Abstract
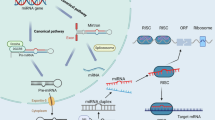
A large amount of hidden biological information is contained in the human genome, which is not expressed or revealed in the form of proteins; the usual end product form of gene expression. Instead, most of such information is in the form of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). ncRNAs correspond to genes that are transcribed, but do not get translated into proteins. This part of the genome was, till recently, considered as ‘junk’. The term ‘junk’ implied lack of any discernible function of these RNA. More than 98% of the human genomic size encompasses these non-coding RNAs. But, recent research has evidently brought out the indispensible contribution of non-coding RNA in controlling and regulating gene expression. ncRNA such as siRNAs and microRNAs have been reported to greatly help in causing post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) in cells through RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. In this work, we have investigated the possibility of using siRNAs and microRNAs to aid in gene silencing of early onset Alzheimer’s disease genes. Alzheimer’s disease specific mutations and their corresponding positions in mRNA have been identified for six genes; Presenilin-1, Presenilin-2, APP (amyloid beta precursor protein), APBB3, BACE-1 and PSENEN. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) that can cause PTGS through RNA interference pathway have been designed. RNA analysis has been done to verify complementarity of antisense siRNA sequence with target mRNA sequence. Interaction studies have been done computationally between these antisense siRNA strands and seven Argonaute proteins. From the interaction studies, only one of the seven Argonaute proteins; 1Q8K, was found to have interaction with the siRNAs indicating the importance and uniqueness of this particular protein in RISC (RNA induced silencing complex). The interaction studies have been carried out for the microRNAs also. Out of the 700 mature human microRNAs collected, 394 microRNAs have been identified to show partial complementarity with their target sequence on PSEN-1 mRNA. Of these 394, five microRNAs have shown partial complementarity to early onset Alzheimer’s disease specific mutations in PSEN-1 mRNA. Interaction studies have been done between these microRNAs and Argonaute proteins. Thus, design, characterization and analysis of ncRNAs that contribute to post transcriptional gene silencing of Alzheimer’s disease have been achieved.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namboori, K., Mohan, A., K.U., R. et al. Effect of Non-Coding RNA on Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing of Alzheimer Disease. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4467.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4467.1