Abstract
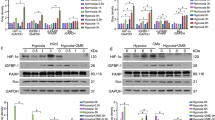
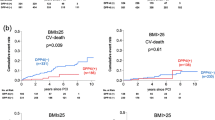
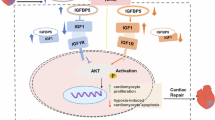
Cardiovascular disease is the major cause of disability and premature death throughout the world and contributes substantially to the escalating costs of health care. Insulin like growth factor binding protein 4 (IGFBP-4) mainly belongs to the family of IGFB protein. Over expression of IGFBP-4 leads to cardiovascular diseases namely stroke, acute myocardial infarction and heart failure. IGFBP-4 serves as an effective drug target against cardiovascular disease. Hence, ligand based virtual screening was persuaded in the present study to propose potential inhibitors of IGFBP-4. Two inhibitors (mainly from literature search) were selected to initiate high throughput virtual screening from small molecule databases namely, NCI, ChemBank, ChemPDB, AKos GmbH, Asinex Ltd and KEGG ligand. The structures listed through database search were docked with IGFBP-4 using virtual screening workflow of Maestro v9.2. Three leads that showed better binding affinity and good correlation with two published inhibitors were proposed as potential IGFBP-4 inhibitors. The three proposed leads showed good pharmacological properties in comparison to the two existing inhibitors. The analyses supported efficiency of three leads for next generation drug designing for cardiovascular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roopesh, K., Munikumar, M. & Umamaheswari, A. In-silico analysis and identification of novel lead molecule for human IGFBP-4 involved in cardiovascular diseases. Nat Prec (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2011.6530.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2011.6530.1