Abstract
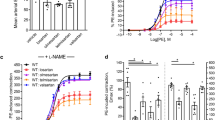
The release of endogenous vasoconstrictors together with changes in the vascular responses are central to the pathophysiology of sepsis. The effects of in vitro incubation for 20 h with heat-killed group B Streptococcus (GBS, 3 × 107 colonyforming units mL-1) on the vasoconstrictor responses to noradrenaline (NA, 10-8 to 10-4 M), the thromboxane A2 analog 9,11-dideoxy-11α,9α-epoxymethanoprostaglandin F2α(U46619; 10-10 M to 10-6 M) and endothelin-1 (ET-1, 10-11 to 3 × 10-9 M) were evaluated on isolated intrapulmonary and mesenteric arteries from 10-17-d-old piglets. The incubation with GBS reduced the maximal contractile response to NA and ET-1 (p < 0.01) in both arteries. The nitric oxide (NO) synthase (NOS) inhibitorNω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; 10-4 M) completely reversed this hyporesponsiveness. GBS-treated mesenteric arteries also showed a significant reduction of the maximal contractions induced by U46619 (p < 0.05) and this effect was inhibited by 10-4 M L-NAME. In contrast, the maximal contractile responses to U46619 were similar in control and in GBS-treated pulmonary arteries. Addition of L-NAME did not modify the contractile responses to U46619 in GBS-treated pulmonary arteries. In conclusion, GBS-treated systemic arteries from neonatal piglets showed decreased responses to NA, U46619, and ET-1 due to enhanced NO release. GBS-treated pulmonary arteries also exhibited decreased responses to NA and ET-1 but not to U46619. Induction of NOS in vascular smooth muscle may play a key role in the hypotension and loss of systemic vascular responsiveness that occurs in GBS sepsis. The absence of pulmonary hyporesponsiveness to U46619 may partially explain the coexistence during sepsis of pulmonary hypertension and lung NOS induction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- GBS:
-
Group B Streptococcus
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- ET-1:
-
endothelin-1
- TXA2:
-
thromboxane A2
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- iNOS:
-
inducible nitric oxide synthase
- NA:
-
noradrenaline
- U46619:
-
9,11-dideoxy-11α,9α-epoxymethanoprostaglandin F2α
- L-NAME:
-
Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester
- cfu:
-
colony-forming units
REFERENCES
Mayon-White RT 1985 The incidence of GBS disease in neonates in different countries. Antibiot Chemother 35: 17–27
Baker CJ, Edwards MS 1991 Group B streptococcal infections. In: Remington JS, Klein JO (eds) Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 820–881
Ferrieri P 1985 GBS infections in the newborn infant: diagnosis and treatment Antibiot C. hemother 35: 211–224
Cabal LA, Siassi B, Cristofani C, Cabal C, Hodgman JE 1990 Cardiovascular changes in infants with β-hemolytic streptococcus sepsis. Crit Care Med 18: 715–718
Brigham KL, Meyrick B 1986 Endotoxin and lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis 133: 913–927
Gibson RL, Truog WE, Redding GJ 1987 Thromboxane-associated pulmonary hypertension during three types of Gram-positive bacteriemia in piglets. Pediatr Res 23: 553–556
Runkle B, Goldberg RN, Streitfeld MM, Clark MR, Buron E, Setzer ES, Bancalari E 1984 Cardiovascular changes in group B streptococcal sepsis in the piglet: response to indomethacin and the relationship to prostacyclin and thromboxane A2. Pediatr Res 18: 874–878
Groves AC, Griffiths J, Leung F, Meek RN 1972 Plasma catecholamines in patients with serious postoperative infection. Ann Surg 178: 102–107
Groeneveld ABJ, Nauta JJP, Thijs LG 1988 Peripheral vascular resistance in septic shock: its relation to outcome. Intensive Care Med 14: 141–147
Takakashi K, Silva A, Cohen J, Lam HC, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR 1990 Endothelin immunoreactivity in mice with Gram-negative bacteriemia: relation to tumor necrosis factor-α. Clin Sci 79: 619–623
