Abstract
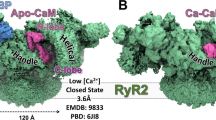
Here we present the determination of the three-dimensional structure of the skeletal muscle Ca2+-release channel in an open state using electron cryomicroscopy and angular reconstitution. In contrast to our reconstruction of the channel in its closed state, the density map of the channel driven towards its open state, by the presence of Ca2+ and ryanodine, features a central opening in the transmembrane region—the likely passageway for Ca2+ ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol. The opening of the channel is associated with a 4° rotation of its transmembrane region with respect to its cytoplasmic region, and with significant mass translocations within the entire cytoplasmic region of the channel tetramer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebashi, S. & Endo, M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 18, 123–183 (1968).
Franzini-Armstrong, C. Studies of the triad.I. Structure of the junction in frog twitch fibers. J. Cell Biol. 47, 488–499 (1970).
Saito, A., Inui, M., Radermacher, M., Frank, J. & Fleischer, S. Ultrastructure of the calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol. 107, 211–219 (1988).
Campbell, K., Knudson, C. & Imagawa, T. Identification and characterization of the high affinity [3H]-ryanodine receptor of the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 6460–6463 (1987).
Inui, M., Saito, A. & Fleischer, S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 1740–1747 (1987).
Imagawa, T., Smith, J. & Coronado, R. Purified ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum is the Ca2+ -permeable pore of theCa2+-release channel. J Biol. Chem. 262, 16636–16643 (1987).
Lai, F.A., Erickson, H.P., Rousseau, E., Liu, Q.-Y. & Meissner, G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature 331, 315–319 (1988).
Lai, F.A., Misra, M. & Xu, L. The ryanodine receptor Ca2+ release channel complex of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum: evidence for a cooperatively charged homotetramer. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 16776–16785 (1989).
Takeshima, H. et al. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature 339, 439–445 (1989).
Jayaraman, T. et al. FK506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor). J. Biol. Chem. 267, 9474–9477 (1992).
Lu, X., Xu, L. & Meissner, G. Activation of the skeletal muscle calcium release channel by a cytoplasmic loop of the dihydropyridine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 6511–6516 (1994).
Smith, J.S., Coronado, R. & Meissner, G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Gen. Physiol. 88, 573–588 (1986).
Cifuentes, M.E., Ronjat, M. & Ikemoto, N. Polylysine induces a rapid Ca++ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles by mediation of its binding to the foot protein. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 273, 554–561 (1989).
Pessah, I.N., Stambuk, R.A. & Casida, J.E. Ca++ -activated ryanodine binding: mechanisms of sensitivity and intensity modulation by Mg++, caffeine, and adenine nucleotides. Mol. Pharmacol. 31, 232–238 (1987).
Chu, A., Diaz-Muñoz, M., Hawkes, M.J., Brush, K. & Hamilton, S.L. Ryanodine as a probe for the functional state of the skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic calcium release channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 37, 735–741 (1990).
Radermacher, M. et al. Cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional reconstruction of the calcium channel/ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle. J.Cell Biol. 127, 411–423 (1994).
Serysheva, I.I., Orlova, E.V., Chiu, W., Sherman, M.B., Hamilton, S.L. & van Heel, M. Electron cryomicroscopy and angular reconstitution to visualize the skeletal muscle calcium-release channel. Nature Struct. Biol. 2, 18–24 (1995).
van Heel, M. Angular reconstitution: A posteriori assignment of projection directions for 3D reconstruction. Ultramicroscopy 21, 111–124 (1987).
van Heel, M., Winkler, H., Orlova, E. & Schatz, M. Structural analysis of ice-embedded single particles. Scanning Microscopy Suppl. 6, 23–42 (1992).
Tinker, A. & Williams, A.J. Probing the structure of the conduction pathway of the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium-release channel with permanent and impermeant organic cations. J. Gen. Physiol. 102, 1107–1129 (1993).
