Abstract
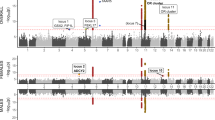
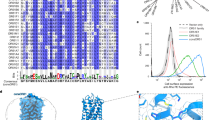
As per conservative estimate, approximately (51-105) Olfactory Receptors (ORs) loci are present in human genome occurring in clusters. These clusters are apparently unevenly spread as mosaics over 21 pair of human chromosomes. Olfactory Receptor (OR) gene families which are thought to have expanded for the need to provide recognition capability for huge number of pure and complex odorants. ORs form the largest known multi-gene family in the human genome. Recent studies have shown that 388 full length and 414 OR pseudo-genes are present in these OR genomic clusters. In this paper, the authors report a classification method for all human ORs based on their sequential quantitative information like presence of poly strings of nucleotides bases, long range correlation and so on. An L-System generated sequence has been taken as an input into a star-model of specific subfamily members and resultant sequence has been mapped to a specific OR based on the classification scheme using fractal parameters like Hurst exponent and fractal dimensions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, S., Pal Choudhury, P. & Goswami, A. Underlying Mathematics in Diversification of Human Olfactory Receptors in Different Loci. Nat Prec (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.5475.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.5475.1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
DNA sequence evolution through Integral Value Transformations
Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences (2012)