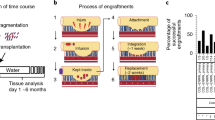
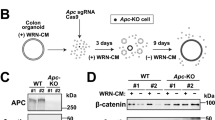
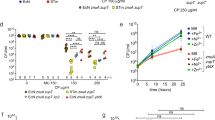
Abstract
Summary: Two patients with acrodermatitis enteropathica had abnormal lysosomal inclusion bodies in the intestinal epithelial cells while in relapse but fewer smaller ones after zinc therapy. The third patient with acrodermatitis enteropathica in remission on zinc therapy had no inclusion bodies. The smaller inclusion bodies were similar to those found in coeliac disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, J., Elmes, M., Aggett, P. et al. The Effect of Zinc Therapy on Lysosomal Inclusion Bodies in Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Acrodermatitis Enteropathica. Pediatr Res 17, 354–357 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-198305000-00009
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-198305000-00009
This article is cited by
-
Zinc deficiency and its inherited disorders -a review
Genes & Nutrition (2006)
-
Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of acrodermatitis enteropathica
European Journal of Pediatrics (1989)
-
Fatty acid composition of plasma lipids in acrodermatitis enteropathica before and after zinc supplementation
European Journal of Pediatrics (1985)