Abstract
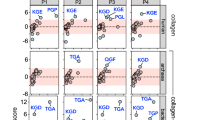
The relationship between molten globules and transient intermediates in protein folding has been explored by equilibrium and kinetic analysis of the compact acid-denatured A-state of cytochrome c. The chloride-induced formation of the A-state is a complex reaction with structural intermediates resembling those found under native refolding conditions, including a rapidly formed compact state and a subsequent intermediate with interacting N- and C-terminal helices. Together with mutational evidence for specific helix–helix packing interactions, this shows that the A-state is a stable analogue of a late folding intermediate. The L94A mutation blocks all folding steps after the initial collapse and its equilibrium state resembles early kinetic intermediates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobson, C.M. Solid evidence for molten globules. Curr. Biol. 4, 636–640 (1994).
Ptitsyn, O.B. Molten globule and protein folding. Adv. Prot. Chem. 47, 83–229 (1995).
Baum, J., Dobson, C.M., Evans, P.A. & Hanley, C. Characterization of a partly folded protein by NMR methods: Studies on the molten globule state of Guinea pig α-lactalbumin. Biochemistry 28, 7–13 (1989).
Wu, L.C., Peng, Z.-y. & Kim, P.S. Bipartite structure of the α-lacatalbumin molten globule. Nature Struct. Biology 2, 281–286 (1995).
Kuwajima, K. The molten globule state of α-lactalbumin. FASEB J. 10, 102–109 (1996).
Hughson, F.M., Wright, P.E. & Baldwin, R.L. Structural characterization of a partly folded apomyoglobin intermediate. Science 249, 1544–1548 (1990).
Kay, M.S. & Baldwin, R.L. Packing interactions in the apomyoglobin folding intermediate. Nature Struct. Biology 3, 439–445 (1996).
Kuwajima, K. The molten globule state as a clue for understanding the folding and cooperativity of globular-protein structure. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet 6, 87–103 (1989).
Ptitsyn, O.B., Pain, R.H., Semisotnov, G.V., Zerovnik, E. & Razgulyaev, O.I. Evidence for a molten globule state as a general intermediate in protein folding. FEBS Lett. 262, 20–24 (1990).
Baldwin, R.L. Molten globules: Specific or nonspecific folding intermediates. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2, 379–389 (1991).
Matthews, C.R. Pathways of protein folding. A. Rev. Biochem. 62, 653–683 (1993).
Roder, H. & Elöve, G.A. Early stages of protein folding. In Mechanisms of Protein Folding: Frontiers in Molecular Biology. (ed. R.H. Pain) 26–55 (Oxford University Press, New York; 1994).
Evans, P.A. & Radford, S.E. Probing the structure of folding intermediates. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 4, 100–106 (1994).
Fink, A.L. Compact intermediate states in protein folding. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 24, 495–522 (1995).
Jennings, P.A. & Wright, P.E. Formation of a molten globule intermediate early in the kinetic folding pathway of apomyoglobin. Science 262, 892–895 (1993).
Balbach, J. et al. Following protein folding in real time using NMR spectroscopy. Nature Struct. Biology 2, 865–870 (1995).
Ohgushi, M. & Wada, A. ‘Molten-globule state’: a compact form of globular proteins with mobile side-chains. FEBS Lett. 164, 21–24 (1983).
Robinson, J.B.J., Strottmann, J.M. & Stellwagen, E. A globular high spin form of ferricytochrome c. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 6772–6776 (1983).
Potekhin, S. & Pfeil, W. Microcalorimetric studies of conformational transitions of f erricytochrome c in acidic solution. Biophysical Chemistry 34, 55–62 (1989).
Jeng, M.-F., Englander, S.W., Elöve, G.A., Wand, A.J. & Roder, H. Structural description of acid-denatured cytochrome c by hydrogen exchange and 2D NMR. Biochemistry 29, 10433–10437 (1990).
Goto, Y., Calciano, L.J. & Fink, A.L. Acid-induced folding of proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 573–577 (1990).
Jeng, M.-F. & Englander, S.W. Stable submolecular folding units in a non-compact form of cytochrome c. J. Mol. Biol. 221, 1045–1061 (1991).
Kuroda, Y., Kidokoro, S. & Wada, A. Thermodynamic characterization of cytochrome c at low pH. J. Mol. Biol. 223, 1139–1153 (1992).
Kataoka, M., Hagihara, Y., Mihara, K. & Goto Molten globule of cytochrome c studied by small angle X-ray scattering. J. Mol. Biol. 229, 591–596 (1993).
Hagihara, Y., Tan, Y. & Goto, Y. Comparison of the conformational stability of the molten globule and native states of horse cytochrome c. J. Mol. Biol. 237, 336–348 (1994).
Chalikian, T.V., Gindikin, V.S. & Breslauer, K.J. Volumetric characterizations of the native, molten globule and unfolded states of cytochrome c at acidic pH. J. Mol. Biol. 250, 291–306 (1995).
Kuroda, Y., Endo, S., Nagayama, K. & Wada, A. Stability of α-helices in a molten globule state of cytochrome c by hydrogen-deuterium exchange and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 247, 682–688 (1995).
Jordan, T., Eads, J.C. & Spiro, T.G. Secondary and tertiary structure of the A-state of cytochrome c from resonance Raman spectroscopy. Protein Sci. 4, 716–728 (1995).
Marmorino, J.L. & Pielak, G.J. A native tertiary interaction stabilizes the A state of cytochrome c. Biochemistry 34, 3140–3143 (1995).
Dyson, H.J. & Beattie, J.K. Spin state and unfolding equilibria of ferricytochromec in acidic solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 2267–2273 (1982).
