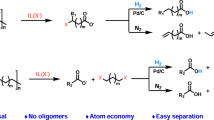
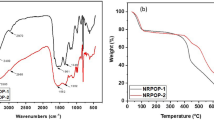
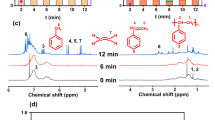
Abstract
Polyethylene surfaces were treated with I2 plasma. From ESCA analysis, it became apparent that iodine atoms were bound chemically to the surface of polyethylene substrate by the treatment of I2 plasma. Also, iodine bonded chemically to polyethylene increased by the exposure of I2 Vapor after I2-plasma treatment of the substrate. The reaction of I2-plasma treated polyethylene with aminoalcohol made the polyethylene substrate hydrophilic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
H. K. Yasuda, “Plasma Polymerization and Plasma Treatment of Polymers,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., Appl. Polym. Symp., 42 (1988).
Y. Nakagawa, Y. Yoshida, and T. Yamashita, Kobunshi Ronbunsyu, 46, 209 (1989).
Y. Yoshida and Y. Nakagawa, “Proceedings of Japanese Symposium on Plasma Chemistry,” Vol. 2, Organizing Committee Japanese Symosium on Plasma Chemistry, Ed., Shinzansha Scitech Co. Ltd., Tokyo, 1989, p 225.
M. Strobel, S. Corn, C. S. Lyons, and G. Korba, J. Polym. Sci., A: Polym. Chem. Ed., 25, 1295 (1987).
N. Inagaki, S. Tasaka, Y. Suzuki, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 13, 51 (1994).
J. H. Dully, F. J. Wodarczyk, and J. J. Ratto, J. Polym. Sci., A: Polym. Chem. Ed., 25, 1187 (1987).
D. T. Clark, Adv. Polym. Sci., 24, 125 (1977).