Abstract
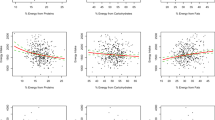
ABSTRACT: Our study was undertaken in preterm infants to examine the relationship of whole body protein kinetics with protein intake and energy expenditure. Leucine kinetics were determined in seven low birth wt preterm infants fed human milk or human milk enriched with protein (2.5 to 4.3 g protein/kg.d). The infants received a short (4-h) constant infusion of l-[1-13C]leucine and leucine turnover and oxidation were calculated from 13C-plasma leucine and expired 13CO2 enrichments measured by mass spectrometry. Energy expenditure was measured by indirect calorimetry. Nonoxidative leucine disposal (an estimate of protein synthesis) and leucine derived from protein (an estimate of protein breakdown) were, respectively, 2.98 ± 0.82 and 2.06 ± 0.74 μmol/kg.min. Whole body protein turnover and deposition, derived from leucine kinetics, were 8.22 ± 2.31 and 2.17 ± 0.50 g/kg.d, whereas energy expenditure was 56.3 kcal/kg.day. Protein turnover was correlated with protein intake but not with protein deposition. Energy expenditure was correlated with protein turnover, synthesis, and breakdown but not with protein deposition. These data are in agreement with the fact that protein deposition depends upon protein intake, but they also suggest that an elevated protein deposition is not necessarily the result of a rapid protein turnover or associated with an elevated energy expenditure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beaufrere, B., Putet, G., Pachiaudi, C. et al. Whole Body Protein Turnover Measured with 13C-Leucine and Energy Expenditure in Preterm Infants. Pediatr Res 28, 147–152 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199008000-00014
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199008000-00014
This article is cited by
-
δ15N and δ13C in hair from newborn infants and their mothers: a cohort study
Pediatric Research (2012)
-
A comparison of15N proline and13C leucine for monitoring protein biosynthesis in the skin
Amino Acids (1999)
-
An improved scheme of leucine derivative fragmentation in mass spectrometry
Amino Acids (1996)