Pittet JF, Morel DR, Hemsen A, Gunning K, Lacroix JS, Suter PM, Lundberg JM 1991 Elevated plasma endothelin-1 concentrations are associated with the severity of illness in patients with sepsis. Ann Surg 213: 261–264
McKenna TM 1990 Prolonged exposure of rat aorta to low levels of endotoxin in vitro results in impaired contractility. Association with vascular cytokine release. J Clin Invest 86: 160–168
Julou-Schaeffer G, Gray GA, Fleming I, Schott C, Parratt JR, Stoclet J-C 1990 Loss of vascular responsiveness induced by endotoxin involves L-arginine pathway. Am J Physiol 259:H1038–H1043
Thiemermann 1994 The role of the L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway in circulatory shock. Adv Pharmacol 28: 45–79
Szabó C, Mitchell JA, Thiemermann C, Vane JR 1993 Nitric oxide-mediated hyporeactivity to noradrenaline precedes the induction of nitric oxide synthase in endotoxin shock. Br J Pharmacol 108: 786–792
Zelenkov P, McLoughlin T, Johns RA 1993 Endotoxin enhances hypoxic constriction of rat aorta and pulmonary artery through induction of EDRF/NO synthase. Am J Physiol 265:L346–L354
Rees DD, Cunha FQ, Assreuy J, Herman AG, Moncada S 1995 Sequential induction of nitric oxide synthase by Corynebacterium parvum in different organs of the mouse. Br J Pharmacol 114: 689–693
Cunha FQ, Moss DW, Leal LM, Moncada S, Liew FY 1993 Induction of macrophage parasiticidal activity by Staphylococcus aureus and exotoxins through the nitric oxide synthase pathway. Immunology 78: 563–567
Goodrum KJ, McCormick LL, Schneider B 1994 Group B Streptococcus-induced nitric oxide production in murine macrophages is CR3(CD11b/CD18) dependent. Infect Immun 62: 3102–3107
Goodrum KJ, Dierksheide J, Yoder BJ 1995 Tumor necrosis factor alpha acts as an autocrine second signal with γ interferon to induce nitric oxide in group B Streptococcus-treated macrophages. Infect Immun 63: 3715–3717
Villamor E, Pérez-Vizcaíno F, Ruiz T, Leza JC, Moro M, Tamargo J 1995 Group B Streptococcus and E. coli LPS produce nitric oxide-dependent hyporesponsiveness to noradrenaline in isolated intrapulmonary arteries of neonatal piglets. Br J Pharmacol 115: 261–266
Mitchell JA, Kohlhass KL, Sorrentino R, Warner TD, Murad M, Vane J 1993 Induction by endotoxin of nitric oxide synthase in the rat mesentery: lack of effect on action of vasoconstrictors. Br J Pharmacol 109: 265–270
Auguet M, Lonchampt MO, Delaflotte S, Goulin-Schulz J, Chabrier PE, Braquet P 1992 Induction of nitric oxide synthase by lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett 297: 183–185
De Kimpe SJ, Thiemermann C, Vane JR 1994 Lipoteichoic acid, a cell wall component of Gram-positive bacteria, causes hypotension and induction of nitric oxide synthase in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol 112: 442P
Griffiths MJD, Messent M, McAllister RJ, Evans TW 1993 Aminoguanidine selectively inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase. Br J Pharmacol 110: 963–968
Curzen NP, Griffiths MJD, Evans TW 1995 Contraction to endothelin-1 in pulmonary arteries from endotoxin-treated rats is modulated by endothelium. Am J Physiol 268:H2260–H2266
Pérez-Vizcaíno F, Villamor E, Ruiz T, Fernández del Pozo B, Moro M, Tamargo J 1995 E. coli and group B Streptococcus reduce pulmonary artery responses to noradrenaline but not to U46619. Pharmacol Res 35: 238
Tod ML, O'Donnell DC, Gordon JB 1995 Sites of inhaled NO-induced vasodilation during hypoxia and U46619 infusion in isolated lamb lungs. Am J Physiol 268:H1422–H1427
Berger JI, Gibson RL, Redding GJ, Standaert TA, Clarke WR, Truog WE 1993 Effect of inhaled nitric oxide during group B streptococcal sepsis in piglets. Am Rev Respir Dis 147: 1080–1086
Abman SH, Kinsella JP, Schaffer MS, Wilkening RB 1993 Inhaled nitric oxide in the management of a premature newborn with severe respiratory distress and pulmonary hypertension. Pediatrics 92: 606–609
