Abstract
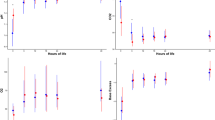
In utero breathing activity is present periodically, but it must become continuous at birth. We investigated the effect of hypercapnia and of hypercapnia combined with central cooling on fetal breathing in seven chronically instrumented fetal lambs of 131-134-d gestation, using an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) system to control fetal blood gases and fetal temperature. During fetal hypercapnia (from a partial pressure of arterial CO2 (Paco2) 6.18 ± 0.11 kPa to Paco2 7.39± 0.15 kPa) frequency, amplitude, and incidence of fetal breathing movements during low voltage electrocortical activity (LV ECoG) increased significantly compared with isocapnic control on ECMO, but breathing remained absent during high voltage electrocortical activity (HV ECoG). During hypercapnia accompanied by central cooling (Paco2 7.90 ± 0.13 kPa, temperature decreased by 2.1°C) there were similar changes in fetal breathing movements during LV ECoG, but in four out of seven fetuses fetal breathing movements continued throughout HV ECoG. Hypercapnia accompanied by central cooling can thus override the inhibitory effects of HV ECoG on fetal breathing movements. This may be due to changes in sensitivity to CO2 produced by an increase in afferent input to the CNS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ECMO:
-
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- HV ECoG:
-
high voltage electrocortical activity
- LV ECoG:
-
low voltage electrocortical activity
- Paco2:
-
partial pressure of arterial CO2
- Pao2:
-
partial pressure of arterial O2
- EMG:
-
electromyography
References
Dawes GS, Fox HE, Leduc BM, Liggins GC, Richards RT 1972 Respiratory movements and rapid eye movement sleep in the foetal lamb. J Physiol 220: 119–143.
Dawes GS, Gardner WN, Johnston BM, Walker DW 1983 Breathing in fetal lambs: the effect of brain stem section. J Physiol 335: 535–553.
Blanco CE, Martin CB, Hanson MA, McCooke HB 1987 Determinants of the onset of continuous air breathing at birth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 26: 175–182.
Berger PJ, Horne RSC, Soust M, Walker AM, Maloney JE 1990 Breathing at birth and the associated blood gas and pH in the lamb. Respir Physiol 82: 251–266.
Boddy K, Dawes GS, Fisher R, Pinter S, Robinson JS 1974 Foetal respiratory movements, electrocortical and cardiovascular responses to hypoxaemia and hypercapnia in sheep. J Physiol 243: 599–618.
Chapman RLK, Dawes GS, Rurak DW, Wilds PL 1980 Breathing movements in fetal lambs and the effect of hypercapnia. J Physiol 302: 19–29.
Ritchie JWK, Lakhani K 1980 Fetal breathing movements in response to maternal inhalation of 5% carbon dioxide. Am J Obstet Gynecol 136: 386–388.
Bowes G, Wilkinson MH, Dowling M, Ritchie BC, Brodecky V, Maloney JE 1981 Hypercapnic stimulation of respiratory activity in unanesthetized fetal sheep in utero. J Appl Physiol 50: 701–708.
Dawes GS, Gardner WN, Johnston BM, Walker DW 1982 Effects of hypercapnia on tracheal pressure, diaphragm and intercostal electromyograms in unanesthetized fetal lambs. J Physiol 326: 461–474.
Connors G, Hunse C, Carmichael L, Natale R, Richardson B 1988 The role of carbon dioxide in the generation of human fetal breathing movements. Am J Obstet Gynecol 158: 322–327.
Connors G, Hunse C, Carmichael L, Natale R, Richardson B 1989 Control of fetal breathing in the human fetus between 24 and 34 weeks' gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 160: 932–938.
Johnston BM, Gluckman PD 1989 Lateral pontine lesions effect central chemosensitivity in unanesthetized fetal lambs. J Appl Physiol 67: 1113–1118.
Gluckman PD, Gunn TR, Johnston BM 1983 The effect of cooling on breathing and shivering in unanesthetized fetal lambs in utero. J Physiol 343: 495–506.
