Abstract
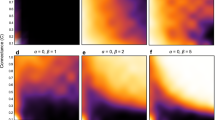
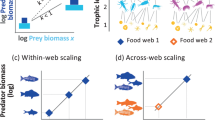
Theoretical studies predict that the stability of an ecosystem is negatively correlated with its complexity, measured by the number of interacting species. On the other hand, empirical evidence indicates that food webs are highly interconnected. In this manuscript we present results on the stability two-level predator-prey food webs. We analyzed exhaustively all possible topologies of connections among species. Our findings show that those food webs fall into two classes with clearly distinct stability properties. In one of them stability is negatively correlated with complexity, and in the other group stability is positively correlated. For a positive relationship our results reveals highly structured food webs. The positive or negative relationship is related only to the topological structure of the food web. It is independent of the number of connections, strengths of predator-prey interactions or number of species. We review empirical evidence that corroborates our results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burgoa Rosso, K., Nogales Vera, J., Faria, L. et al. The architecture of predator-prey and the relationship between complexity and stability. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4396.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4396.1