Abstract
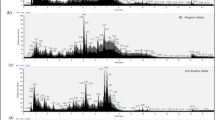
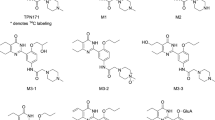
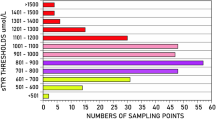
Summary: Metabolic studies on two patients with defects in the tyrosine oxidation pathway arc reported. Scrum tyrosine was greatly elevated in both patients (1.37 and 1.52 mmol/liter, respectively) and both excreted large quantities of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, p-hydroxyphenyllactie acid, and p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid. Deuterated tyrosine loads were administered to both patients, before and after lowering of the serum tyrosine concentration by dietary treatment, and to a normal adult control subject.
In one patient the excretion of the deutcrated (D2)-tyrosine load was more than 300 times that found in the control subject whether the test was done at high or low scrum tyrosine level and the pattern of metabolites indicated a persistent defect in p- hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid oxidasc. Enzyme assays on needle liver biopsy supported this finding. In the second patient excretion of the D2 label was 300 times that of the control at high scrum tyrosine levels, but only 5 times normal at low serum tyrosine levels. This finding was interpreted as indicating substrate inhibition of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid oxidase. The primary defect has not been established in this patient, but the findings are compatible with a defect in hepatic-soluble tyrosine aminotransfcrase.
Speculation: We have shown that loading rates of 220 μmol deuteratcd tyrosine/kg body weight are adequate for precise measurement of the stable isotope content of urinary tyrosine and tyrosine metabolites. This load approximates that provided by a protein containing meal; therefore, stable isotope load studies can be claimed to mimic physiologic events.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faull, K., Gan, I., Halpern, B. et al. Metabolic Studies on Two Patients with Nonhepatic Tyrosinemia Using Deuterated Tyrosine Loads. Pediatr Res 11, 631–637 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-197705000-00002
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-197705000-00002
This article is cited by
-
Maternal tyrosinaemia II: Management and successful outcome
European Journal of Pediatrics (1992)
-
The effect of various amino acids and drugs on thepara-andmeta-hydroxyphenylacetic acid concentrations in the mouse caudate nucleus
Neurochemical Research (1983)
-
Hepatic tyrosine aminotransferase in tyrosinaemia type II
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (1982)