Tu, Q., Velez, P., Browick, M. & Fill, M. Streaming potentials reveal a short ryanodine-sensitive selectivity filter in cardiac Ca2+ release channel. Biophys. J. 67, 2280–2285 (1994).
Tinker, A. & Williams, A.J. Measuring the length of the pore of the sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium-release channel using related trimethylammonium ions as molecular calipers. Biophys. J. 68, 111–120 (1995).
Zhang, Y., Chen, H.S. & Khanna, V.K. A mutation in the human ryanodine receptor gene associated with central core disease. Nature Genetics 5, 46–50 (1993).
Fujii, J., Otsu, K. & Zorzoto, F. Identification of a mutation in porcine ryanodine receptor associated with malignant hyperthermia. Science 253, 448–451 (1991).
Ikemoto, N., Antoniuu, B. & Meszaros, L.G. Rapid flow chemical quench studies of calcium release from isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 14096–14100 (1985).
Unwin, P.N.T. & Ennis, P.D. Calcium-mediated changes in gap junction structure: Evidence from the low angle X-ray pattern. J. Cell Biol. 97, 1459–1466 (1983).
Unwin, P.N.T. Acetylcholine receptor channel imaged in the open state. Nature 373, 37–43 (1995).
Flagg-Newton, J., Simpson, I. & Loewenstein, W.R. Permeability of the cell-to-cell membrane channels in mammalian cell junction. Science 205, 404–407 (1979).
Schwarzmann, G., Wiegandt, H. & Rose, B. Diameter of the cell-to-cell junctional membrane channels as probed with neutral molecules. Science 213, 551–553 (1981).
Loesser, K.E., Catellani, L. & Franzini-Armstrong, C. Disposition of junctional feet in muscles of invertebrates. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 13, 161–173 (1992).
Schatz, M., Orlova, E.V., Dube, P., Jäger, J. & van Heel, M. Structure of Lumbricus terrestris hemoglobin at 30 Å resolution determined using angular reconstitution. J. Struct. Biol. 114, 28–40 (1995).
Hawkes, M.J., Diaz-Muñoz, M. & Hamilton, S.L. A procedure for purification of the ryanodine receptor from skeletal muscle. Memb. Biochem. 8, 133–145 (1989).
Zhou, Z.H., Hardt, S., Wang, B., Sherman, M.B., Jakana, J. & Chiu, W. CTF determination of images of ice-embedded single particles using a graphics interface. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 216–222 (1996).
van Heel, M., Harauz, G., Orlova, E. V., Schmidt, R. & Schatz, M. A new generation of the IMAGIC image processing system. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 17–24 (1996).
Dube, P., Tavares, P., Lurz, R. & van Heel, M. The portal protein of bacteriophage SPP1: a DNA pump with 13-fold symmetry. EMBOJ. 12, 1303–1309 (1993).
van Heel, M. Classification of very large electron microscopical image data sets. Optik 82, 114–126 (1989).
Harauz, G. & van Heel, M. Exact filters for general geometry three dimensional reconstruction. Optik 73, 146–156 (1986).
van Heel, M. & Harauz, G. Resolution criteria for three dimensional reconstructions. Optik 73, 119–122 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlova, E., Serysheva, I., van Heel, M. et al. Two structural configurations of the skeletal muscle calcium release channel. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3, 547–552 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0696-547
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0696-547
This article is cited by
-
The role of RyR2 oxidation in the blunted frequency-dependent facilitation of Ca2+ transient amplitude in rabbit failing myocytes
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2018)
-
Disease mutations in the ryanodine receptor N-terminal region couple to a mobile intersubunit interface
Nature Communications (2013)
-
Role of Ca2+ in the rapid cooling-induced Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum in ferret cardiac muscles
The Journal of Physiological Sciences (2012)
-
Ryanodine receptors
Skeletal Muscle (2011)
-
The structural biology of ryanodine receptors
Science China Life Sciences (2011)