Abstract
Aim:
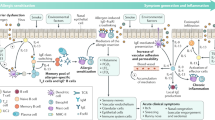
Patients with allergic rhinitis experience a multitude of symptoms that usually compromise some aspect of lifestyle. However, few data are available that specifically address the impact of allergic rhinitis on work productivity.
Methods:
A questionnaire was developed and mailed to 2,065 patients enrolled in a 500,000-member managed care organisation. Patients were identified by diagnostic codes for allergic rhinitis as determined by a retrospective examination of medical and prescription claims records from January 1 2000 to December 31 2000. Patients were divided into three different care groups according to whether they were managed by family physicians, by allergists, or were self-managed.
Results:
Chi-square and analysis of variance tests revealed significant differences among the three care groups (p<0.05) for years with allergies, symptoms, family history, testing, immunotherapy, test value, and prescribed antihistamine use. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that sleep, health, certain allergy symptoms and prescribed antihistamines were significantly related to work productivity.
Conclusions:
The results of this study revealed that the ability of individuals with allergic rhinitis to engage in productive work is influenced by sleep, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), specific symptoms, and prescribed antihistamine use.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Change history
08 August 2007
In our article entitled 'The impact of allergic rhinitis on work productivity'1 which was published in this year's Apri issue of the Primary Care Respiratory Journal (PCRJ), we were remiss in not acknowledging the use of the same data source, data collection and background literature that was used in our previous study addressing a different issue relating to lifestyle productivity which was published in the Annals of Allergy Asthma & Immunology (AAAI) in 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szeinbach, S., Seoane-Vazquez, E., Beyer, A. et al. The impact of allergic rhinitis on work productivity. Prim Care Respir J 16, 98–105 (2007). https://doi.org/10.3132/pcrj.2007.00015
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3132/pcrj.2007.00015
This article is cited by
-
An Observational Study to Determine the Real-Life Effectiveness of MP-AzeFlu® in Austrian Patients with Persistent Allergic Rhinitis
Drugs - Real World Outcomes (2024)
-
An algorithm recommendation for the pharmacological management of allergic rhinitis in the UK: a consensus statement from an expert panel
npj Primary Care Respiratory Medicine (2017)
-
Analysis and forecasting of airborne pollen–induced symptoms with the aid of computational intelligence methods
Aerobiologia (2013)
-
The burden of allergic rhinitis (AR) in Canada: perspectives of physicians and patients
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology (2012)
-
Impacto presupuestario del uso de furoato de fluticasona para el manejo de la rinitis alérgica en atención primaria en España
PharmacoEconomics Spanish Research Articles (2011)