stress in gulo(-/-) mice which cannot synthesize vitamin C. Vitamin C-insufficient gulo(-/-) mice under stress showed prominent cardiac damage and expired within 2 weeks. It was accompanied with structural changes in the heart, cardiac dysfunction and severe emphysema. These changes were caused by the elevation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, especially TNF-&x03B1;, the activation of MMP-2/MMP-9, an increase in oxidative stress and a remarkable decrease in noradrenaline production. Thus, vitamin C insufficiency causes extensive cardiac damage under stress through regulating cytokine and hormone production as well as redox homeostasis, which results in stress-induced sudden death.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, J., Kim, S., Bae, S. et al. Vitamin C insufficiency causes the stress-induced sudden death through the induction of extensive heart injury.. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4320.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4320.1