Abstract
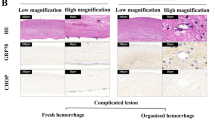
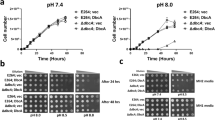
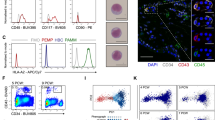
The effect of E. coli endotoxin on the heamolymph coagulation response of Archachatina marginata was studied. Heamocyte Lysate(HL), Haemocyte Lysate Supernatant(HLS) and Haemocyte Lysate Debris (HLD) were exposed to Escherichia coli endotoxin. Controls were prepared with endotoxin-free water(<0.025 EU/ml). The differential protein coagulation was estimated in each mixture. Fractions of the haemolymph exposed to endotoxin produced higher protein coagulates than endotoxin-free fractions when incubated at 37 °C for 1 h (p<0.05). The results showed significantly higher (p<0.05) concentrations of protein coagulated when HL/plasma mixture were used than when either fraction was used. At a ratio 1:1 of HL:Plasma, highest protein coagulation was recorded. This study revealed that maximum protein coagulation in response to endotoxin was elicited by a synergy between plasma and haemocyte lysate(HL). From this research haemolymph fractions of Archachatina marginata may provide an alternative test material for endotoxin in medical preparations in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salawu, M., Oloyede, O., Oladiji, A. et al. Effect of Escherichia coli endotoxin on Archachatina marginata haemolymph coagulation system. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4552.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4552.1