Kuipers IM, Maertzdorf WJ, de Jong DS, Hanson MA, Blanco CE 1994 The effect of mild hypocapnia on breathing and behavior in unanesthetized normoxic fetal lambs. J Appl Physiol 76: 1476–1480.
Kuipers IM, Maertzdorf WJ, de Jong DS, Hanson MA, Blanco CE 1994 The effect of maternal hypoxemia on behavior in unanesthetized normoxic or mildly hyperoxic fetal lambs. J Appl Physiol 76: 2535–2540.
Kuipers IM, Maertzdorf WJ, de Jong DS, Hanson MA, Blanco CE 1992 Fetal breathing is not initiated after cord occlusion in the unanesthetized fetal lamb in utero. J Dev Physiol 17: 233–240.
Clewlow F, Dawes GS, Johnston BM, Walker DW 1983 Changes in breathing, electrocortical and muscle activity in unanaesthetized fetal lambs with age. J Physiol 341: 463–476.
Ioffe S, Jansen AH, Chernick V 1987 Maturation of spontaneous fetal diaphragmatic activity and fetal response to hypercapnia and hypoxemia. J Appl Physiol 62: 609–622.
Jansen AH, Ioffe S, Russell BJ, Chernick V 1982 Influence of sleep state on the response to hypercapnia in fetal lambs. Respir Physiol 48: 125–142.
Rigatto H, Lee D, Davi M, Moore M, Rigatto E, Cates D 1988 Effect of increased arterial CO2 on fetal breathing and behavior in sheep. J Appl Physiol 64: 982–987.
Faucher DJ, Laptook AR, Porter JC, Rosenfeld CR 1991 Effects of acute hypercapnia on maternal and fetal vasopressin and catecholamine release. Pediatr Res 30: 368–374.
Blanco CE, Martin CB, Hanson MA, McCooke HB 1987 Breathing activity in fetal sheep during mechanical ventilation of the lungs in utero. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 26: 175–182.
Osborne S, Milsom WK 1993 Ventilation is coupled to metabolic demands during progressive hypothermia in rodents. Respir Physiol 92: 305–318.
Phillipson EA, Bowes G 1986 Control of breathing during sleep. In: Fishman AP, Cherniack NS, Widdicombe JG (eds) Handbook of Physiology, Section 3: The Respiratory System, Vol. II, Part 2. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, MD, pp 649–689.
Walker AM, Oakes GK, Ehrenkranz R, McLaughlin M, Chez RA 1976 Effects of hypercapnia on uterine and umbilical circulations in conscious pregnant sheep. J Appl Physiol 41: 727–733.
Moss IR, Scarpelli EM 1979 Generation and regulation of breathing in utero: fetal CO2 response test. J Appl Physiol 47: 527–531.
Kuipers IM, Maertzdorf WJ, de Jong DS, Hanson MA, Blanco CE 1994 The effect of central cooling in unanesthetized fetal lambs: the role of CO2 . Pediatr Res 35:A408.
Wanatabe T, Kumar P, Hanson MA 1993 Effects of warm environmental temperature on the gain of the respiratory chemoreflex in the kitten. J Physiol 459: 336P
Sidi D, Kuipers JRG, Heymann MA, Rudolph AM 1983 Effects of ambient temperature on oxygen consumption and the circulation in newborn lambs at rest and during hypoxemia. Pediatr Res 17: 254–258.
Gunn TR, Johnston BM, Iwamoto HS, Fraser M, Nicholls MG, Gluckman PD 1985 Haemodynamic and catecholamine responses to hypothermia in the fetal sheep in utero. J Dev Physiol 7: 241–249.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jan Geilen, Ton van den Bogaard, May Bost, Joyce Suyk, Frans Slangen, and Peter Franssen for the technical assistance and for the animal care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant (900-519-105) from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO). M.A.H. is supported by the Wellcome Trust.
Cardiothoracic Surgery, and Extra Corporeal Circulation, London, United Kingdom
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuipers, I., Maertzdorf, W., De Jong, D. et al. The Effect of Hypercapnia and Hypercapnia Associated with Central Cooling on Breathing in Unanesthetized Fetal Lambs. Pediatr Res 41, 90–95 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199701000-00014
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199701000-00014