Abstract
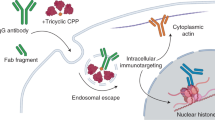
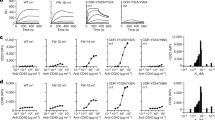
It is already more than a century since the pioneering work of the Nobel Laureate Ehrlich gave birth to the side chain theory1, which helped to define antibodies and their ability to target specific biological sites. However, the use of antibodies is still restricted to the extracellular space due to the lack of a suitable delivery vehicle for the efficient transport of antibodies into live cells without inducing toxicity. In this work, we report the efficient encapsulation and delivery of antibodies into live cells with no significant loss of cell viability or any deleterious affect on the cell metabolic activity. This delivery system is based on poly(2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl phosphorylcholine)-block-(2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate), (PMPC-PDPA), a pH sensitive diblock copolymer that self-assembles to form nanometer-sized vesicles, also known as polymersomes, at physiological pH. These polymersomes can successfully deliver relatively high antibody payloads within live cells. Once inside the cells, we demonstrate that these antibodies can target their epitope by immune-labelling of cytoskeleton, Golgi, and transcription factor proteins in live cells. We also demonstrate that this effective antibody delivery mechanism can be used to control specific subcellular events, as well as modulate cell activity and pro-inflammatory process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massignani, M., Canton, I., Patikarnmonthon, N. et al. Cellular delivery of antibodies: effective targeted subcellular imaging and new therapeutic tool. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4427.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4427.1