Abstract
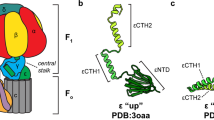
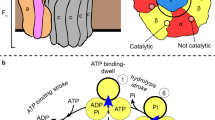
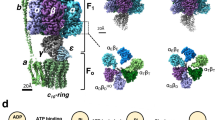
ATP synthases (F1Fo-ATPases) use energy released by the movement of protons down a transmembrane electrochemical gradient to drive the synthesis of ATP, the universal biological energy currency. Proton flow through Fo drives rotation of a ring of c-subunits and a complex of the γ and ɛ-subunits, causing cyclical conformational changes in F1 that are required for catalysis. The crystal structure of a large portion of F1 has been resolved. However, the structure of the central portion of the enzyme, through which conformational changes in Fo are communicated to F1, has until now remained elusive. Here we report the crystal structure of a complex of the ɛ-subunit and the central domain of the γ-subunit refined at 2.1 Å resolution. The structure reveals how rotation of these subunits causes large conformational changes in F1, and thereby provides new insights into energy coupling between Fo and F1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Senior, A.E. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 19, 7– 41 (1990).
Fillingame, R.H., Jones, P.C., Jiang, W., Valiyaveetil, F.I. & Dmitriev, O.Y. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1365, 135–142 ( 1998)
Boyer, P.D. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1140, 215–250 (1993)
Duncan, T.M., Bulygin, V.V., Zhou, Y., Hutcheon, M.L. & Cross, R.L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 10964–10968 (1995).
Sabbert, D., Engelbrecht, S. & Junge, W. Nature 381, 623– 625 (1996).
Noji, H., Yasuda, R., Yoshida, M., & Kinosita, K., Jr. Nature 386, 299–302 ( 1997).
Bulygin, V.V., Duncan, T.M. & Cross, R.L. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 31765– 31769 (1998)
Kato-Yamada, Y., Noji, H., Yasuda, R., Kinosita, K. and Yoshida, M. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 19375–19377 (1998)
Abrahams, J.P., Leslie, A.G., Lutter, R. & Walker, J.E. Nature 370, 621–628 ( 1994).
Bianchet, M.A., Hullihen, J., Pedersen, P.L. & Amzel, L.M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11065–11070 (1998).
Hausrath, A.C., Grüber, G., Matthews, B.W. & Capaldi, R.A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96, 13697 –13702 (1999).
Wilkens, S., Dahlquist, F.W., McIntosh, L.P., Donaldson, L.W. & Capaldi, R.A. Nature Struct. Biol. 2, 961–967 ( 1995).
Uhlin, U., Cox, G.B. & Guss, J.M. Structure 5, 1219– 1230 (1997).
Dunn, S.D. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 7354–7359 (1982).
Tang, C. & Capaldi, R.A. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 3018–3024 (1996).
Xiong, H., Zhang, D. & Vik, S.B. Biochemistry 37, 16423– 16429 (1998).
Stock, D., Leslie, A.G. & Walker, J.E. Science 286, 1700– 1705 (1999).
Schulenberg, B. & Capaldi, R.A. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28351–28355 ( 1999).
Wilkens, S. & Capaldi, R.A. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 26645–26651 (1998).
Mendel-Hartvig, J. & Capaldi, R.A. Biochemistry 30, 1278–1284 ( 1991).
Weber, J., Dunn, S.D. & Senior, A.E. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 19124– 19128 (1999).
Kuki, M., Noumi, T., Maeda, M., Amemura, A. & Futai, M. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 17437–17442 (1988).
Wang, H. & Oster, G. Nature 396 , 279–282 (1998).
Hermolin, J., Dmitriev, O.Y., Zhang, Y. & Fillingame, R.H. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 17011–17016 (1999).
Watts, S. D., Tang, C. & Capaldi, R.A. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 28341– 28347 (1996).
Schulenberg, B., Aggeler, R., Murray, J. & Capaldi, R.A. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 34233–34237 (1999).
Watts, S.D. & Capaldi, R.A. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 15065–15068 (1997).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J-Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Acta Crystallogr. , A 47, 110–119 ( 1991).
Brunger, A.T. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D. 54, 905– 921 (1998).
Laskowski, R.J., MacArthur, M.W., Moss, D.S. & Thornton, J.M. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 283–290 (1993).
Dmitriev O.Y., Jones P.C. & Fillingame R.H., Proc .Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7785–7790 (1999).
Acknowledgements
Use of the APS was supported by the US Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences, Office of Science. Use of the BioCARS Sector 14 was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Research Resources. This research was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Foundation (M.C.J.W.), University of Western Australia Medical Research Fellowship (A.J.W.R.) and The Raine Medical Research Foundation (M.C.J.W.). Travel to the APS was funded from a grant from the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodgers, A., Wilce, M. Structure of the γ–ɛ complex of ATP synthase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 7, 1051–1054 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/80975
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/80975
This article is cited by
-
Distance measurements in the F0F1-ATP synthase from E. coli using smFRET and PELDOR spectroscopy
European Biophysics Journal (2020)
-
Control of rotation of the F1FO-ATP synthase nanomotor by an inhibitory α-helix from unfolded ε or intrinsically disordered ζ and IF1 proteins
Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes (2018)
-
Structure of the ATP synthase catalytic complex (F1) from Escherichia coli in an autoinhibited conformation
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2011)
-
High-resolution structure of the rotor ring of a proton-dependent ATP synthase
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2009)
-
Regulation of the F1F0-ATP Synthase Rotary Nanomotor in its Monomeric-Bacterial and Dimeric-Mitochondrial Forms
Journal of Biological Physics (2008)