Abstract
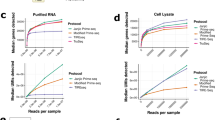
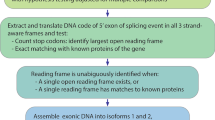
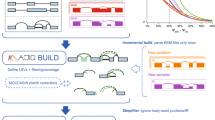
RNA-Seq is a powerful tool for the study of alternative splicing and other forms of alternative isoform expression. Understanding the regulation of these processes requires comparisons between treatments, tissues or conditions. For the analysis of such experiments, we present DEXSeq, a statistical method to test for differential exon usage in RNA-Seq data. DEXSeq employs generalized linear models and offers good detection power and reliable control of false discoveries by taking biological variation into account. An implementation is available as an R/Bioconductor package.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anders, S., Reyes, A. & Huber, W. Detecting differential usage of exons from RNA-Seq data. Nat Prec (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.6837.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.6837.1