Abstract
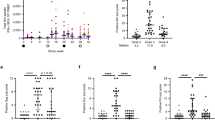
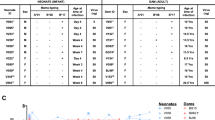
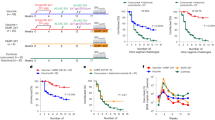
Six newborn rhesus macaques were experimentally infected with pathogenic Simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques (SIVmac251), and three newborn macaques were infected with avirulent SIVmac1A11. The former developed rapidly fatal simian AIDS and died within 26 wk of age, whereas the latter remained clinically normal. Infant monkeys that developed rapidly progressive disease had rapid declines in CD4+ cells and were unable to mount IgG and IgA antibody responses to SIV or to an unrelated antigen, tetanus toxoid. IgM antibody responses were near normal to both SIV-specific and nonspecific antigens. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses to SIV envelope were observed in animals infected with either virulent or avirulent SIV. These studies demonstrated that virulent SIVmac infection induced a rapid immunosuppression that was both SIV-specific and nonspecific in nature. The observation that virulent strains of SIV can rapidly induce a global immunosuppression provides one explanation for the rapid disease course in some HIV-infected children and supports the strategy of early and vigorous antiviral drug therapy to alter the disease course even if this does not prevent infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CTL:
-
cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- SIV:
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus
- SIVmac:
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques
- PBMC:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- TCID50:
-
tissue culture infectious dose, 50%
- CAPS:
-
3-(cyclohexylamino)-1-propanesulfonic acid
- TBST:
-
10 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 0.15 M NaCl, and 0.05% Tween 20
References
Delfraissy JF, Blanche S, Rouzioux C, Mayaux MJ 1992 Perinatal HIV transmission facts and controversies. Immunodefic Rev 3: 305–327.
Boylon L, Stein ZA 1991 The Epidemiology of HIV infection in children and their mothers-vertical transmission. Epidemiol Rev 13: 143–177.
European Collaborative Study 1991 Children born to women with HIV-1 infection: natural history and risk of transmission. Lancet 337: 253–260.
Blanche S, Tardieu M, Duliege AM, Rouzioux C, Le Deist F, Fukunaga K, Caniglia M, Jacomet C, Messiah A, Griscelli C 1990 Longitudinal study of 94 symptomatic infants with perinatally acquired human immunodeficiency virus infection. Evidence for a bimodal expression of clinical and biological symptoms. Am J Dis Child 144: 1210–1215.
Tovo PA, De Martino M, Gabiano C, Cappello N, D'Elia R, Loy A, Plebani A, Zuccotti GV, Dallacasa P, Ferraris G, Caselli D, Fundaro C, D'Argenio P, Galli L, Principi N, Stegagno M, Ruga E, Palomba E, and The Italian Register for HIV Infection in Children Register for HIV Infection in Children 1992 Prognostic factors and survival in children with perinatal HIV-1 infection. Lancet 339: 1249–1253.
Auger I, Thomas P, De Grutolla V, Morse D, Moore D, Williams R, Truman B, Lawrence CE 1988 Incubation period for pediatric AIDS patients. Nature 336: 575–577.
Bernstein LJ, Rubinstein A 1986 Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in infants and children. Prog Allergy 37: 194–206.
Roilides E, Clerici M, Depalma L, Rubin M, Pizzo PA, Shearer GM 1991 Helper T-cell responses in children infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Pediatr 118: 724–730.
Henrard D, Fauvel M, Samson J, Delage G, Boucher M, Hankins C, Stephens J, Lapointe N 1993 Ontogeny of the humoral immune response to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in infants. J Infect Dis 168: 288–291.
Marthas ML, Van Rompay KKA, Otsyula M, Miller CJ, Tarantal AF, Canfield D, Pedersen NC, McChesney MB 1995 Viral variants determine progression to AIDS in SIV-infected newborn rhesus macaques. J Virol 69: 4198–4205.
Sutjipto S, Pedersen NC, Miller CJ, Gardner MB, Hanson CV, Gettie A, Jennings M, Higgins J, Marx PA 1990 Inactivated simian immunodeficiency virus vaccine failed to protect rhesus macaques from intravenous or genital mucosal infection but delayed disease in intravenously exposed animals. J Virol 64: 2290–2297.
Gallarda JL, Henrard DR, Lui D, Harrington S, Stramer SL, Valinsky JE, Wu P 1992 Early detection of antibody to human immunodeficiency virus type I by using an antigen conjugate immunoassay correlates with the presence of immunoglobulin M antibody. J Clin Microbiol 30: 2379–2384.
Myers G, Korber B, Smith RF, Pavlakis N 1983 Human retroviruses and AIDS I-II, Los Alamos National Laboratory, New Mexico, pp–A–17
Gnann JW, McCormick JB, Mitchell S, Nelson JA, Oldstone MB 1987 Synthetic peptide immunoassay distinguishes HIV type 1 and HIV type 2 infections. Science 237: 1346–1349.
Lohman BL, McChesney MB, Miller CJ, McGowan E, Joye SM, Van Rompay KKA, Reay E, Antipa L, Pedersen NC, Marthas ML 1994 A partially attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus induces host immunity that correlates with resistance to pathogenic virus challenge. J Virol 68: 7021–7029.