Schneidkraut MJ, Carlson RW 1990 Bacterial sepsis-induced decrease in lung vascular reactivity to 9,11-dideoxy-11α,9α-epoxymethanoprostaglandin F2α(U46619) in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253: 1171–1176
Baydoun AR, Foale RD, Mann GE 1993 Bacterial endotoxin rapidly stimulates prolonged endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in the rat isolated perfused heart. Br J Pharmacol 109: 987–991
Smith REA, Palmer RMJ, Moncada S 1991 Coronary vasodilatation induced by endotoxin in the rabbit isolated perfused heart is nitric oxide-dependent and inhibited by dexamethasone. Br J Pharmacol 104: 5–6
Ferro TJ, Hocking DC, Johnson A 1993 Tumor necrosis factor-α alters pulmonary vasoreactivity via neutrophil-derived oxidants. Am J Physiol 265:L462–L471
Williams PA, Bohnsack JF, Augustine NH, Drummond WK, Rubens CE, Hill HR 1993 Production of tumor necrosis factor by human cells in vitro and in vivo, induced by group B streptococci. J Pediatr 123: 292–300
Mancuso G, Tomasello F, Hunelstoin C, Orefici G, Teti G 1994 Induction of tumor necrosis factor α by the group- and type-specific polysaccharides from type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun 62: 2748–2753
Bowdy BD, Schewan MA, Marple SL, Yoneda K, Pauli TH, Coonrod JD, Gillespie MN 1990 Organ-specific disposition of group B streptococci in piglets: evidence for a direct interaction with target cells in pulmonary circulation. Pediatr Res 27: 344–348
Hocker JR, Simpsom PM, Rabalais GP, Stewart DL, Cook LN 1992 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis. Pediatrics 89: 1–4
Shi Y, Li H-Q, Shen C-K, Wang J-H, Qin S-W, Liu R, Pan J 1993 Plasma nitric oxide levels in newborn infants with sepsis. J Pediatr 123: 435–438
Moncada S, Palmer RMJ, Higgs EA 1991 Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 43: 109–142
Wei X, Charles IC, Smith A, Ure J, Feng G, Huang F, Xu D, Muller W, Moncada S, Liew FY 1995 Altered immune responses in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nature 375: 408–411
Petros A, Lamb G, Leone A, Moncada S, Bennet D, Vallance P 1994 Effects of a nitric oxide inhibitor in humans with septic shock. Cardiovasc Res 28: 34–39
Klemm P, Thiemermann C, Winklmaier G, Martorana PA, Henning R 1995 Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibition combined with nitric oxide inhalation in a porcine model of endotoxin shock. Br J Pharmacol 114: 363–368
Gibson RL, Berger JI, Redding GJ, Standaert TA, Mayock DE, Truog WE 1994 Effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition during group B streptococcal sepsis in neonatal piglets. Pediatr Res 36: 776–783
Meadow W, Rudinsky B, Bell A, Hipps R 1995 Effects of inhibition of endothelium-derived relaxation factor on hemodynamics and oxygen utilization during group B streptococcal sepsis in piglets. Crit Care Med 23: 705–714
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Romero and Dr. Elorza for providing heat-killed GBS and to C. Rivas, R. Vara, and M. R. Gaítan for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a CICYT (SAF 96/0042) and FIS Grants (95/0308 and 95/0318) Grants. E. Villamor is a recipient of the Asociación Espanola de Pediatría/Arbora S.A. Grant for Pediatric Research.
Presented at the 1st European Congress of Pharmacology (EPHAR) and the 65th Annual Meeting of the Society for Pediatric Research, Washington, DC.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villamor, E., Pérez-Vizcaíno, F., Tamargo, J. et al. Effects of Group B Streptococcus on the Responses to U46619, Endothelin-1, and Noradrenaline in Isolated Pulmonary and Mesenteric Arteries of Piglets. Pediatr Res 40, 827–833 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199612000-00009
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199612000-00009