Abstract
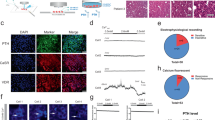
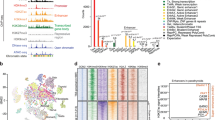
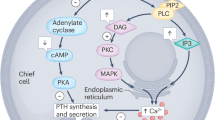
The parathyroid hormone (PTH) (1-34) gene was inserted into a pcDNA3 promoter and E. coli competent cells were used to amplify the cDNA. C3H/10T1/2 stem cells were transfected with PTH (1-34) cDNA using Lipofectamine reagents. After G418 treatment live cells at a density of 4x107 were loaded onto a TheraCyte unit. After parathyroidectomy, rats were either the implanted with 4x107 TheraCyte-encapsulated cells (group A), subcutaneously injected with 4x107 live cells containing PTH (1-34) cDNA (group B) or injected with nothing (group C).Serum levels of calcium, phosphorus and PTH (1-34) were measured at baseline, 1 month, 2 months, 3 months and 4 months after therapy. Immunohistochemical staining and RT-PCR were performed to find PTH (1-34)-positive cells and to detect PTH (1-34) mRNA.Serum calcium and PTH (1-34) levels were significantly higher in group A than in group B or C. PTH (1-34)-positive cells were found in the TheraCyte group 4 months after implantation. PTH (1-34) mRNA was detected in stem cells 48 hr after transfection and also in stem cells after transfection and 72 hr after G418 treatment.Implantation of the TheraCyte-encapsulated stem cells, which were tranfected with PTH (1-34) cDNA can treat hypoparathyroidism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choulu, F., Huang, SC., Hsieh, KC. et al. Gene therapy of hypoparathyroidism with TheraCyte-encapsulated stem cells. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4534.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4534.1