Abstract
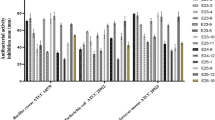
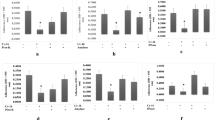
New molecule discovery from natural sources, such as that of actinobacteria, has proved to be an interesting area in antibiotic research, as most of these antibiotics are difficult to synthesize. Out of 30 actinobacterial cultures screened for antimicrobial activity, 28 cultures were found to produce active products against various pathogenic microorganisms such as Gram-negative, Gram-positive bacteria and yeast, using a ‘modified cross streak method.' The modified method helped in easy quantification of results and also in ruling out probable mutual antibiosis. 53%, 13% and 10% of tested actinobacterial strains belonging to Streptomyces, Micromonospora and Actinomadura genera, respectively, showed the ability of producing antimicrobial compounds. Streptomyces sp. strain MMA-5 showed the highest percentage multispecific antibiosis efficiency score value. Broad antibiotic spectrum activity was exhibited by Streptomyces sp. strain MMA-2 and Micromonospora sp. strain MMA-8. The multidrug resistant human pathogenic yeast strain Candida albicans was inhibited by 18 actinobacterial strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamat, N., Velho-Pereira, S. Screening of actinobacteria for antimicrobial activities by a modified "Cross-Streak" method. Nat Prec (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.6765.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.6765.1