Abstract
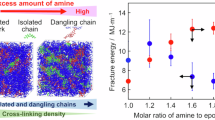
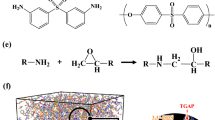
We present a mechanistic study of the curing process of liquid–crystalline epoxy resins by the simultaneous measurement of small-angle X-ray scattering/wide-angle X-ray scattering using synchrotron radiation. The systems studied consist of a diglycidyl ether of terephthalydene-bis(4-amino-3-methylphenol) epoxy component and three types of aromatic amine-type curing agents 4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane, 4,4′-diaminodiphenylethane and m-phenylenediamine. The systems studied all exhibit similar thermosetting behaviors; first, the epoxide group reacts with an amine moiety of the curing agent, followed by the formation of the nematic domains in the early stage of the process. The nematic-to-smectic conversion proceeds after an incubation period, implying that a critical amount of nematic volume is necessary for phase transition. We found that the transformation continues beyond the conversion of 80% of the epoxide-amine bond formation and the corresponding entire polymer network formation. The volume fraction of smectic phases after completion of the reaction differs according to the structure of the curing agents. The study clarifies the mechanistic sequence and the preference for smectic phase formation both in terms of time sequence and the dependence of the structure on the curing agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ochi, M., Tsuyuno, N., Sakaga, K., Nakanishi, Y. & Murata, Y. Effect of network structure on thermal and mechanical properties of biphenol-type epoxy resins cured with phenols. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 56, 1161–1167 (1995).
Ochi, M., Shimizu, Y., Nakanishi, Y. & Murata, Y. Effect of the network structure on thermal and mechanical properties of mesogenic epoxy resin cured with aromatic amine. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 35, 397–405 (1997).
Sue, H. J., Earls, J. D. & Hefner, R. E. Fracture behaviour of liquid crystal epoxy resin systems based on the diglycidyl ether of 4,4′-dihydroxy-α-methylstilbene and sulphanilamide: Part I Effects of curing variations. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 4031–4037 (1997).
Ortiz, C., Belenky, L., Ober, C. K. & Kramer, J. Microdeformation of a polydomain, smectic liquid crystalline thermoset. J. Mater. Sci. 35, 2079–2086 (2000).
Ortiz, C., Kim, R., Rodighiero, E., Ober, C. K. & Kramer, E. J. Deformation of a polydomain, liquid crystalline epoxy-based thermoset. Macromolecules 31, 4074–4088 (1998).
Harada, M., Aoyama, K. & Ochi, M. Fracture mechanism of liquid-crystalline epoxy resin systems with different phase structures. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 42, 4044–4052 (2004).
Harada, M., Watanabe, Y., Tanaka, Y. & Ochi, M. Thermal properties and fracture toughness of a liquid-crystalline epoxy resin cured with an aromatic diamine crosslinker having a mesogenic group. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 44, 2486–2494 (2006).
Harada, M., Sumitomo, K., Nishimoto, Y. & Ochi, M. Relationship between fracture toughness and domain size of liquid-crystalline epoxy resins having polydomain structure. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 47, 156–165 (2009).
Harada, M., Okamoto, N. & Ochi, M. Fracture toughness and fracture mechanism of liquid-crystalline epoxy resins with different polydomain structures. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 48, 2337–2345 (2010).
Harada, M., Ochi, M., Tobita, M., Kimura, T., Ishigaki, T., Shimoyama, N. & Aoki, H. Thermomechanical properties of liquid-crystalline epoxy networks arranged by a magnetic field. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 42, 758–765 (2004).
Potitie, L., Torro, F., Tessier, M., Davidson, P. & Fradet, A. Investigation of anisotropic epoxy–amine thermosets synthesised in a magnetic field. Liquid Crystal 35, 913–924 (2008).
Akatsuka, M. & Takezawa, Y. Study of high thermal conductive epoxy resins containing controlled high-order structures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 89, 2464–2467 (2003).
Harada, M., Ochi, M., Tobita, M., Kimura, T., Ishigaki, T., Shimoyama, N. & Aoki, H. Thermal-conductivity properties of liquid-crystalline epoxy resin cured under a magnetic field. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 41, 1739–1743 (2003).
Liu, L., Gao, J., Du, Y. & Chai, Z. Synthesis and characterization of the two novel liquid crystalline epoxy resins based on bisphenol-s mesogen. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 110, 3671–3677 (2008).
Lee, J. & Jang, J. The effect of mesogenic length on the curing behavior and properties of liquid crystalline epoxy resins. Polymer 47, 3036–3042 (2006).
Liu, G., Zhou, B., Zhao, D., Li, Q. & Gao, J. Novel triaromatic ester mesogenic liquid crystalline epoxy resin containing both methyl substituent and ethoxy flexible spacer: synthesis and curing. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 209, 1160–1169 (2008).
Choi, E., Seo, J., Bae, H. & Lee, J. Synthesis and curing of new aromatic azomethine epoxies with alkoxy side groups. Eur. Polym. J. 40, 259–265 (2004).
Lee, J. Y. & Jang, J. Effect of substituents on the curing of liquid crystalline epoxy resin. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 36, 911–917 (1998).
Liu, W. & Carfagna, C. Synthesis of liquid crystalline epoxy oligomers: effect of molecular weight on the phase behavior. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 22, 1058–1062 (2001).
Castell, P., Galia, M. & Serra, A. Synthesis of new epoxy liquid-crystalline monomers with azo groups in the central mesogenic core. Crosslinking with amines. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 202, 1649–1657 (2001).
Ribera, D., Montecon, A. & Serra, A. Synthesis and crosslinking of a series of dimeric liquid crystalline epoxy resins containing imine mesogens. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 202, 1658–1671 (2001).
Masunaga, H., Ogawa, H., Takano, T., Sasaki, S., Goto, S., Tanaka, T., Seike, T., Takahashi, S., Takeshita, K., Nariyama, N., Ohashi, H., Ohata, T., Furukawa, Y., Matsushita, T., Ishizawa, Y., Yagi, N., Takata, M., Kitamura, H., Sakurai, K., Tashiro, K., Takahara, A., Amamiya, Y., Horie, K., Takenaka, M., Kanaya, T., Jinnai, H., Okuda, H., Akiba, I., Takahashi, I., Yamamoto, K., Hikosaka, M., Sakurai, S., Shinohara, Y., Okada, A. & Sugihara, Y. Multipurpose soft-material SAXS/WAXS/GISAXS beamline at SPring-8. Polym. J. 43, 471–477 (2011).
Acknowledgements
The simultaneous SAXS and WAXS measurements were carried out at the second hutch of SPring-8 BL03XU constructed by the Consortium of Advanced Softmaterial Beam line (FSBL), with the proposal number 2010A7201, 2010B7251, 2011A7201 and 2011B7251.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harada, M., Ando, J., Hattori, S. et al. In-situ analysis of the structural formation process of liquid–crystalline epoxy thermosets by simultaneous SAXS/WAXS measurements using synchrotron radiation. Polym J 45, 43–49 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2012.196
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2012.196