Abstract
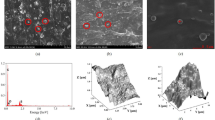
We attempted to estimate the distribution ratio of carbon black (CB) in blends of polyisobutyrene rubber and polyisoprene rubber using high-resolution solid-state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Our NMR analysis revealed that, in polyisobutyrene rubber/polyisoprene rubber/CB composites, CB more easily distributes in polyisoprene rubber than in polyisobutyrene rubber. We found that more than 70% of CB is distributed into the polyisoprene rubber phase. The sum of the amounts of CB in both the polyisobutyrene rubber and polyisoprene rubber phases estimated by our method using 13C NMR closely corresponds with the amount of CB originally added to the compound, verifying the validity of the NMR method. Further, we observed the distribution of CB in polyisobutyrene/polyisoprene rubber blends using transmission electron microscopy and the Carbon-Black-Gel method, which can only be used for unvulcanized rubber blends, for comparison. The results obtained using these three methods show similar tendencies, which confirms the accuracy of this method of using 13C NMR to determine CB distribution in rubber blends.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Change history
05 June 2015
This article has been corrected since Advance Online Publication, and a corrigendum is also printed in this issue.
References
Railsback, H. E., Cooper, W. T. & Stumpe, N. A. Cis-polybutadiene-natural rubber blends. Rubber Plast. Age 39, 867–887 (1958).
Hess, W. M. & Chirico, V. E. Elastomer blend properties-influence of carbon black type and location. Rubber Chem. Technol. 50, 301–326 (1977).
Hess, W. M., Vegvari, P. C. & Swor, R. A. Carbon black in NR/BR blends for truck tires. Rubber Chem. Technol. 58, 350–382 (1985).
Hess, W. M., Scott, C. E. & Callan, J. E. Carbon black distribution in elastomer blends. Rubber Chem. Technol. 40, 371–384 (1967).
Karásek, L. & Sumita, M. Characterization of dispersion state of filler and polymer-filler interactions in rubber-carbon black composites. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 281–289 (1996).
Ziegel, K. D. & Romanov, A. Modulus reinforcement in elastomer composites. I. Inorganic fillers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 17, 1119–1131 (1973).
Ziegel, K. D. & Romanov, A. Modulus reinforcement in elastomer composites. II. Polymeric fillers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 17, 1133–1142 (1973).
Payne, A. R. & Whittaker, R. E. Reinforcement of rubber with carbon black. Composites 1, 203–214 (1970).
Datta, S. in Handbook of the Science and Technology of Rubber (eds Erman, B., Mark, J. E., Roland, M. ) Ch. 12, 547–589 (2013).
Naitoh, S. Imbalance distribution in rubber blend. Nippon Gomu Kyokaishi 70, 632–640 (1997).
Sirisinha, C. & Prayoonchatphan, N. Study of carbon black distribution in BR/NBR blends based on damping properties: Influences of carbon black particle size, filler, and rubber polarity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 81, 3198–3203 (2001).
Callen, J. E., Hess, W. M. & Scott, C. E. Elastomer blends. Compatibility and relative response to fillers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 44, 814–837 (1971).
Cotton, G. R. & Murphy, L. J. Mixing of carbon black with rubber. VI. Analysis of natural rubber (NR)/SBR blends. Rubber Chem. Technol. 61, 609–618 (1988).
Fouche, P. M. & MacGill, W. J. A study of the transfer of carbon black between the phases of polyisoprene-polybutadiene blends by differential scanning calorimetry and electron microscopy. Plast. Rubber Process Appl. 12, 227–234 (1989).
Galuska, A. A., Poulter, R. R. & McElrath, K. O. Force modulation AFM of elastomer blends: morphology, fillers and crosslinking. Surf. Interface Anal. 25, 418–429 (1997).
Tsou, A. H. & Waddell, W. H. Morphology of elastomer blends by dynamic AFM. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst 55, 382–387 (2002).
