Abstract
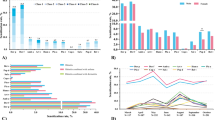
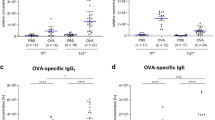
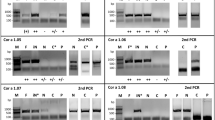
Pollen contact in early infancy may enhance the risk for subsequent pollen allergy. In this study likelihood of a prenatal antigen contact, as a result of inhalation of pollen allergens by the mother, was investigated. Due to the seasonal occurrence of allergens studied, the date of priming can be estimated, and this can supply data about the maturation of the fetal immune system. Proliferative responses of umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells (UCB MNCs) to the recombinant major allergens of birch (rBet v 1) and timothy grass(rPhl p 1) were analyzed throughout the whole year. A positive proliferative response was regarded as the criterion for a prenatal contact of the immune system with the allergen. Prenatal priming with both allergens was observed. Timothy grass pollen displayed considerably higher antigenicity than did birch pollen. The susceptibility of the fetal immune system to be primed by these allergens varies during the gestation period. The majority of positive responses to rPhl p 1 and rBet v 1 were found in UCB samples in which antigen contact (the respective pollen season) took place in the first 6 mo of pregnancy. Our results offer indirect evidence that, shortly after migration of T cell precursors to the epithelial thymus, T cells are mature enough for priming with antigens. No relationship was found between the susceptibility of the fetal immune system to be primed by these allergens and the clinical history of the family concerning type I allergy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- SI:
-
stimulation index
- Phl p:
-
major allergen of Phleum pratense
- r:
-
recombinant
- UCB:
-
umbilical cord blood
- MNC:
-
mononuclear cell
- Bet v:
-
major antigen of Betula verrucosa
References
Clough JB 1993 Pre- and post-natal events leading to allergen sensitization. Clin Exp Allergy 23: 462–465.
Björksten F, Suoniemi I, Koski V 1980 Neonatal birch pollen contact and subsequent allergy to birch pollen. Clin Allergy 10: 585–591.
Buscino L, Cantani F, Farinella F, Businco E 1988 Month of birth and grass pollen or mite sensitization in children with respiratory allergy: a significant relationship. Clin Allergy 18: 269–274.
Holt PG, McMenamin C, Nelson D 1990 Primary sensitisation to inhalant allergens during infancy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 1: 3–13.
Aalberse RC, Nieuwenhuys EJ, Hey M, Stapel SO 1992 Horoscope effect not only for seasonal but also for non-seasonal allergens. Clin Exp Allergy 22: 1003–1006.
Piccinni MP, Mecacci F, Sampognaro S, Manetti R, Parronchi P, Maggi E, Romagnani S 1993 Aeroallergen sensitization can occur during fetal life. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 102: 301–303.
Szépfalusi Z, Huber WD, Ebner C, Granditsch G, Urbanek R 1995 Early sensitization to airborne allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 107: 595–598.
Hayward AR 1981 Development of lymphocyte responses and interactions in the human fetus and newborn. Immunol Rev 57: 39–59.
Ferreira FD, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Ferreira FD, Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Breiteneder HH, Pettenburger K, Ebner C, Sommergruber W, Steiner R, Bohle B, Sperr WR, Valent P, Kungl AJ, Breitenbach M, Kraft D, Scheiner O 1993 Purification and characterization of recombinant Bet v I, the major birch pollen allergen. J Biol Chem 268: 19574–19580.
Laffer S, Valenta R, Vrtala S, Susani M, van Ree R, Kraft D, Scheiner O, Duchenne M 1994 Complementary DNA cloning of the major allergen Phl p 1 from timothy grass (Phleum pratense); recombinant Phl p 1 inhibits IgE binding to group I allergens from eight different grass species. J Allergy Clin Immunol 94: 689–698.
Haynes BF, Martin ME, Kay HH, Kurtzberg J 1988 Early events in human T cell ontogeny. J Exp Med 168: 1061–1080.
Lobach DF, Hensley LL, Ho W, Haynes BF 1985 Human T cell antigen expression during the early stages of fetal thymic maturation. J Immunol 135: 1752–1758.
Lobach DF, Haynes BF 1987 Ontogeny of the human thymus during fetal development. J Clin Immunol 7: 81–89.
Haynes BF, Singer KH, Denning SM, Martin ME 1988 Analysis of expression of CD2, CD3 and T cell antigen receptor molecules during early human fetal thymic development. J Immunol 141: 3776–3784.
Byrne JA, Stankovic AK, Cooper MD 1994 A novel subpopulation of primed T cells in the human fetus. J Immunol 152: 3098–3105.
Jones AC, Miles EA, Warner JA, Warner JO 1995 IFNγ production and proliferative responses from fetal leucocytes during 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 95: 380
Piastra M, Stabile A, Fioravanti G, Castagnola M, Pani G, Ria F 1994 Cord blood mononuclear cell responsiveness toβ-lactoglobulin:T-cell activity in “atopy-prone” and“non-atopy-prone” newborns. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 104: 358–365.
Kobayashi Y, Kondo N, Shinoda S, Agata H, Fukutomi O, Orii T 1994 Predictive values of cord blood IgE and cord blood lymphocyte responses to food antigens in allergic disorders during infancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 94: 907–916.
Romagnani S 1992 Induction of Th1 and Th2 responses: a key role for the natural immune response? Immunol Today 13: 379–380.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank U. Sieman for her very helpful technical advice. The recombinant allergens were kindly provided by D. Kraft and O. Scheiner, Institute of General and Experimental Pathology, University of Vienna.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Grant S06701 and S06704-MED of FWF (Austria).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Duren-Schmidt, K., Pichler, J., Ebner, C. et al. Prenatal Contact with Inhalant Allergens. Pediatr Res 41, 128–131 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199701000-00020
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199701000-00020
This article is cited by
-
Fetal Programming: Early-life Modulations that Affect Adult Outcomes
Current Allergy and Asthma Reports (2010)
-
Risk factors for food allergy
Current Allergy and Asthma Reports (2004)
-
Allergie op de kinderleeftijd – een rol voor primaire preventie
Tijdschrift voor kindergeneeskunde (2003)