Luciw PA, Shaw KE, Unger RE, Planelles V, Stout MW, Lackner JE, Pratt-Lowe E, Leung NJ, Banapour B, Marthas ML 1992 Genetic and biological comparisons of pathogenic and nonpathogenic molecular clones of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVmac). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 8: 395–402.
Fleiss JL 1981 Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions, 2nd Ed. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 24–26.
Erickson AL, Walker CM 1994 An epitope in the V1 domain of the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) gp120 protein is recognized by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes from an SIV-infected rhesus macaque. J Virol 68: 2756–2759.
Yamamoto H, Miller MD, Tsubota H, Watkins DI, Mazzara GP, Stallard V, Panicali DL, Aldovini A, Young RA, Letvin NL 1990 Studies of cloned simian immunodeficiency virus-specific T lymphocytes gag-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes exhibit a restricted epitope specificity. J Immunol 144: 3385–3391.
Callahan KM, Rowell JF, Soloski MJ, Machamer CE, Sliciciano RF 1993 HIV-1 envelope protein is expressed on the surface of infected cells before its processing and presentation to class II-restricted T-lymphocytes. J Immunol 151: 2928–2942.
Van Rompay KKA, Otsyula MG, Marthas ML, Miller CJ, McChesney MB, Pedersen NC 1995 Immediate zidovudine treatment protects simian immunodeficiency virus-infected newborn macaques against rapid onset of AIDS. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39: 125–131.
Miller CJ, Alexander NJ, Sutjipto S, Lackner AA, Gettie A, Hendrickx AG, Lowenstine LJ, Jennings M, Marx PA 1989 Genital mucosal transmission of simian immunodeficiency virus: animal model for heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 63: 4277–4284.
Van Rompay KK, Marthas ML, Ramos RA, Mandell CP, McGowan EK, Joye SM, Pedersen NC 1992 Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection of infant rhesus macaques as a model to test antiretroviral drug prophylaxis and therapy: oral 3-azido-3-deoxythymidine prevents SIV infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36: 2381–2386.
Luzuriaga K, Koup RA, Pikora CA, Brettler DB, Sullivan JL 1991 Deficient human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T cell responses in vertically infected children. J Pediatr 119: 230–236.
Buseyne F, Blanche S, Schmitt D, Griscelli C, Riviere Y 1993 Detection of HIV-specific cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the peripheral blood from infected children. J Immunol 150: 3569–3581.
Lohman BL, McChesney MB, Miller CJ, Otsyula M, Berardi CJ, Marthas ML 1994 Mucosal immunization with a live, virulence-attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) vaccine elicits antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocytes and antibodies in rhesus macaques. J Med Primatol 23: 95–101.
Luzuriaga K, Holmes D, Hereema A, Wong J, Panicali DL, Sullivan JL 1995 HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in the first year of life. J Immunol 154: 433–443.
Bernstein LJ, Ochs HD, Wedgewood RJ, Rubinstein A 1985 Defective humoral immunity in pediatric acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Pediatr 107: 352–357.
Yanese Y, Tango T, Okamura K, Tada T, Kawasaki T 1986 Lymphocytes subsets identified by monoclonal antibodies in healthy children. Pediatr Res 20: 1147–1151.
Erkeller-Yuksel FM, Deneys V, Yuksel B, Hannet I, Hulstaert F, Hamilton C, Mackinnon H, Stokes L, Munhyeshuli V, Vanlangendonck F 1992 Age-related changes in human blood lymphocyte subpopulations. J Pediatr 120: 216–222.
de Martino M, Tovo PA, Galli L, Gabiano C, Cozzani S, Gotta C, Scarlatti G, Fiocchi A, Cocchi P, Marchisio P, Canino R, Mautone A, Chiappe F, Campelli A, Consolini R, Izzi G, Laverda A, Alberti S, Tozzi AE, Duse M 1991 Prognostic significance of immunologic changes in 675 infants perinatally exposed to human immunodeficiency virus. The Italian Register for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection in Children. J Pediatr 119: 702–709.
Maschese V, Martino A, Fundaro C, Plebani A, Cappelli G, Lombardi V, Alimandi M, Scaccia S, Galli E, Rossi P, Orlandi P 1994 Response to tetanus toxoid in children born to HIV seropositive mothers. Pediatr AIDS HIV Infect 5: 79–85.
Leibovitz E, Rigaud M, Pollack H, Lawrence R, Chandwani S, Krasinski K, Barkowsky W 1990 Pneumocystic carinii pneumonia in infants infected with the human immunodeficiency virus with more than 450 CD4 T-lymphocytes per cubic millimeter. N Engl J Med 323: 531–533.
Connor E, Bagarazzi M, McSherry G, Holland B, Boland M, Denny T, Oleske J 1991 Clinical and laboratory correlates ofPneumocystis carinii pneumonia in children infected with HIV. JAMA 265: 1693–1697.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Linda Antipa, David Bennet, Abbie Spinner, Harry Louie, Todd Greene, Brenda Graf, David Robb, Steve Joye, and Ron Walgenbach for expert technical assistance, and Dr. Nick Lerche for help with statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otsyula, M., Miller, C., Marthas, M. et al. Virus-Induced Immunosuppression Is Linked to Rapidly Fatal Disease in Infant Rhesus Macaques Infected with Simian Immunodeficiency Virus. Pediatr Res 39, 630–635 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199604000-00012
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199604000-00012