Wang, C. C., Donnet, J. B. & Wang, T. K. AFM study of rubber compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 78, 17–27 (2005).
Jeon, I. H., Kim, H. & Kim, S. G. Characterization of rubber micro-morphology by atomic force microscopy (AFM). Rubber Chem. Technol. 76, 1–11 (2003).
Kunizawa, T. & Ni, Q. -Q. Characterization of carbon black distribution and mechanical properties in NR/SBR blend rubber composites. Japan Soc Compos Mater 35, 157–164 (2009).
Hu, W., Ellul, M. D., Tsou, A. H. & Datta, S. Filler distribution and domain size of elastomer compounds by solid-state NMR and AFM. Rubber Chem. Technol. 80, 1–13 (2007).
Massie, J. M., Hirst, R. C. & Halasa, A. F. Carbon black distribution in NR/polybutadiene blends. Rubber Chem. Technol. 66, 276–285 (1993).
Portal, J., Carrot, C., Majeste, J. C., Cocard, S., Pelissier, V. & Anselme-Bertrand, I. Quantification of the distribution of carbon black in natural rubber/polybutadiene blends by differential scanning calorimetry. Polymer Eng. Sci. 49, 1544–1552 (2009).
Maiti, S., De, S. K. & Bhowmick, A. K. Quantitative estimation of filler distribution in immiscible rubber blends by mechanical damping studies. Rubber Chem. Technol. 65, 293–302 (1992).
Klüppel, M., Schuster, R. H. & Schaper, J. Carbon black distribution in rubber blends: a dynamic-mechanical analysis. Rubber Chem. Technol. 72, 91–108 (1999).
Naitoh, S., Tajima, H., Wada, S. & Inoue, S. Studies on the structure of rubber. 1. Studies on carbon black distribution in elastomer blends. Nippon Gomu Kyokaishi 49, 476–480 (1976).
Cotton, G. R. & Murphy, L. J. Mixing of carbon black with rubber. Part 5. Analysis of SBR/BR blends. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst 41, 54–58 (1988).
Kotani, M., Dohi, H., Kimura, H., Muraoka, K. & Kaji, H. Characterization of carbon filler distribution ratio in polyisoprene/polybutadiene rubber blends by high-resolution solid-state 13C NMR. Macromolecules 40, 9451–9454 (2007).
Litvinov, V. M. & Steeman, P. A. M. EPDM-carbon black Interactions and the reinforcement mechanisms, as studied by low-resolution 1H NMR. Macromolecules 32, 8476–8490 (1999).
McBrierty, V. J. in Eurofillers 97: Int. Conf. on Filled Polymers and Fillers; Extended Abstracts 67–75, http://www.eurofillers2013.sav.sk/ (Manchester, UK, 8-11 September 1997).
Simon, G., Götschmann, B., Matzen, D. & Schneider, H. Proton NMR spin-spin relaxation in crosslinked SBR with and without carbon black filling. Polym. Bull. 21, 475–482 (1989).
Leisen, J., Breidt, J. & Kelm, J. 1H NMR relaxation studies of cured natural rubbers with different carbon black fillers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 72, 1–14 (1999).
NMR database at http://polymer.nims.go.jp/NMR/
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr W-G Hu for his help in initiating this study. We also wish to thank Mr Naoki Tsukamori, Mr Masaya Sakai, Ms Wakana Ito, Mr Yasufumi Kuwauchi and Ms Miyo Miki for analyzing the TEM results and performing image processing system calculations. We gratefully acknowledge the helpful discussions that were held with Mr Takahiro Mabuchi regarding the CB-Gel method. We would also like to thank Dr Sherif Rashed and Mr Jesse Gruber for their English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotani, M., Dohi, H., Kimura, H. et al. Distribution ratio of carbon black in polyisobutyrene/polyisoprene rubber blends using high-resolution solid-state 13C NMR. Polym J 47, 422–427 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2015.3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2015.3