Hamada, D. et al. Role of heme axial ligands in the conformational stability of the native and molten globule states of horse cytochrome c. J. Mol. Biol. 256, 172–186 (1996).
Goto, Y. & Nishikiori, S. Role of electrostatic repulsion in the acidic molten globule of cytochrome c. J. Mol. Biol. 222, 679–686 (1991).
Jamin, M. & Baldwin, R.L. Refolding and unfolding kinetics of the equilibrium molten globule intermediate of apomyoglobin. Nature Struct. Biology 3, 613–618 (1996).
Sosnick, T.R., Mayne, L., Hiller, R. & Englander, S.W. The barriers in protein folding. Nature Struct. Biology 1, 149–156 (1994).
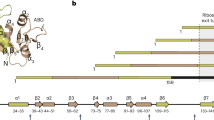
Colón, W., Elöve, G.A., Wakem, L.P., Sherman, F. & Roder, H. Side chain packing of the N- and C-terminal helices plays a critical role in the kinetics of cytochrome c folding. Biochemistry 35, 5538–5549 (1996).
Stellwagen, E. & Babul, J. Stabilization of the globular structure of ferricytochrome c by chloride in acidic solvents. Biochemistry 14, 5135–5140 (1975).
Tsong, T.Y. An acid induced conformational transition of denatured cytochrome c in urea and guanidine hydrochloride solutions. Biochemistry 14, 1542–1547 (1975).
Misra, V.K., Sharp, K.A., Friedman, R.A. & Honig, B. Salt effects on ligand-DNA binding. J. Mol. Biol. 238, 245–263 (1994).
Fersht, A. Enzyme structure and mechanism. (W.H. Freeman and company, New York; 1985).
Elöve, G.A., Chaffotte, A.F., Roder, H. & Goldberg, M.E. Early steps in cytochrome c folding probed by time-resolved circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry 31, 6876–6883 (1992).
Roder, H., Elöve, G.A. & Englander, S.W. Structural characterization of folding intermediates in cytochrome c by H-exchange labelling and proton NMR. Nature 335, 700–704 (1988).
Elöve, G.A. & Roder, H. Structure and stability of cytochrome c folding intermediates. ACS Symposium Series 470, 50–63 (1991).
Elöve, G.A., Bhuyan, A.K. & Roder, H. Kinetic mechanism of cytochrome c folding: involvement of the heme and its ligands. Biochemistry 33, 6925–6935 (1994).
Bai, Y., Sosnick, T.R., Mayne, L. & Englander, S.W. Protein folding intermediates: native-state hydrogen exchange. Science 269, 192–197 (1995).
Babul, J. & Stellwagen, E. Participation of the protein ligands in the folding of cytochrome c. Biochemistry 11, 1195–1200 (1972).
Shechter, E. & Saludjian, P. Conformation of ferricytochrome c. IV. Relationship between optical absorption and protein conformation. Biopolymers 5, 788–790 (1967).
Uversky, V.N. & Ptitsyn, O.B. “Partly folded” state, a new equilibrium state of protein molecules: Four-state guanidinium chloride-induced unfolding of β-lactamase at low temperature. Biochemistry 33, 2782–2791 (1994).
Uversky, V.N. & Ptitsyn, O.B. Further evidence on the equilibrium “pre-molten globule state”: four-state guanidinium chloride-induced unfolding of carbonic anhydrase B at low temperature. J. Mol. Biol. 255, 215–228 (1996).
Khorasanizadeh, S., Peters, I.D. & Roder, H. Evidence for a three-state model of protein folding from kinetic analysis of ubiquitin variants with altered core residues. Nature Struct. Biology 3, 193–205 (1996).
Sosnick, T.R., Mayne, L. & Englander, S.W. Molecular collapse: the rate-limiting step in two-state cytochrome c folding. Proteins 24, 413–426 (1996).
Tsong, T.Y. The Trp-59 fluorescence of ferricytochrome c as a sensitive measure of the over-all protein conformation. J. Biol. Chem. 249, 1988–1990 (1974).
Scholtz, J.M. & Baldwin, R.L. The mechanism of alpha-helix formation by peptides. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 21, 95–118 (1992).
Chan, H.S. & Dill, K.A. Origins of structure in globular proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 6388–6392 (1990).
Agashe, V.R., Shastry, M.C.R. & Udgaonkar, J.B. Initial hydrophobic collapse in the folding of barstar. Nature 377, 754–757 (1995).
Privalov, P.L. Intermediate states in protein folding. J. Mol. Biol. 258, 707–725 (1996).
Khorasanizadeh, S., Peters, I.D., Butt, T.R. & Roder, H. Stability and folding of a tryptophan-containing mutant of ubiquitin. Biochemistry 32, 7054–7063 (1993).
Bushnell, G.W., Louie, G.V. & Brayer, G.D. High-resolution three-dimensional structure of horse heart cytochrome c. J. Mol. Biol. 214, 585–595 (1990).
Kraulis, P.J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Pace, C.N. Determination and analysis of urea and guanidine hydrochloride denaturation curves. Meth. Enzymol. 131, 266–280 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colón, W., Roder, H. Kinetic intermediates in the formation of the cytochrome c molten globule. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3, 1019–1025 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1296-1019
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1296-1019
This article is cited by
-
The role of key residues in structure, function, and stability of cytochrome-c
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2014)
-
Versatility of non-native forms of human cytochrome c: pH and micellar concentration dependence
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2013)
-
A single mutation induces molten globule formation and a drastic destabilization of wild-type cytochrome c at pH 6.0
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2009)
-
The 40s ?-loop plays a critical role in the stability and the alkaline conformational transition of cytochrome c
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2004)
-
Stepwise formation of α-helices during cytochrome c folding
Nature Structural Biology (2000)