Abstract
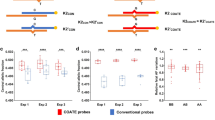
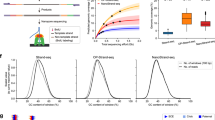
We illustrate the concept of noninvasive determination of the fetal genome by shotgun sequencing maternal plasma. The approach is based on molecular counting of alleles in maternal cell-free DNA: the inheritance of paternal haplotypes can be determined by counting paternal specific alleles present on each of the paternal haplotypes; the inheritance of maternal haplotypes can be revealed by counting the alleles on each maternal haplotype and determining the relative representation of the two maternal haplotypes. The concept was experimentally proven by sequencing a synthetic mixture of genomic DNA samples from a child and her mother, whose whole-genome haplotypes (defined by ~800,000 SNPs), together with those of the father, were previously determined. Light sequencing (0.25x) of such sample containing ~16% child’s DNA enabled the inheritance of parental haplotypes to be correctly resolved over most part of the genome, and partially resolved when prior knowledge of paternal whole-genome haplotypes is absent. Translating this approach to maternal plasma DNA samples, together with increased sequencing depth and phase knowledge of additional numbers of parental SNPs, should enable clinically practical sequencing of the fetal genome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, C., Quake, S. In Principle Method for Noninvasive Determination of the Fetal Genome. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.5373.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.5373.1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetic screening and democracy: lessons from debating genetic screening criteria in the Netherlands
Journal of Community Genetics (2012)
-
Get ready for the flood of fetal gene screening
Nature (2011)